Biochemical marker for CVD risk evaluation
A bioassay, C-terminal technology, applied in the field of biochemical markers for CVD risk assessment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
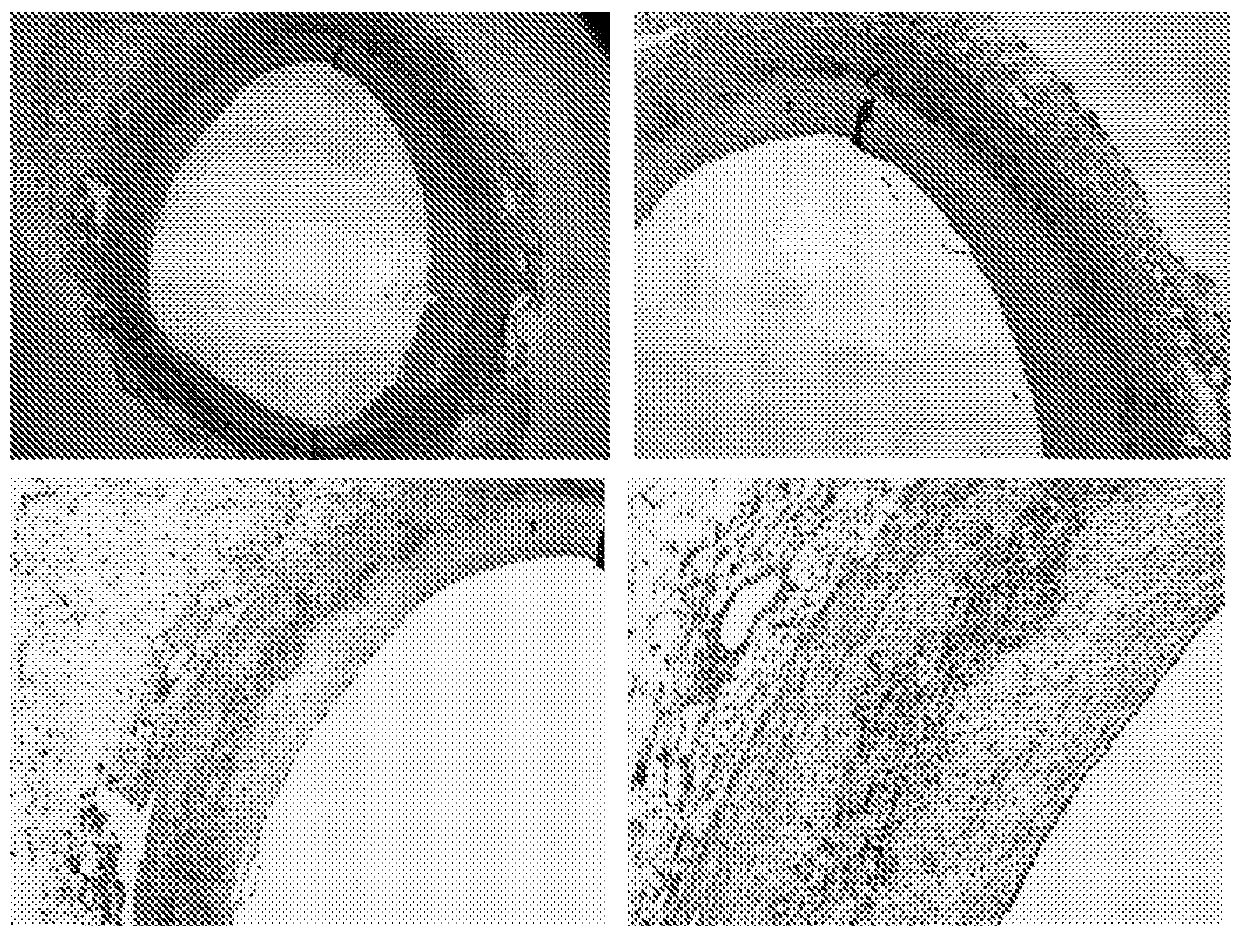
[0265] To analyze the localization of proteoglycans and proteases, we performed immunohistochemical staining on human arterial samples from left anterior descending coronary arteries (LAD). In the following, it is demonstrated that the cathepsin K protease colocalizes with biglycan.
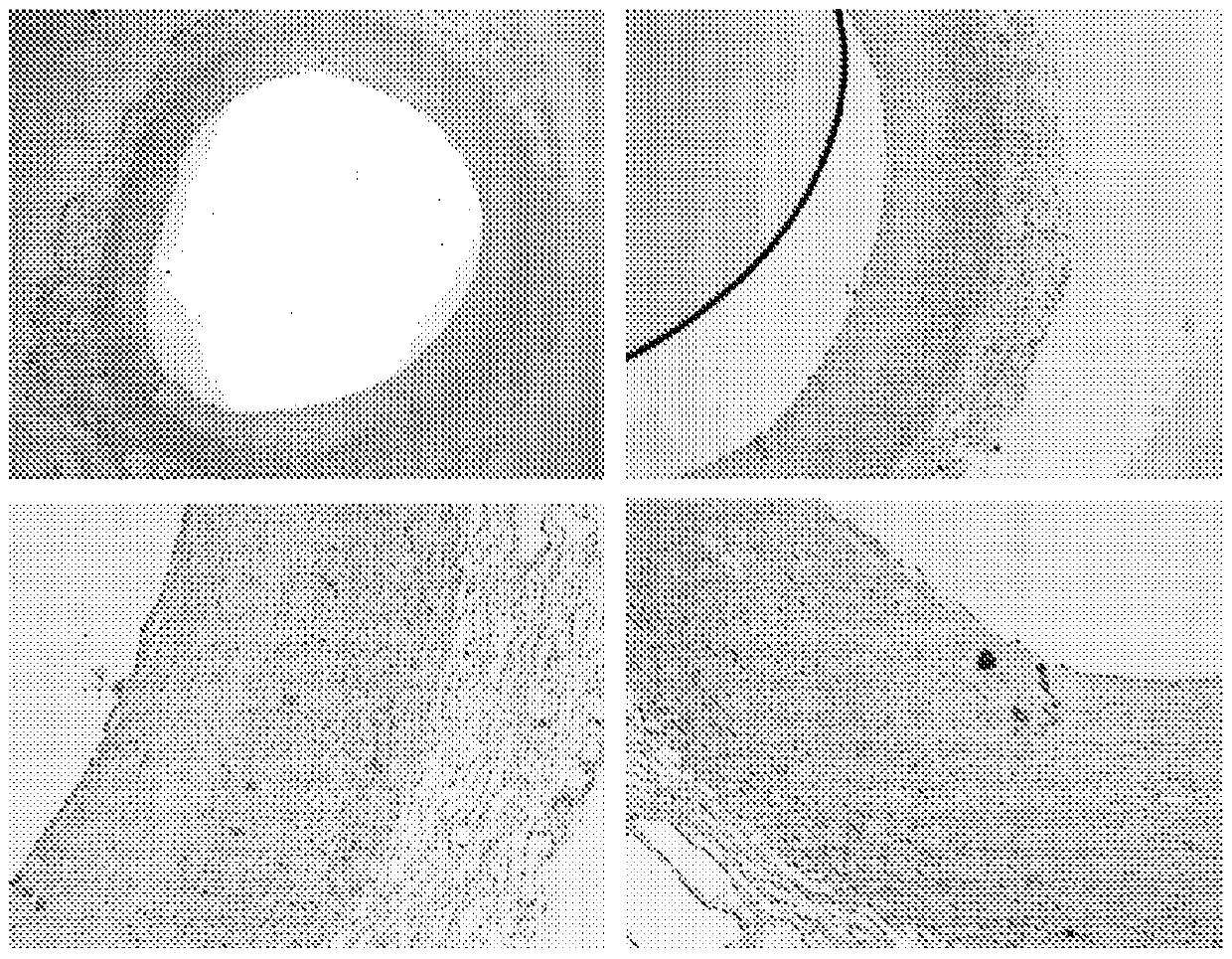
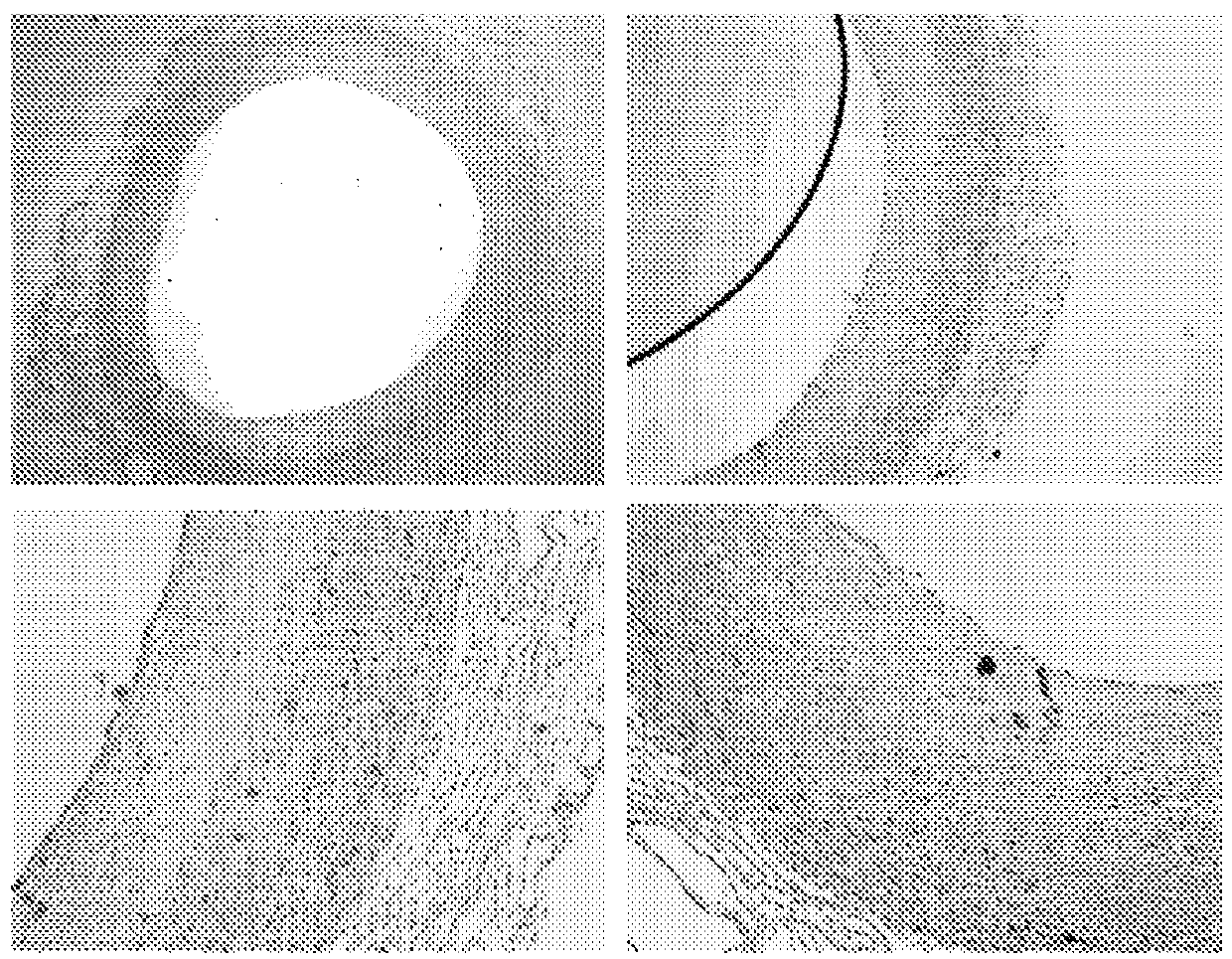
[0266] Such as figure 1 with 2 Immunohistochemical staining shown in shows colocalization of biglycan with cathepsin K. This may indicate that biglycan is a preferred substrate for cathepsin K. The same immunohistochemical staining was performed on samples of aorta in which atherosclerotic plaques formed and consequently resulted in macrophage foam cell infiltrates and calcifications replacing normal aortic structures. The results of these immunostainings are summarized in image 3 with 4 middle.
[0267] Immunohistochemical staining of biglycan and cathepsin K revealed co-localization in developing atherosclerotic lesions. Combining these results led to the hypothesis that a specific cle...
Embodiment 2
[0269] Biglycan degradation for assessment of degraded fragments. Biglycan from bovine articular cartilage (B8041-Sigma-Aldrich) was cleaved by the following proteases: MMP2, MMP3, MMP8, Cathepsin K, Cathepsin S, Cathepsin B, and Cathepsin L. The proteoglycan fragments produced by the enzymatic cleavage of the above proteases were treated at 10% Separation on a Bis-Tris gel followed by silver staining by the "SilverExpress" silver staining kit (Invitrogen Cat# LC6100, Lot# 341099). Separation of proteolytically produced biglycan and silver staining results in Figure 5 displayed in .
Embodiment 3
[0271] Mice were immunized with peptides from type III collagen conjugated to ovalbumin. Serum was screened for reactivity with biotin-conjugated screened peptide sequences. Monoclonal antibody-secreting clones are generated and screened using the selection sequence. Clones were examined for lack of reactivity with an extended form of the target peptide that continues an adjacent sequence in type III collagen (reverse selection peptide) and for lack of reactivity with a nonsense peptide. All target sequence positive clones did not react with extended or nonsense sequences.
[0272] The target sequence, immunogen, screening sequence and counter-selection sequence are as follows:
[0273]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com