High resolution radar fast imaging method based on generalized reflectivity model
A technology of radar imaging and imaging method, which is applied in the direction of radio wave reflection/re-radiation, utilization of re-radiation, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as ghosting, high computational complexity of tomographic methods, target recognition and classification burden, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
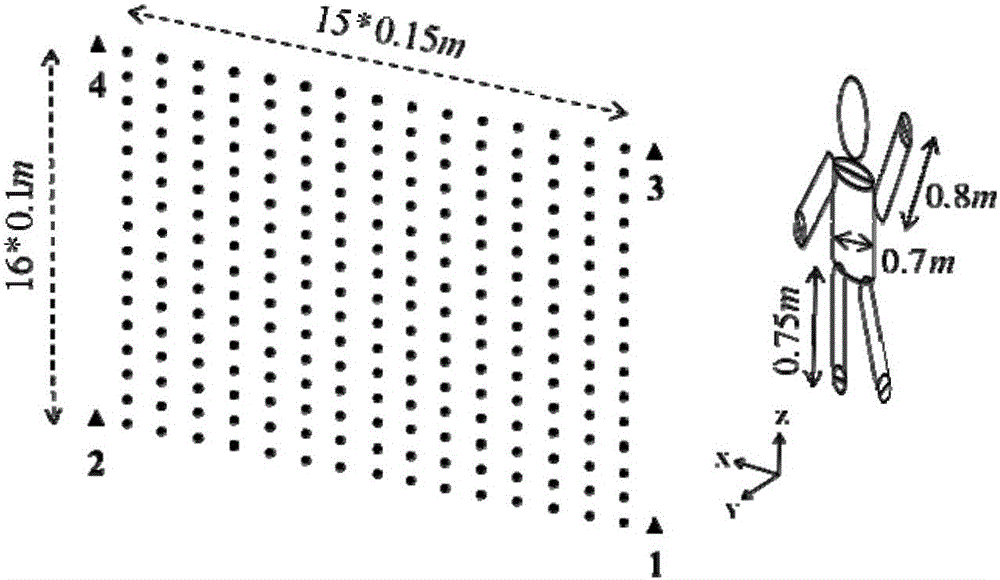
[0067] In this embodiment, the structure of the 3D simulation system is as follows figure 1 As shown, the radar imaging system adopts the multiple-input multiple-output antenna technology MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) radar imaging system with separate transceivers.
[0068] The high-resolution radar rapid imaging method based on the generalized reflectivity model of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0069] 1) Establish a radar imaging system to obtain radar scattering data:
[0070] The radar imaging system includes four transmitters 1-4, 240 receivers, the bandwidth of the transmitted signal is 1-3Ghz, the transmitter transmits the signal to the target imaging area, the receiver receives the echo signal, and the tth transmitter transmits the signal After that, the echo signal at each receiver can be expressed as y F,t =[y F,t,1 ; у F,t,2 ;… у F,t,R ]; figure 1 The four triangles in the figure represent the four transmitters 1-4; the dots o...
Embodiment 2
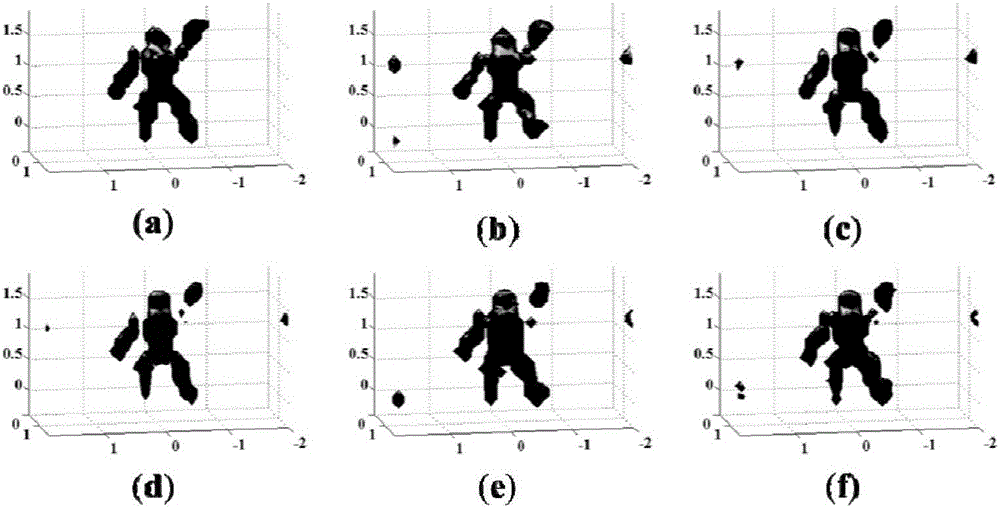
[0093] In this embodiment, according to the second sub-imaging region division method in b) of step 3), that is, the neighbor element constant method divides the target imaging region into B sub-imaging regions, and in this embodiment, the target imaging region is divided into B= 1, 4, 8, 12, 24 and 32 sub-imaging areas. Others are the same as embodiment one. The number of divided sub-imaging areas is different, and different imaging effects are obtained respectively, such as image 3 shown.
[0094] In this embodiment, the relationship between dividing different numbers of sub-imaging regions and the average imaging time is shown in Table 2 below:
[0095]
[0096]
[0097] Table 2
[0098] As can be seen from Table 2, Embodiment 2 verifies the correctness of the conclusion of Embodiment 1: as the number of sub-imaging regions increases, the average imaging time decreases exponentially, and it can be seen that the division of sub-imaging regions is greatly accelerate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com