A new rice gene wbph9(t) resistant to white-backed planthopper and its molecular marker method and application
A white-backed planthopper and molecular marker technology, applied in the field of plant molecular genetics, can solve problems such as unclear Wbph1, and achieve the effects of facilitating timely hybridization and breeding, improving the resistance level, and speeding up the breeding process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
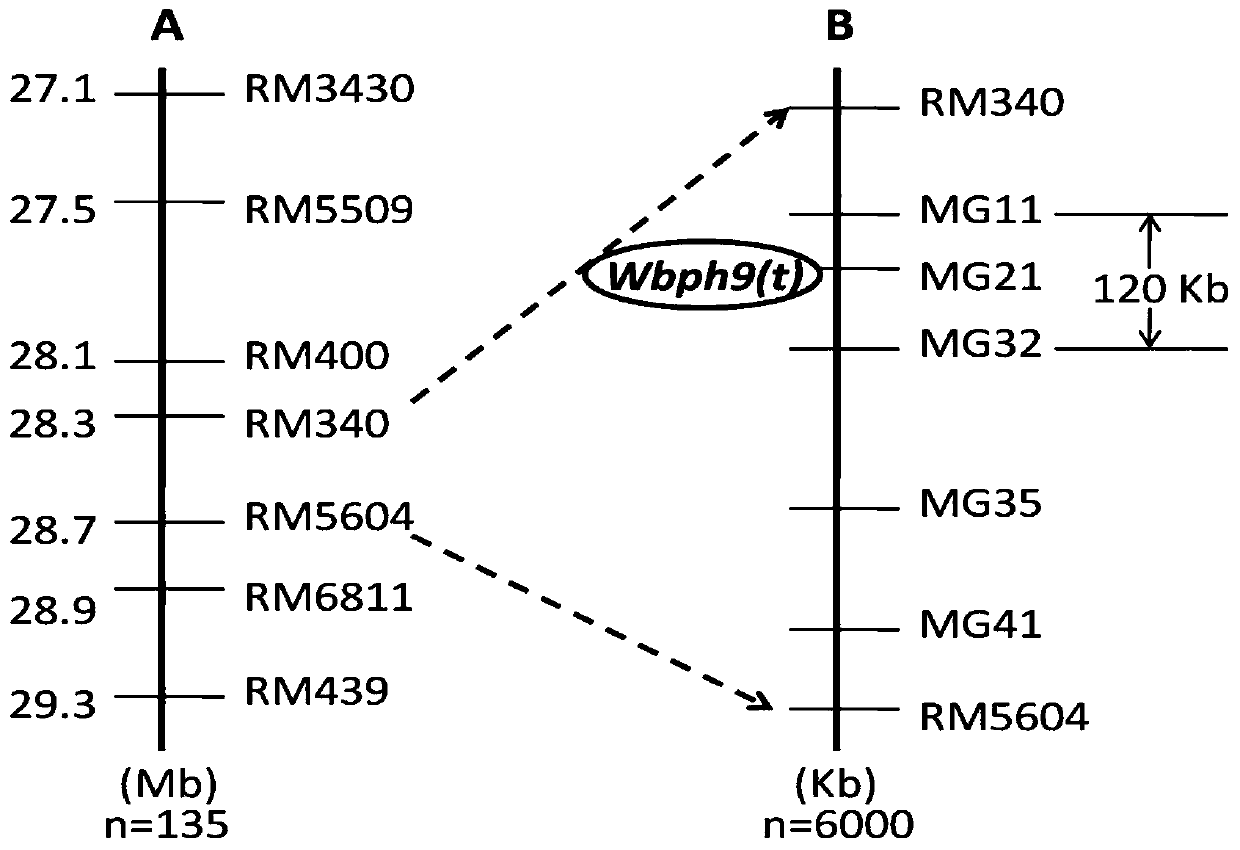
[0026] Example 1 : Obtaining molecular markers
[0027] (1) Gui 1025 / K41 F 2 Construction and phenotyping of family groups and RILs
[0028] 1. In the previous study, we used the hybridization and backcrossing of small-grain wild rice and cultivated rice IR24, combined with embryo rescue and molecular marker-assisted selection technology, to construct a set of small-grain wild rice introduction lines, which were identified and screened against white-backed planthopper. A rice line K41 with high resistance to white-backed planthopper and stable agronomic traits was obtained. In order to excavate the resistance gene in K41 and its closely linked molecular markers, the present invention takes the insect-susceptible variety Gui 1025 as the female parent and the insect-resistant strain K41 as the male parent to cross, and the obtained F 1 self-cross again, thus constructing F 2 separate groups, each F 2 The corresponding F was obtained from the individual plant through selfin...
Embodiment 2
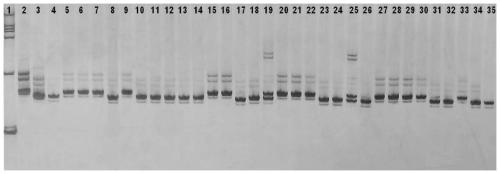
[0045] Example 2 : Validation of molecular markers
[0046] (1) Materials and methods
[0047] Negative varieties: 30 copies. Insect-sensitive lines Gui 1025, Lemont and TN1 are all conventional rice materials preserved in the laboratory. Among the progeny of the hybrid combination Gui 1025 / K41, there are 27 susceptible families.
[0048] Positive varieties: 30 copies, and 29 copies of insect-resistant families in the descendants of the hybrid combination of the insect-resistant lines K41 and Gui 1025 / K41.
[0049] The upstream primer of the primer pair of GM21 is the sequence shown in Seq ID No.3, and the downstream primer of the primer pair is the sequence shown in SeqID No.4;
[0050] Seq ID No.3: AAAGAGATTTATAATCCAAATTTTGGCCA;
[0051] Seq ID No. 4: GCCAAAGTAATTTAGGCCTGA.
[0052] The DNA extraction method and the molecular marker analysis method are the same as in Example 1.
[0053] (2) Results
[0054]Using the above method, PCR amplification was performed on the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com