A non-contact shock wave excitation device for testing the dynamic characteristics of mems metal microstructures
A technology of metal microstructure and dynamic characteristics, applied in the direction of microstructure devices, microstructure technology, etc., can solve problems such as difficult disassembly, poor safety, and poor connection stiffness, and achieve easy and safe operation, guaranteed accuracy, and good connection stiffness Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
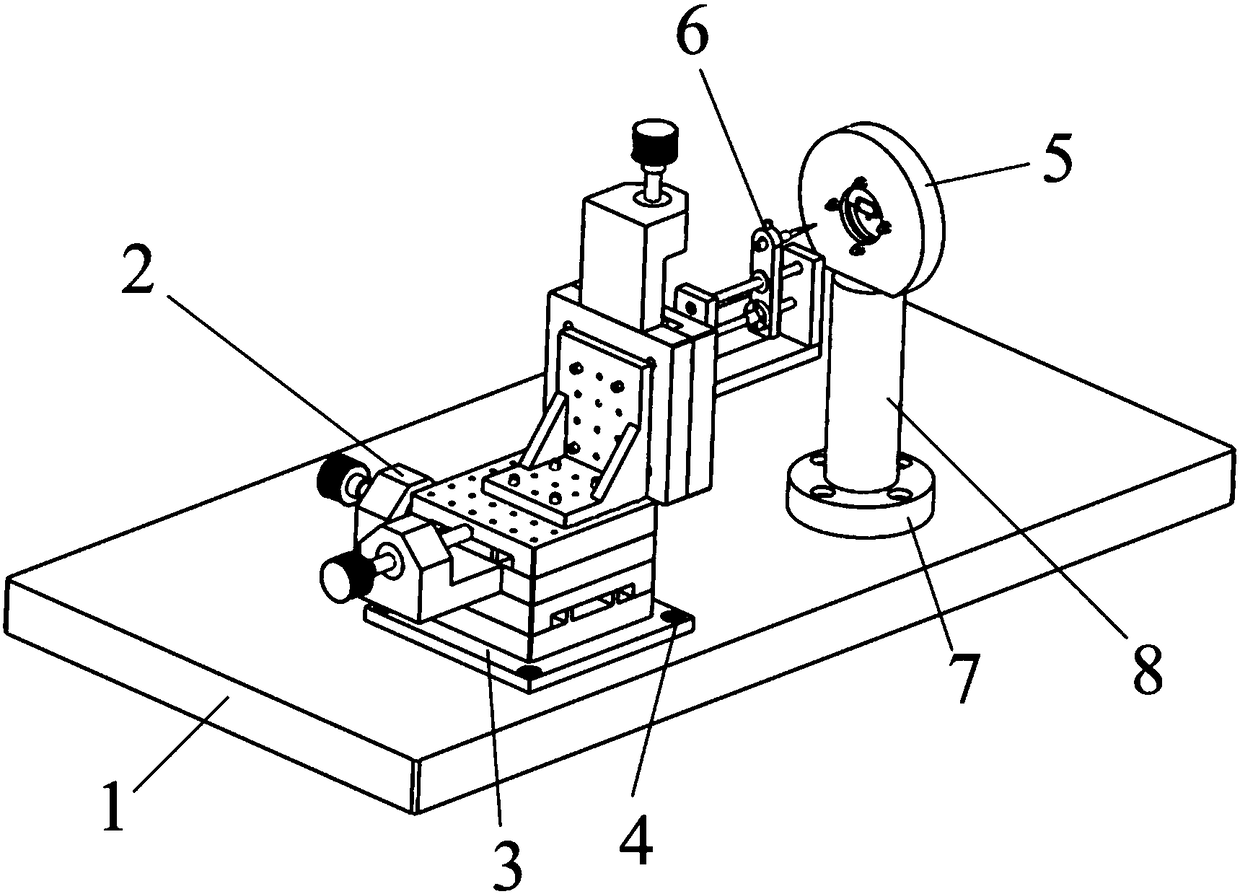
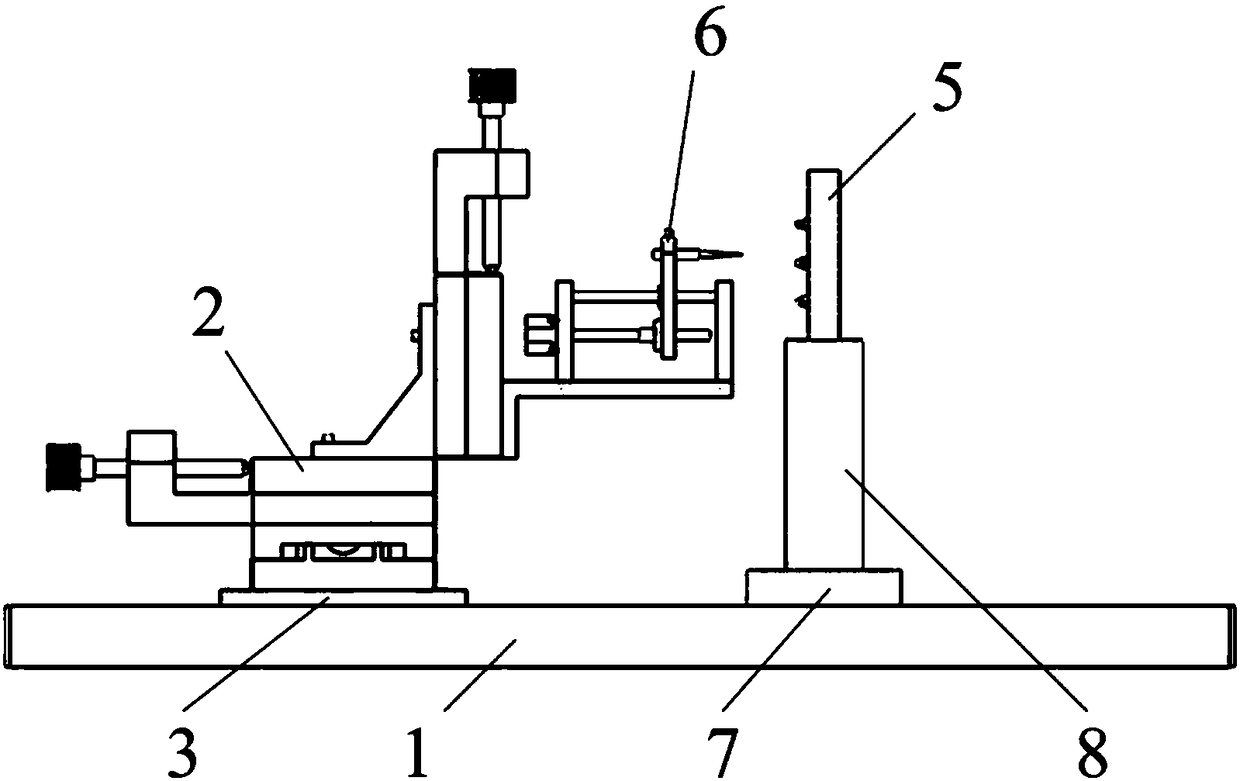
[0028] Such as Figure 1-Figure 3 As shown, the present invention relates to a non-contact shock wave excitation device for testing the dynamic characteristics of MEMS metal microstructures. The manual three-axis displacement stage 2 is installed on a base plate 3, and the base plate 3 is fixed on the base plate 1 by screws 4. A needle electrode unit 6 is installed on the Z-axis slide plate of the manual three-axis displacement table 2 .
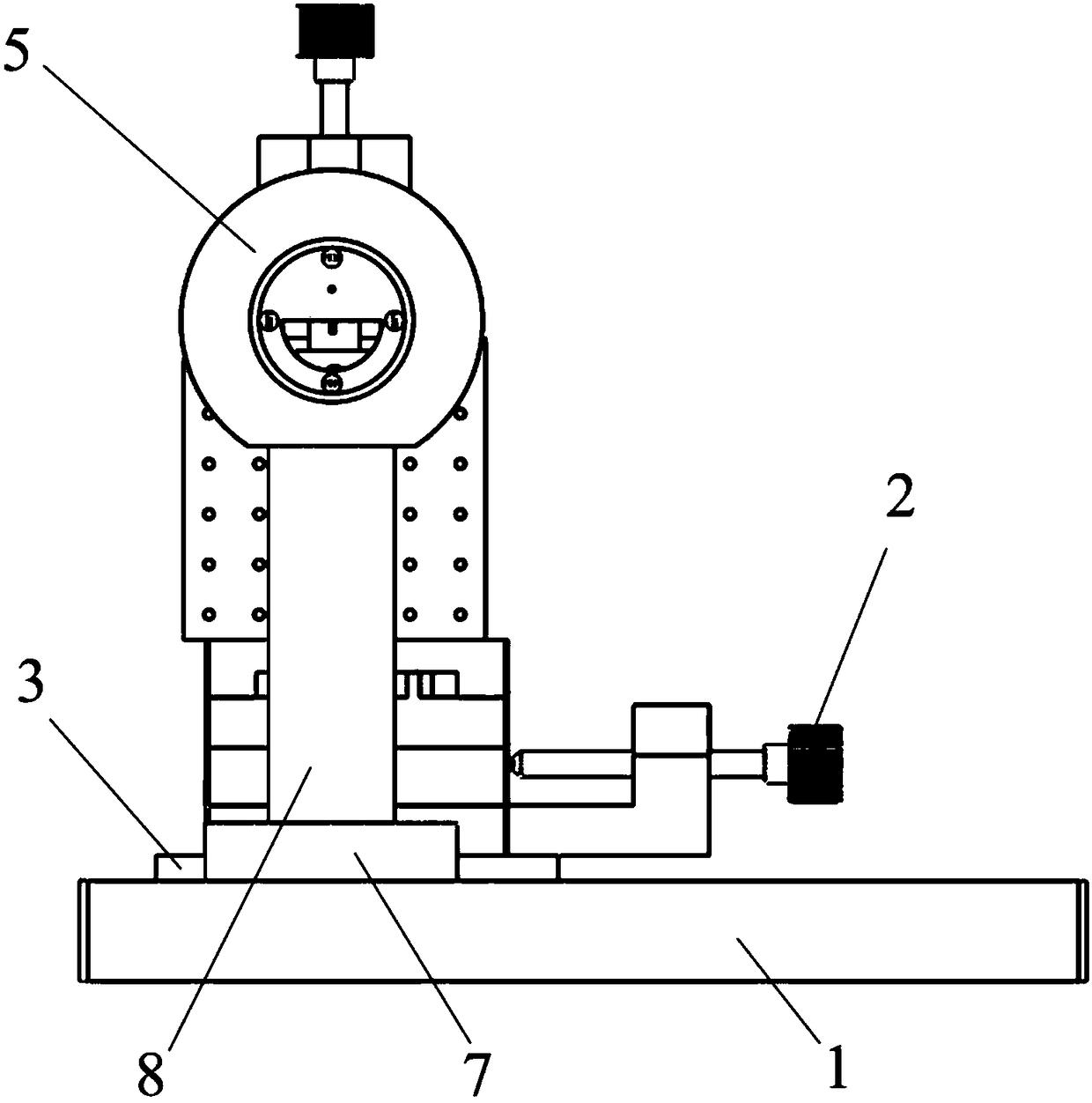
[0029] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the needle electrode unit 6 includes an L-shaped right-angle connecting plate 601 fixed on the Z-axis sliding plate by screws, and two supporting plates 605 parallel to each other are fixed on the right-angle connecting plate 601 by screws. A guide shaft 606 and a lead screw 614 arranged in parallel up and down are arranged between the plates 605, and a transmission plate 610 is sleeved on the guide shaft 606, and the corresponding guide shaft 606 on the transmission plate 610 is inlaid with a sliding fit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com