Phthalic acid derivative gelator and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of phthalic acid and phthalic anhydride, applied in the field of phthalic acid-derived gelling factors, can solve problems such as not forming industrialization advantages, achieve superior gel ability, reduce gel concentration, and improve thermodynamics The effect of stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Embodiment 1 phthalic acid organogel preparation
[0055] (1) Phthalic acid gelling factor
[0056] Preparation method: Dissolve 148.12mg (1mmol) of phthalic anhydride in excess dichloromethane, stir at room temperature and dissolve completely, then dissolve 269.31mg (1mmol) of octadecylamine (NH 2 (CH 2 ) 17 CH 3 ) slowly poured into the solution, and mechanically stirred for 6 hours to obtain a white precipitate, which was filtered, and the filter cake was recrystallized with methanol and dried in vacuum to obtain the phthalic acid gel factor. Its structural formula is as follows,
[0057]
[0058] (2) Test results
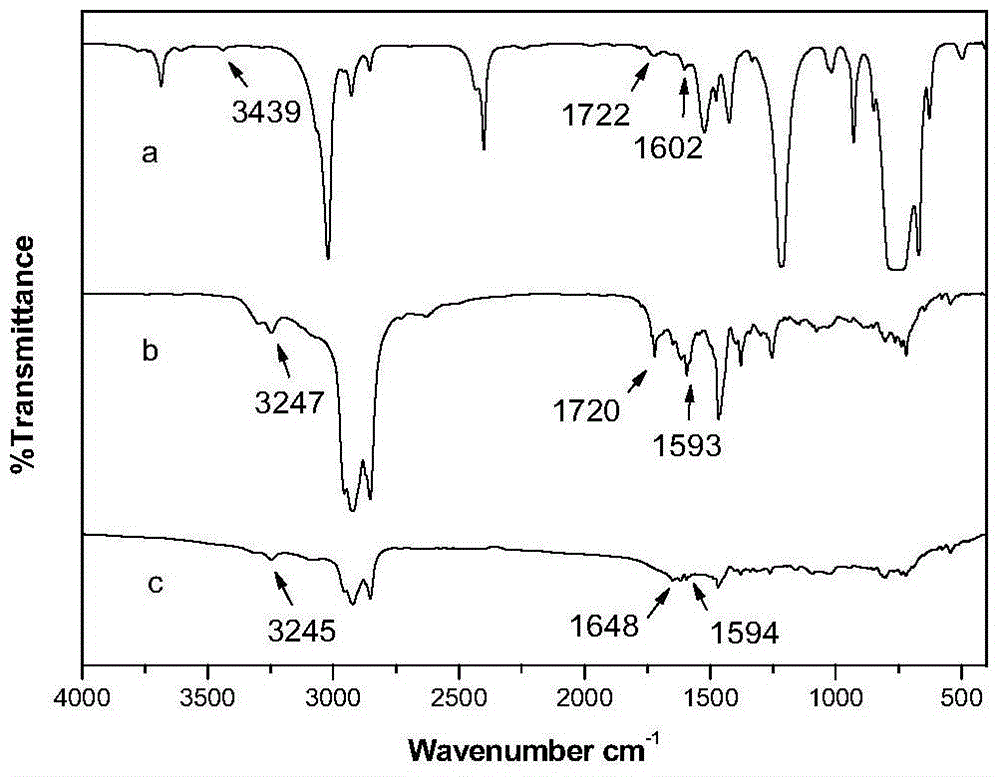
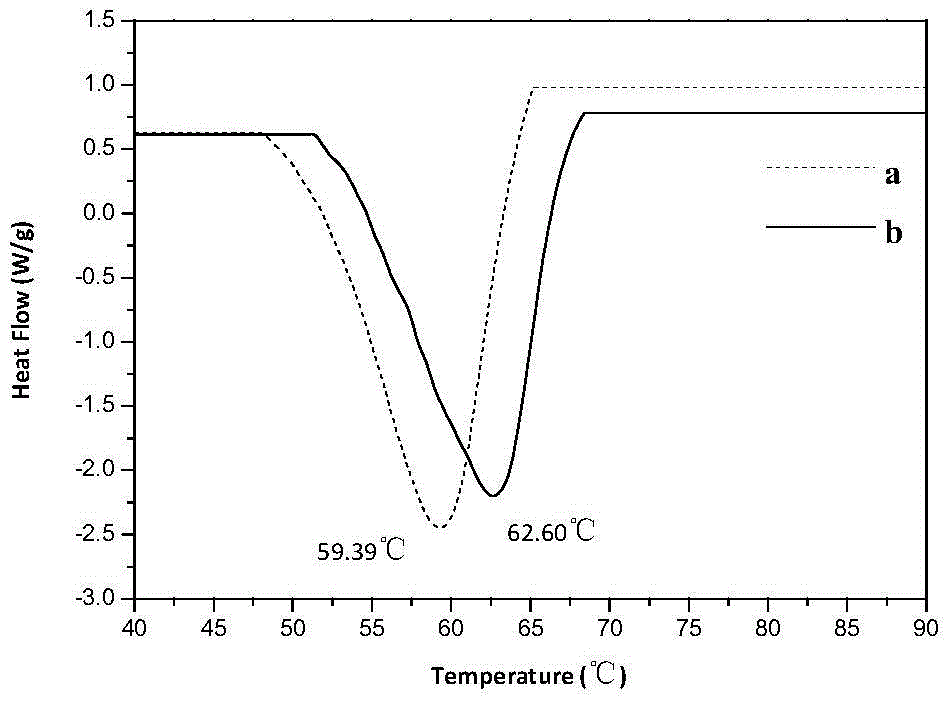
[0059] Such as figure 1 As shown, the FT-IR detection results showed that the gels formed by the two gelling factors had hydrogen bonding. Such as figure 2 with Figure 5 As shown, the DSC and rheological spectra show that the gel formed by the two-component gelling factor has higher thermodynamic stability and greater mechanical strength. S...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Embodiment 2 phthalic acid organogel preparation
[0066] (1) Phthalic acid gelling factor
[0067] The preparation method is as follows: Dissolve 205.17mg (1mmol) of 3-acetamidophthalic anhydride in excess dichloromethane, stir at room temperature to dissolve completely, and dissolve 241.28mg (1mmol) of hexadecylamine (NH 2 (CH 2 ) 15 CH 3 ) slowly poured into the solution, and mechanically stirred for 6 hours to obtain a white precipitate, which was filtered, and the filter cake was recrystallized with methanol and dried in vacuum to obtain the phthalic acid gel factor. Its structure is as follows,
[0068]
[0069] (2) Test results
[0070] Such as Image 6 As shown, the FT-IR detection results showed that the gels formed by the two gelling factors had hydrogen bonding. Such as Figure 7 with Figure 10 As shown, the DSC and rheological spectra show that the gel formed by the two-component gelling factor has higher thermodynamic stability and greater mech...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Embodiment 3 phthalic acid organogel preparation
[0077] (1) Phthalic acid gelling factor
[0078] The preparation method is as follows: Dissolve 204.8mg (1mmol) of 4-tert-butylphthalic anhydride in excess dichloromethane, stir at room temperature to dissolve completely, then slowly pour 185.21mg (1mmol) of dodecylamine into the solution , and mechanically stirred for 6 hours to obtain a white precipitate, which was filtered, and the filter cake was recrystallized with methanol and dried in vacuum to obtain the phthalic acid gel factor. Its structure is as follows,
[0079]
[0080] (2) Test results
[0081] Such as Figure 11 As shown, the FT-IR detection results indicated that hydrogen bonding existed in the gel formed by the gelling factor (n=12). Such as Figure 12 with Figure 15 As shown, the DSC and rheological spectra show that the gel formed by the phthalic acid gelling factor (n=12) has better thermodynamic stability and mechanical strength. Such as...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com