Surface-plasma-enhanced two-dimensional material/semiconductor heterojunction solar cell and preparation method therefor
A surface plasmon and solar cell technology, applied in semiconductor devices, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of solar cell power generation, high cost of battery manufacturing, low photoelectric conversion efficiency, etc., to achieve Ease of promotion, improvement of conversion efficiency, and remarkable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
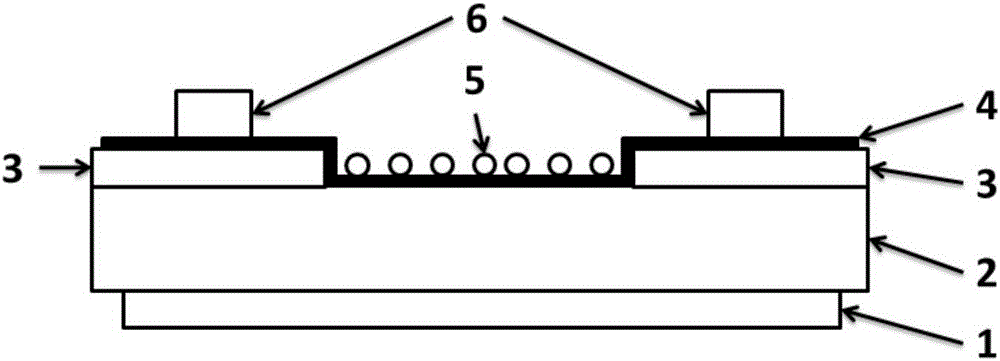
[0023] 1) Using thermal evaporation to deposit chromium-gold composite electrode on the back of n-type gallium arsenide;
[0024] 2) On the other side of the gallium arsenide substrate, a 100 nm thick aluminum oxide electrode insulating layer is deposited by electron beam evaporation and a mask method;
[0025] 3) Transfer 0.4 nanometer thick graphene to the side of the gallium arsenide substrate with the electrode insulating layer using PMMA as a support layer and cover part of the graphene on the aluminum oxide electrode insulating layer;
[0026] 4) Coat the silver paste directly on the graphene within the electrode insulating layer and dry it as the front electrode;
[0027] 5) Spin-coating 80 nanometers of gold quantum dot solution on graphene to obtain a surface plasma enhanced graphene / gallium arsenide heterojunction solar cell.
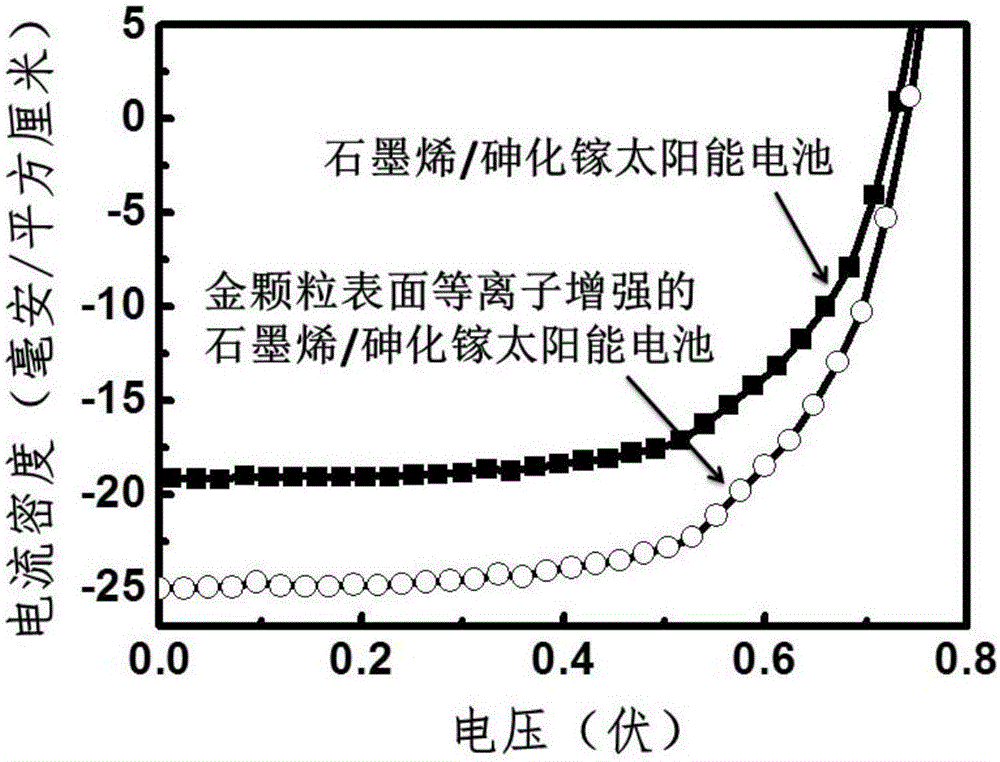
[0028] The obtained surface plasma-enhanced graphene / gallium arsenide heterojunction solar cell produces a local field enhancement on the surface of th...
Embodiment 2
[0030] 1) Using thermal evaporation to deposit titanium-silver composite electrode on the back of n-type silicon;
[0031] 2) Using plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition and a mask method to deposit a silicon nitride electrode insulating layer with a thickness of 200 microns on the other side of the silicon substrate;
[0032] 3) Transfer the 500-nm-thick molybdenum disulfide to the side of the silicon substrate with the electrode insulating layer using PMMA as a support layer and cover part of the molybdenum disulfide on the silicon nitride electrode insulating layer;
[0033] 4) Magnetron sputtering is used to deposit nickel on the molybdenum disulfide in the range of the electrode insulating layer as the front electrode;
[0034] 5) Spin-coating a silver quantum dot solution with a particle diameter of 200 nanometers on graphene to obtain a surface plasma enhanced molybdenum disulfide / silicon heterojunction solar cell.
Embodiment 3
[0036] 1) Using thermal evaporation to deposit a copper-platinum composite electrode on the back of p-type indium phosphide;
[0037] 2) Depositing a 2nm thick titanium oxide electrode insulating layer on the other side of the indium phosphide substrate by atomic layer deposition and masking;
[0038] 3) Transfer the 20-nanometer-thick tungsten disulfide to the side of the indium phosphide substrate with the electrode insulating layer using PMMA as a support layer and cover part of the tungsten disulfide on the aluminum oxide electrode insulating layer;
[0039] 4) Print silver paste on the tungsten disulfide in the range of the electrode insulating layer and dry it as the front electrode;
[0040] 5) Spin-coating a 5 nanometer particle diameter aluminum quantum dot solution on graphene to obtain a surface plasma enhanced tungsten disulfide / indium phosphide heterojunction solar cell.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com