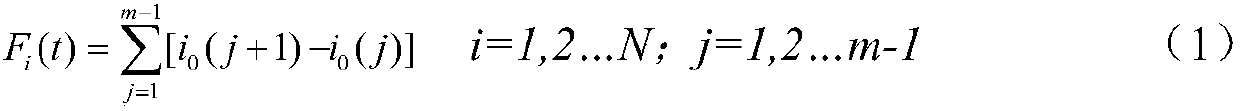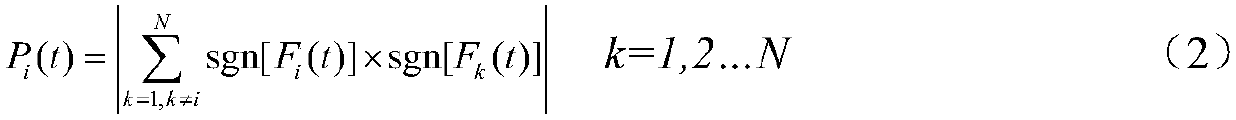A Fault Line Selection Method of Distribution Network Based on Zero Sequence Current Differential Polarity Comparison
A technology for distribution network faults and zero-sequence currents, applied in fault locations, detecting faults according to conductor types, and measuring electricity, etc., can solve problems such as hidden dangers of distribution network safety, and achieve low sampling frequency, easy implementation, and high accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Embodiment 1: A distribution network fault line selection method based on zero-sequence current differential polarity comparison. A simulation model is built according to the parameters of the distribution network operation. By setting different lines and phase-to-phase ground faults in the simulation model, Obtain the line power frequency zero-sequence current signal i generated by each simulated line under the ground fault 0i (t); Select the zero-sequence current i within 10ms after the fault 0i (t); then define the zero-sequence current differential function F of the line i (t), find the zero-sequence current i 0i (t) difference function F i (t), and then use the difference function F i (t) Construct P i (t), using P i (t) Compare the zero-sequence current polarity of each line, when P i (t)=max{P 1 (t),P 2 (t)...,P n (t)}, then line i is a faulty line; when P i (t)≠max{P 1 (t),P 2 (t)...,P n (t)}, then i is a non-faulty line.
[0022] The specific step...
Embodiment 2
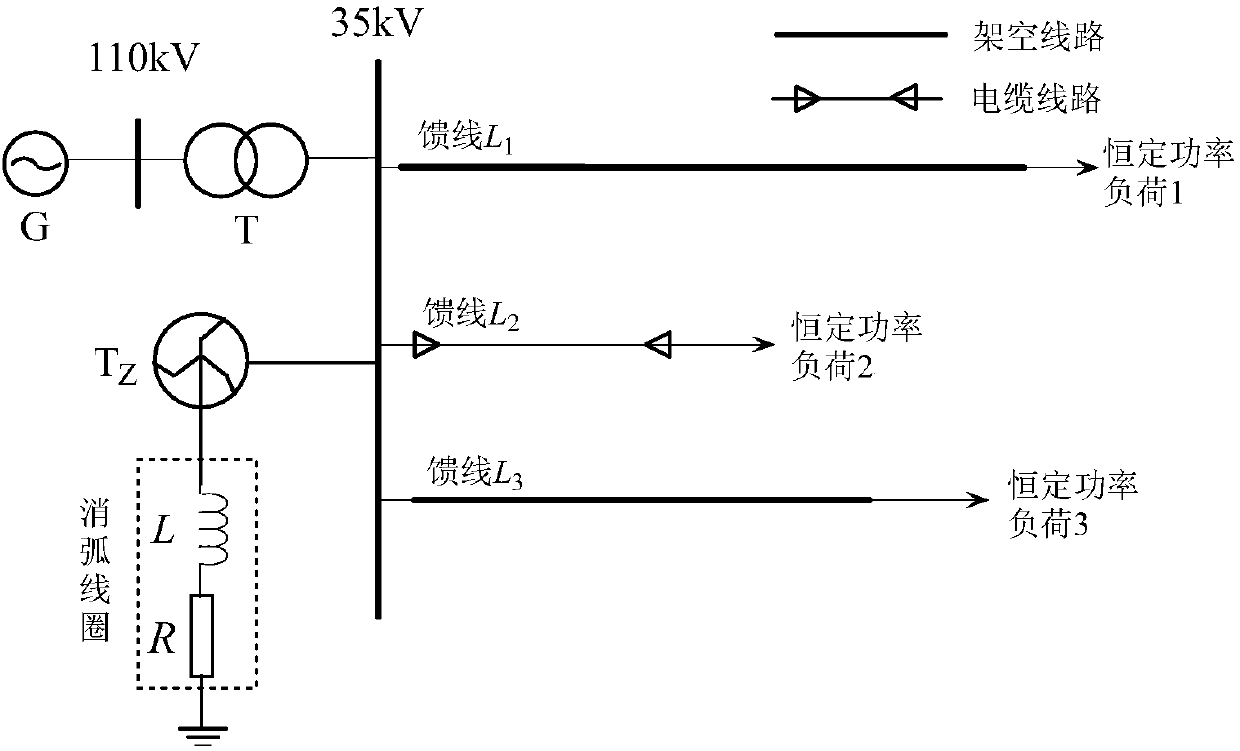
[0035] Embodiment 2: The other parts of this embodiment are the same as Embodiment 1, as shown in Figure 1, the simulation model of 110kV / 35kV distribution network is shown in Figure 1, it has 6 feeders, and the neutral point of the Z-shaped transformer passes through The arc coil series resistor is grounded. Overhead feeder L 1 =18km,L 3 =30km, cable feeder L 2 =7km. G in the power grid is an infinite power source; T is the main transformer, the transformation ratio is 110kV / 35kV, and the connection group is Y N / d11;T Z Is a zigzag transformer; L is the arc suppression coil; R is the damping resistance of the arc suppression coil. The feeder adopts three types of lines: overhead line, overhead line-cable hybrid line and cable line. The load uses a constant power load model.
[0036] (1) Feeder L 2 A single-phase grounding fault occurs in phase B 10 kilometers away from the beginning, the grounding resistance is 10Ω, the fault angle is 60°, and the sampling frequency ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com