Preparation method of two-dimensional ultrathin nanosheets with ferromagnetic b-doped g-c3n4
A technology of g-c3n4 and nanosheets, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, nitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as shortage and difficulty in realization, and achieve convenient operation, low price, The effect of high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
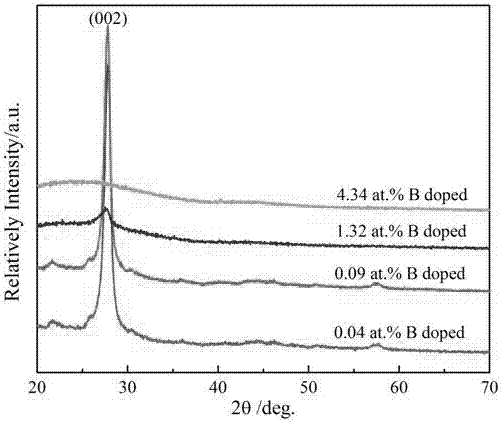
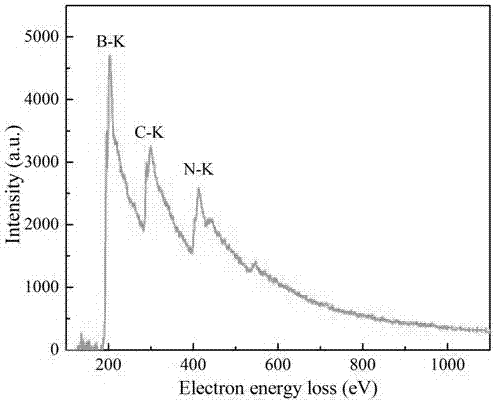
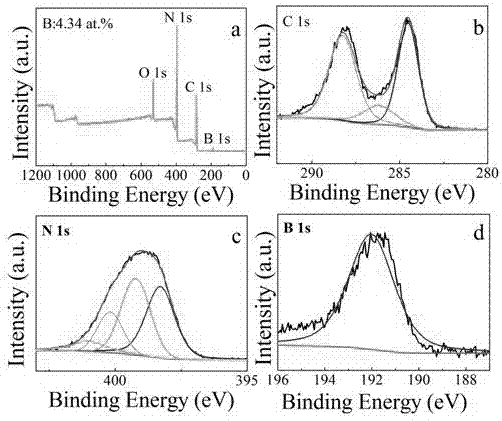
[0024] Dissolve 4 g of melamine and 0.05 g of boron oxide in 20 ml of ethanol and stir until completely mixed. Put the solution into an oven at 80°C and evaporate to dryness to obtain the precursor. The precursors were put into a porcelain boat and sintered in a tube furnace with argon (20 sccm) as a shielding gas. The tube furnace was heated from room temperature to 500 degrees Celsius at a heating rate of 5 degrees Celsius per minute and kept warm for two hours, then raised to 600 degrees Celsius at the same heating rate for two hours, turned off the power and naturally cooled to room temperature, and the obtained samples were taken out with alcohol After cleaning, centrifuge at a speed of 7000 rad / min to remove unreacted boron oxide, dry it, and ultrasonicate in an aqueous solution. The ultrasonic power ratio is set to 80%, and the temperature of the water tank is 30 degrees Celsius. The sample is peeled off by ultrasonication for one hour, and finally B g-C doped at 0.04 ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Dissolve 4 g of melamine and 0.1 g of boron oxide in 80 ml of ethanol and stir until completely mixed. Put the solution into an oven at 80°C and evaporate to dryness to obtain the precursor. The precursors were placed in a porcelain boat and sintered in a tube furnace with argon (50 sccm) as a shielding gas. The tube furnace was heated from room temperature to 550 degrees Celsius at a heating rate of 7 degrees Celsius per minute and kept warm for two hours, then raised to 600 degrees Celsius at the same heating rate for two hours, turned off the power and naturally cooled to room temperature, and the obtained samples were taken out with alcohol After cleaning, centrifuge at a speed of 7000 rad / min to remove unreacted boron oxide, dry it, and ultrasonicate in an aqueous solution. The ultrasonic power ratio is set to 80%, and the temperature of the water tank is 50 degrees Celsius. The sample is peeled off by ultrasonication for one hour, and finally B g-C doped at 0.09 ...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Dissolve 4 g of melamine and 0.15 g of boron oxide in 20 ml of ethanol and stir until completely mixed. Put the solution into an oven at 80°C and evaporate to dryness to obtain the precursor. The precursors were put into a porcelain boat and sintered in a tube furnace with argon (100 sccm) as a shielding gas. The tube furnace was heated from room temperature to 500 degrees Celsius at a heating rate of 9 degrees Celsius per minute and kept warm for two hours, then raised to 650 degrees Celsius at the same heating rate for four hours, turned off the power and naturally cooled to room temperature, and the obtained samples were taken out with alcohol. After cleaning, centrifuge at a speed of 7000 / min to remove unreacted boron oxide, dry it, and ultrasonicate it in an aqueous solution. The ultrasonic power ratio is set to 80%, and the temperature of the water bath is 30 degrees Celsius. The sample is peeled off by ultrasonication for one hour, and finally B-doped g-C with a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com