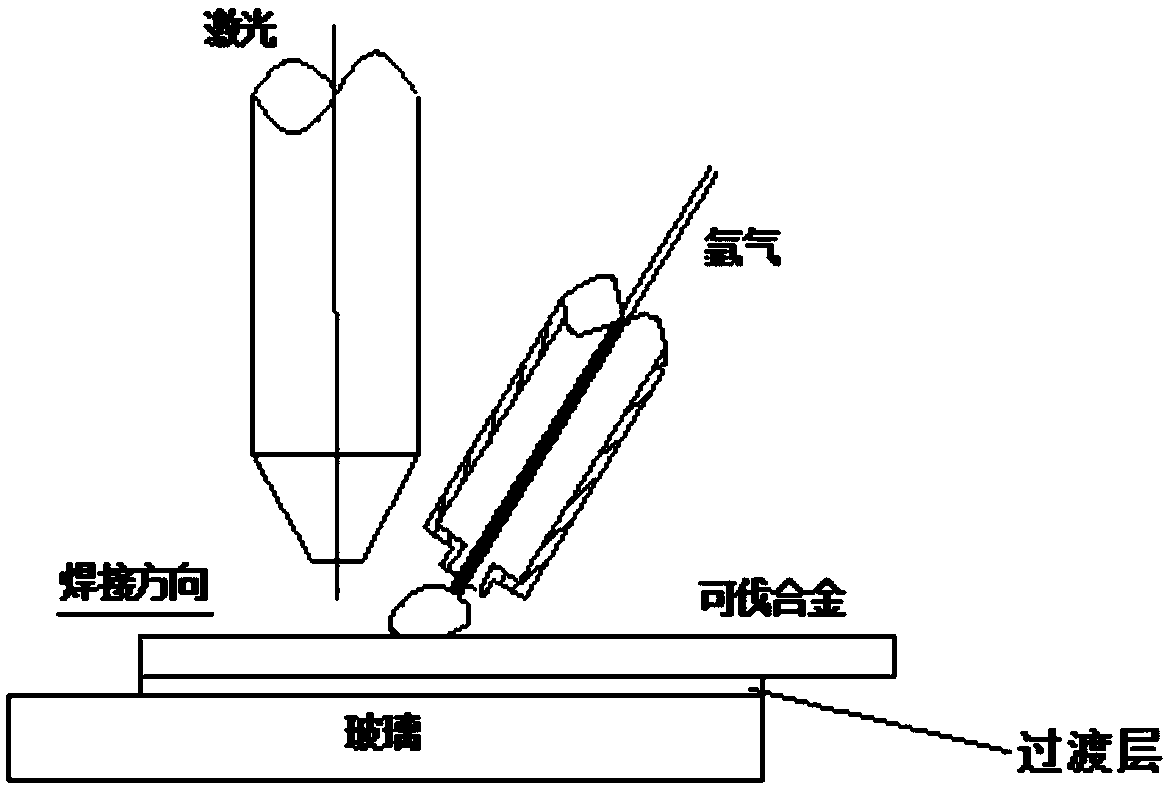
A Laser Welding Method for Joining Molybdenum Group Glass/Kovar Alloy by Adding Mo-Mn–Ni Metal Interlayer
An intermediate layer and laser welding technology, which is applied in the field of laser welding, can solve the problems of large difference in thermal expansion coefficient, poor toughness of non-metallic materials, and difficult interface bonding, so as to reduce welding stress, avoid cracking, and avoid cracking and fusing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] (1) Grind Kovar alloy from 400 mesh to 1200 mesh, and then perform ultrasonic cleaning in acetone solution for 20 minutes;
[0029] (2) Kovar alloy of 40×20×1.1mm is vacuumed at 10 -1 Treat in MPa environment for 20 minutes, then oxidize in a furnace at 800°C for 10 minutes;
[0030] (3) Place the oxidized Kovar alloy sample on the molybdenum group glass sample (20×15×3mm), add an intermediate layer in the middle, and then place it on the fixture;
[0031] (4) The preheating temperature is 300°C, and the preheating time is 20 minutes;
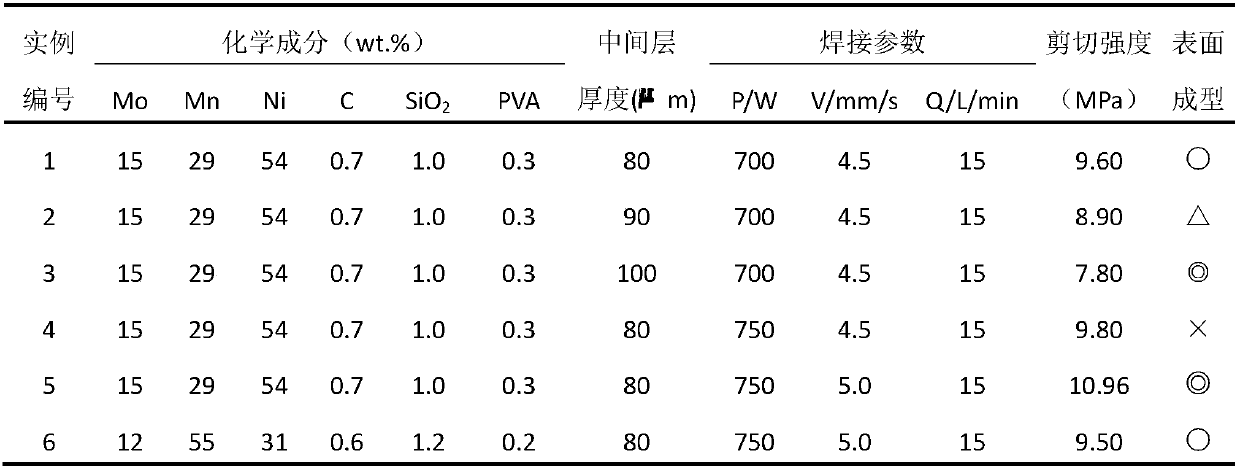
[0032] (5) The mass percentage of the middle layer is selected as: Mo: 15%, Ni: 54%, Mn: 29%, C: 0.7%, SiO 2 : 1.0%, the PVA additive accounts for 0.3%, and the thickness of the middle layer is 80 μm;
[0033] (6) Laser model: YLS-3000-SM, laser parameters: laser power 700W, welding speed 4.5mm / s, gas flow 15L / min;
[0034] (7) The post-weld heat treatment temperature is 350°C, and it is cooled with the furnace;
[0035] According t...
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) Grind Kovar alloy from 400 mesh to 1200 mesh, and then perform ultrasonic cleaning in acetone solution for 20 minutes;
[0038] (2) Kovar alloy of 40×20×1.1mm is vacuumed at 10 -1 Treat in MPa environment for 20 minutes, then oxidize in a furnace at 800°C for 10 minutes;
[0039] (3) Place the oxidized Kovar alloy sample on the molybdenum group glass sample (20×15×3mm), add an intermediate layer in the middle, and then place it on the fixture;
[0040] (4) The preheating temperature is 300°C, and the preheating time is 20 minutes;
[0041] (5) The mass percentage of the middle layer is selected as: Mo: 15%, Ni: 54%, Mn: 29%, C: 0.7%, SiO2: 1.0%, PVA additive accounts for 0.3%, and the thickness of the middle layer is 90 μm;
[0042] (6) Laser model: YLS-3000-SM, laser parameters: laser power 700W, welding speed 4.5mm / s, gas flow 15L / min;
[0043] (7) The post-weld heat treatment temperature is 350°C, and it is cooled with the furnace;
[0044] According to the s...
Embodiment 3
[0046] (1) Grind Kovar alloy from 400 mesh to 1200 mesh, and then perform ultrasonic cleaning in acetone solution for 20 minutes;
[0047] (2) Kovar alloy of 40×20×1.1mm is vacuumed at 10-1 Treat in MPa environment for 20 minutes, then oxidize in a furnace at a temperature of 800°C for 10 minutes;
[0048] (3) Place the oxidized Kovar alloy sample on the molybdenum group glass sample (20×15×3mm), add an intermediate layer in the middle, and then place it on the fixture;
[0049] (4) The preheating temperature is 300°C, and the preheating time is 20 minutes;
[0050] (5) The mass percentage of the middle layer is selected as: Mo: 15%, Ni: 54%, Mn: 29%, C: 0.7%, SiO2: 1.0%, PVA additive accounts for 0.3%, and the thickness of the middle layer is 100 μm;
[0051] (6) Laser model: YLS-3000-SM, laser parameters: laser power 700W, welding speed 4.5mm / s, gas flow 15L / min;
[0052] (7) The post-weld heat treatment temperature is 350°C, and it is cooled with the furnace;
[0053] Ac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shear strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shear strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com