Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane crack short-fiber re-splitting method and device used for same
A technology of polytetrafluoroethylene film and short fiber, which is applied in the direction of textiles and papermaking, and can solve the problems of high fiber branching rate, low percentage of fine fibers, and inability to continue production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
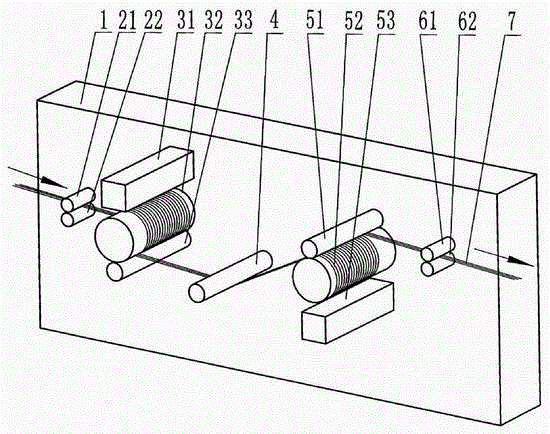
[0062] The polytetrafluoroethylene film-split fiber tow made of flat fibers with a width of 6-140 microns and a thickness of 10-30 microns produced by the conventional film-split method is the primary tow, and then 10 bundles of the primary tow are The tow is synthesized into a strand and primary tow with a width of 15 mm and a thickness of 1.5 mm. After testing, the percentage of fibers with a width of less than 10 microns in the combined and primary tow is 18.6%, and the width is 10 to 30 microns. The percentage of the number of fibers is 36.6%, the percentage of the number of fibers with a width greater than 30 microns is 41.8%, and the fiber splitting rate is 72%.
[0063] Through the counterclockwise rotation of the upper rubber feeding roller 21 and the clockwise rotation of the lower rubber feeding roller 22, the merged tow is first fed with only one spunlace head at a linear speed of 10 m / min. The first drum-type hydroentanglement unit 3 of part 31 makes the tow run on...
Embodiment 2
[0067] The polytetrafluoroethylene film-split fiber tow made of flat fibers with a width of 6-140 microns and a thickness of 10-30 microns produced by the conventional film-split method is the primary tow, and then 22 bundles of the primary tow are The tow is synthesized into a strand and primary tow with a width of 30 mm and a thickness of 3 mm. After testing, the percentage of the number of fibers with a width of less than 10 microns in the combined and primary tow is 19.5%, and the width is 10 to 30 microns. The percentage of the number of fibers is 37.2%, the percentage of the number of fibers with a width greater than 30 microns is 42.3%, and the fiber splitting rate is 75%.
[0068] Through the counterclockwise rotation of the upper rubber feeding roller 21 and the clockwise rotation of the lower rubber feeding roller 22, the merged tow is first fed with only one spunlace head at a linear speed of 6.5 m / min. The first drum type hydroentanglement unit 3 of part 31 makes t...
Embodiment 3
[0072] The polytetrafluoroethylene film-split fiber tow made of flat fibers with a width of 6-140 microns and a thickness of 10-30 microns produced by the conventional film-split method is the primary tow, and then 35 bundles of the primary tow are The tow is synthesized into a strand and primary tow with a width of 50 mm and a thickness of 5 mm. After testing, the percentage of fibers with a width of less than 10 microns in the combined and primary tow is 21.6%, and the width is 10 to 30 microns. The percentage of the number of fibers is 38.6%, the percentage of the number of fibers with a width greater than 30 microns is 42.8%, and the fiber splitting rate is 78%.
[0073] Through the counterclockwise rotation of the upper rubber feeding roller 21 and the clockwise rotation of the lower rubber feeding roller 22, the merged tow is first fed with only one hydroentanglement head at a linear speed of 3 m / min. The first drum-type hydroentanglement unit 3 of part 31 makes the tow ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com