A Visual Terrain Classification Method Based on Multiple Coding and Feature Fusion
A technology of terrain classification and feature fusion, which is applied in the directions of instruments, computing, character and pattern recognition, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory accuracy and stability of underlying features, reduce feature space correlation, improve classification effect, The effect of accuracy and speed improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
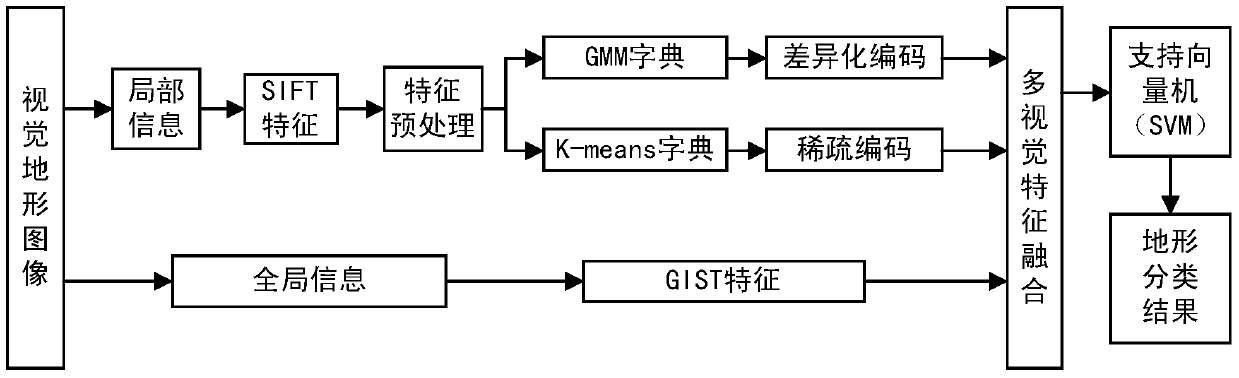
[0029] The embodiment of the present invention provides a visual terrain classification method based on multiple coding and feature fusion, see figure 1 , the method includes the following steps:
[0030] 101: Establish a visual terrain dataset as an evaluation test object, perform key point detection on the visual terrain image, describe the key points of local information in the image using SIFT features, and extract local underlying visual information;
[0031] 102: Use PCA-Whitening to perform feature preprocessing on SIFT features to reduce the correlation of feature spaces;
[0032] 103: Establish K-means (K-means clustering) dictionary and GMM (Gaussian mixture model clustering) dictionary respectively according to the result of feature preprocessing;
[0033] 104: Use sparse coding for the K-means dictionary to describe the 0-order local features of the visual terrain image; use differential coding for the GMM dictionary to describe the 1st-order and 2-order local fea...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The following is combined with specific calculation formulas, examples and figure 2 The scheme in embodiment 1 is described in detail, see below for details:
[0040] (1) Establishment of visual terrain dataset
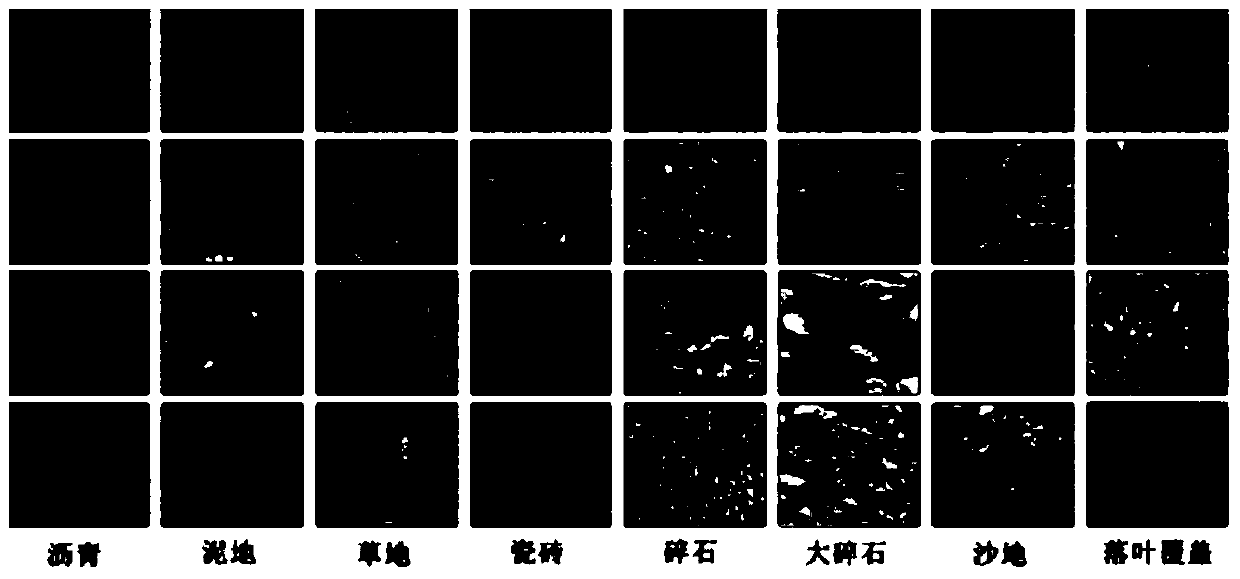
[0041] Because there is no general-purpose data set in the field of terrain recognition, the embodiment of the present invention produced a data set DS1. As an evaluation test object, the data set DS1 contains a total of 8 different typical terrain road surfaces: asphalt road, mud, grass, ceramic tiles, gravel , large gravel, sand and leaf cover. The pictures are acquired under different lighting and weather conditions, with a uniform resolution of 256×256, each category contains at least 300 pictures, and the data set has a total of 2700 pictures. Various types of typical road surfaces such as figure 2 shown.
[0042] The embodiments of the present invention do not limit the resolution of pictures, the number of pictures, and the types of pictures, which ...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Below in conjunction with concrete experiment, the scheme in embodiment 1 and 2 is carried out feasibility verification, see the following description for details:
[0095] see image 3 , In 2012, Filichkin and Byl of the University of California-Santa Barbara (UCSB) Robotics Institute used SIFT features, combined with the word bag method, to generate compact image mid-level descriptors, and input them into support vector machines Classification and recognition in (SVM) has been greatly improved compared with previous methods, and has become the current standard method in the field of terrain recognition. Its research results have also been applied to the US military robot - LittleDog (LittleDog), which has become an important functional load. . In the embodiment of the present invention, this method is used as a baseline method, and a comparison of effects is given at the end.
[0096] The embodiment of the present invention extracts SIFT and GIST features, adopts PC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com