Sole structure of high-heeled shoe, high-heeled shoe and manufacturing method of high-heeled shoe
A technology for high-heeled shoes and insoles, which is applied to soles, footwear, insoles, etc., can solve problems such as tired feet pain, large articular cartilage damage, etc., and achieve the effect of improving cushioning rate, softness, quality and efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
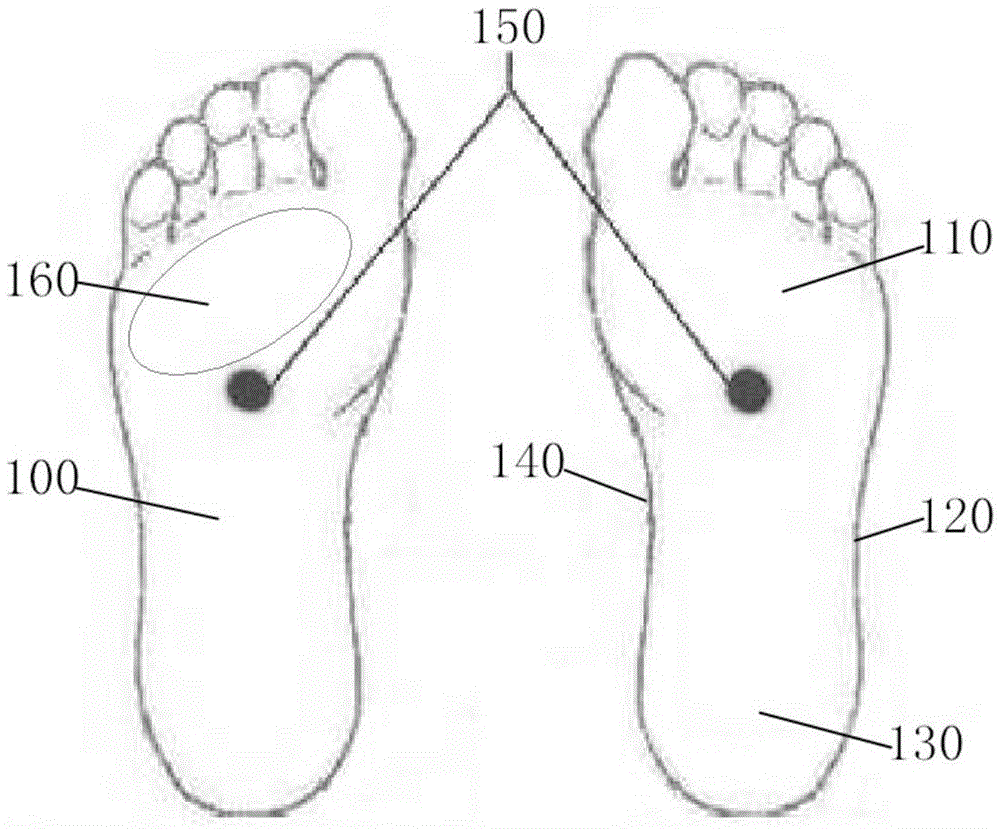
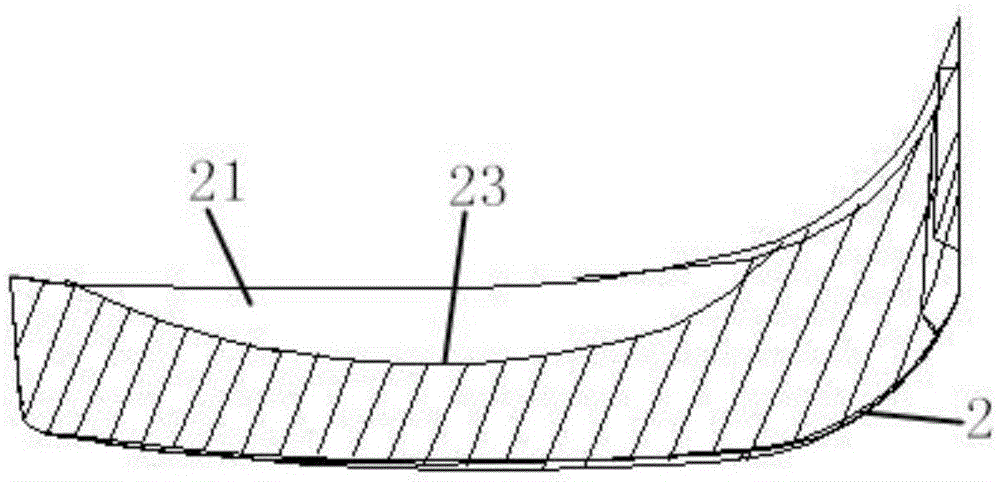
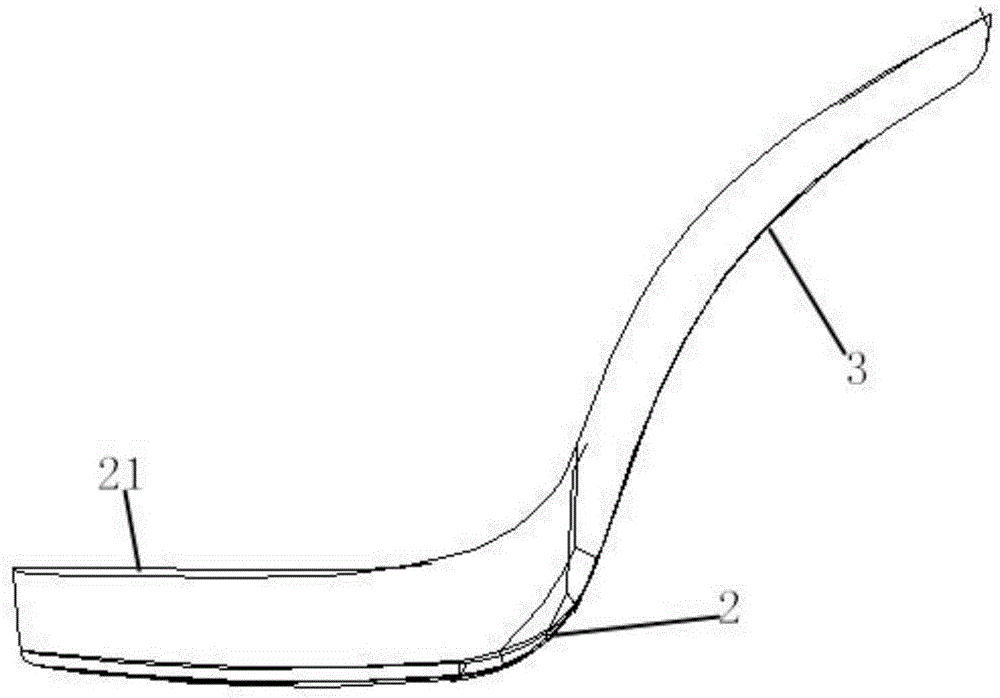
[0041] Such as Figure 2 to Figure 5As shown, a high-heeled shoe sole structure provided in this embodiment includes a waterproof platform 2, a midsole 3 and an insole 4, the waterproof platform 2 is connected with the midsole 3 to form a midsole waterproof platform assembly, and the midsole 3 includes The first arc-shaped portion 31 and the second arc-shaped portion 32, the surface of the first arc-shaped portion 31 is provided with a depression corresponding to the position of the arch 140, that is, the waterproof platform 2, the first arc-shaped portion 31 and the second arc-shaped portion 32 are respectively It is in contact with the forefoot 11, the outer side of the sole 12 and the heel 13 to form a contact surface; the midsole waterproof platform assembly has a contact surface bearing the pressure of the sole 100, and the insole 4 is placed on the contact surface; the insole 4 is located on the The bottom of the contact position with the forefoot 110 is provided with a ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The difference between the sole structure of the high-heeled shoes of this embodiment and that of Embodiment 1 is that when the heel difference of the high-heeled shoes is 9 cm, because the heel difference is relatively large, the force on the forefoot 110 is large, and because the heel 130 is tilted almost to the ground, the sole 100 is stressed. Move the center of gravity forward, refer to the foot shape of women, because the shoe size of women is generally 34 to 40 yards, so the middle thickness point 23 of the groove 21 is set at 25mm in front of the corresponding point 22 of Yongquan point, which is close to the metatarsophalangeal line , in order to hit the direct part, the middle thickness of the groove 21 is set to 3mm, the compression deformation rate of the cushioning material filled is 10%, and the cushioning rate is about 30% as measured by the impact testing machine; the hardness is 20 degrees, Reduced hardness forefoot 110 is more comfortable.
Embodiment 3
[0048] The difference between the high-heeled shoe sole structure of this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that when the heel difference of the high-heeled shoe is 9cm, the middle thickness maximum point of the groove 21 is set at 15mm in front of the corresponding point 22 of the Yongquan point, and the groove 21 The middle thickness is set to 12mm, and the compression deformation rate of the filled cushioning material is 10%, and the cushioning rate is about 90% as measured by the impact testing machine, and the cushioning effect is excellent.
[0049] Preferably, the performance of the cushioning material is adjusted, and the compression deformation rate of the cushioning material is set at 5%, which can effectively control the deformation of the cushioning material, and avoid the gradual sagging of the sole 100 and cause the inner space of the shoe to be too large and not suitable for the foot.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com