Energy-saving dispatching method capable of supporting non-preemptive real-time task set
A technology of real-time tasks and scheduling methods, applied in the fields of instruments, data processing power, computing, etc., can solve the problems of not considering the characteristics of non-preemptive scheduling, unable to fully save system energy consumption, and calculating the deceleration factor too conservatively, etc. The effect of energy consumption, reliable scheduling performance and system energy saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention. In addition, the technical features involved in the various embodiments of the present invention described below can be combined with each other as long as they do not constitute a conflict with each other.
[0042] In the embodiment, the following three periodic tasks are given, expressed as (period, deadline, worst execution time): τ 1 =(5,5,1),τ 1 =(10,10,2),τ 1 =(20, 20, 1); the maximum blocking time of each task is B 1 =2,B 2 =1,B 3 =0.
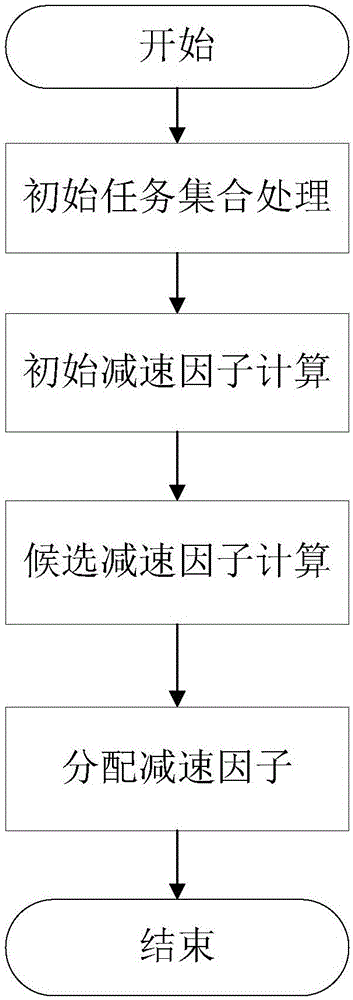
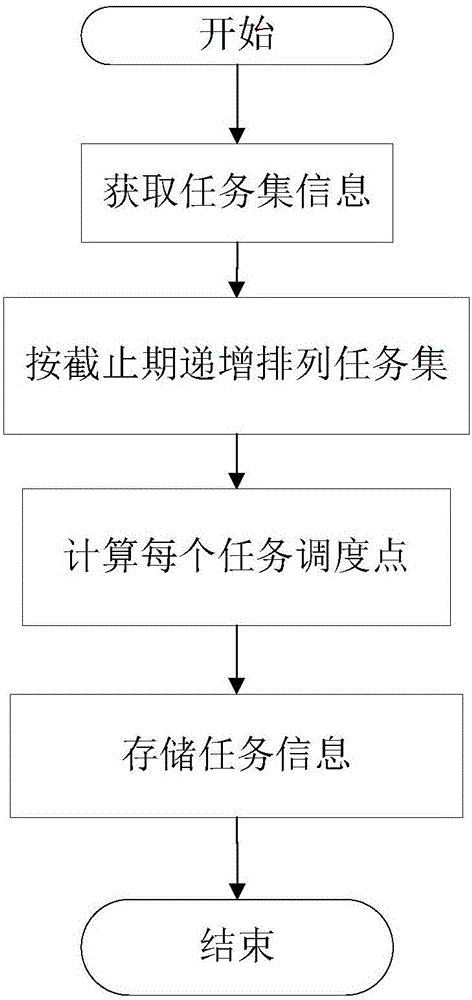
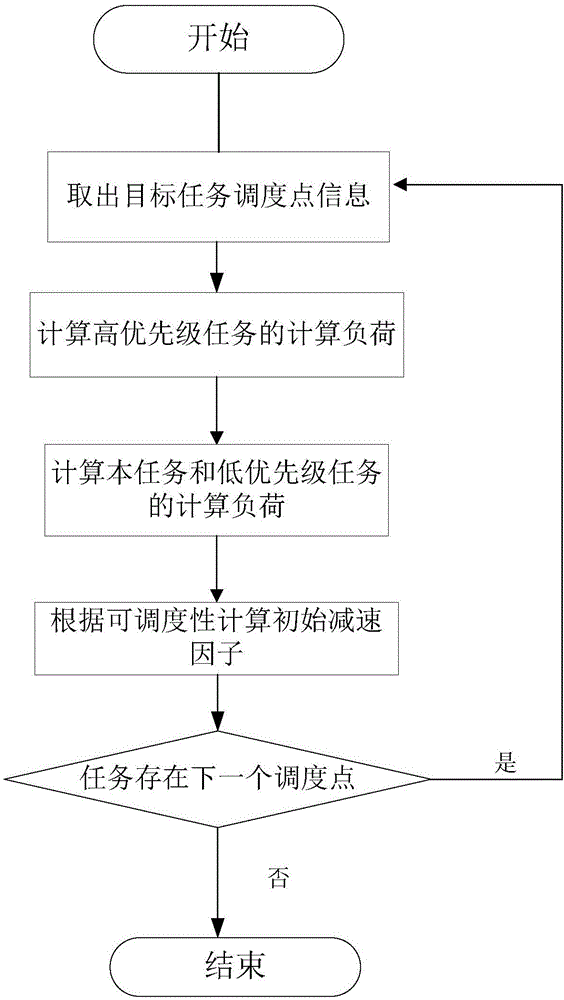
[0043] Such as figure 1As shown, it is a schematic flowchart of an energy-saving scheduling method supporting non-preemptive real-time task sets provide...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com