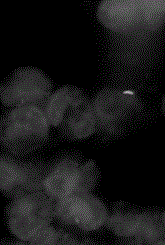
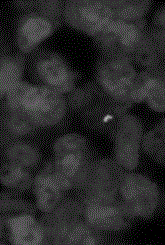
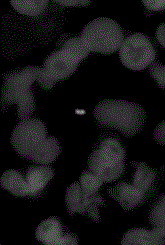
Immuno-fluorescent staining method for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis in leukocytes and kit
A technology for Mycobacterium tuberculosis and white blood cells, applied in the field of immunofluorescence staining and kits for detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis in white blood cells, can solve the problem of inability to obtain bacteriological evidence, high complexity of molecular detection, and inability to distinguish live bacteria from dead bacteria Issues such as false positive results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Detection and Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Example 1 Plasma
[0097] (1) Collect 5-10ml of the subject's blood (anticoagulation, EDTA anticoagulation can help to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis and then do molecular detection and drug resistance test);
[0098] (2) Centrifuge at 500-1500 rpm for 5-10 minutes (it can also allow blood cells to sink naturally and then separate plasma and blood cells);
[0099] (3) Membrane-based microfluidic filtration device to filter and enrich Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
[0100] (4) Plasma 2-10ml, take 2ml as an example to illustrate the method and process;
[0101] (5) Add 2ml of plasma and 2ml of normal saline or PBS, and mix well;
[0102] (6) Add 8ml of 6% sodium hypochlorite, mix well, and let stand for 5-20 minutes;
[0103] (7) Add 48ml of 95 ethanol (containing 1% TritonX-100), mix well, and let stand for 5-15 minutes;
[0104] (8) Add the above liquid into a microfluidic device or filter and enrich Myc...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Example 2 Detection and identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis on white blood cell sheet
[0111] (1) Collect 5-10ml of the subject's blood (anticoagulation, EDTA anticoagulation can help to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis and then do molecular detection and drug resistance test);
[0112] (2) Centrifuge at 500-1500 rpm for 5-10 minutes (it can also allow blood cells to sink naturally and then separate plasma and blood cells);
[0113] (3) Add red blood cell lysate (1:5-10) to the blood cells left after absorbing plasma, and mix slowly on a shaker for 5-15 minutes;
[0114] (4) Centrifuge at 1500-1800 rpm for 5-10 minutes, discard the supernatant;
[0115] (5) Add 5ml of normal saline or PBS, centrifuge at 1500-1800 rpm for 5-10 minutes, and discard the supernatant;
[0116] (6) Add 0.1% BSA (PBS or normal saline) to 0.2ml to suspend leukocytes;
[0117] (7) Spread on glass slides to make white blood cell smears;
[0118] (8) Fix with 1-8% paraformaldehyde (...
Embodiment 3
[0123] Example 3 Detection and identification of mycobacterium tuberculosis in cerebrospinal fluid
[0124] (1) 0.5-2ml of freshly collected cerebrospinal fluid, to avoid cell damage, decomposition of glucose and other substances, bacterial dissolution, etc. due to the specimen being placed for too long, and the specimen should try to avoid coagulation and mixing into the blood;
[0125] (2) Membrane-based microfluidic filtration device to filter and enrich Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
[0126] (3) Cerebrospinal fluid 0.5-2ml, take 0.5ml as an example to illustrate the method and process;
[0127] (4) Add 0.5ml of cerebrospinal fluid to 3.5ml of normal saline or PBS, and mix well;
[0128] (5) Add 8ml of 6% sodium hypochlorite, mix well, and let stand for 5-20 minutes;
[0129] (6) Add 48ml of 95 ethanol (containing 1% TritonX-100), mix well, and let stand for 5-15 minutes;
[0130] (7) Add the above-mentioned liquid into a microfluidic device or filter and enrich Mycobacter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com