Wireless sensor network routing energy saving method based on particle swarm
A wireless sensor and particle swarm algorithm technology, applied in wireless communication, energy consumption reduction, advanced technology, etc., can solve the problems of fast energy consumption, death, and high algorithm overhead of nodes, so as to prolong the life cycle, delay the death rate, and save energy. The effect of load balancing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
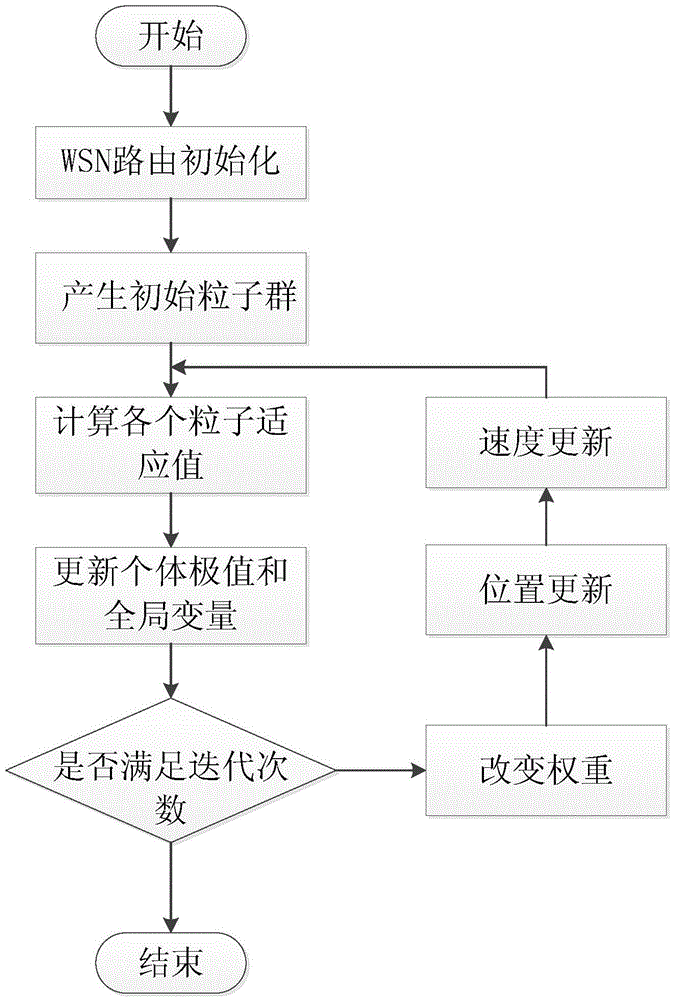
[0037] see figure 1 , the embodiment of the present invention provides a particle swarm based wireless sensor network routing energy saving method, the wireless sensor network routing energy saving method includes the following steps:
[0038] 101: Obtain the fitness value function used to select the cluster head, iterate the fitness value function through the particle swarm optimization algorithm, and find the wireless sensor node with a large fitness value as the cluster head in the network;
[0039] 102: Broadcast the selected cluster head to other wireless sensor nodes, and other wireless sensor nodes perceive the distance from the cluster head according to the strength of the broadcast signal received, so as to select which cluster to join;
[0040] 103: The cluster head receives and fuses the environmental information data sent by other wireless sensor nodes, and then sends the fused environmental information data to the sink node, and the communication ends.
[0041] W...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Combine belowfigure 1 1. The specific calculation formula introduces the scheme in embodiment 1 in detail, see the following description for details:
[0052] 201: Randomly define n wireless sensor nodes in a limited area, and the initial energy E of each wireless sensor node 0 all the same;
[0053] 202: Initialize each wireless sensor node through the LEACH algorithm;
[0054] During specific implementation, other algorithms may also be used to initialize each wireless sensor node. The initialization steps are well known to those skilled in the art, and will not be described in detail in this embodiment of the present invention.
[0055] 203: Obtain the fitness value function used to select the cluster head, iterate the fitness value function through the particle swarm optimization algorithm, and find the sensor node with a larger fitness value as the cluster head in the network;
[0056] Wherein, after the initialization of each wireless sensor node in step 202, so...
Embodiment 3
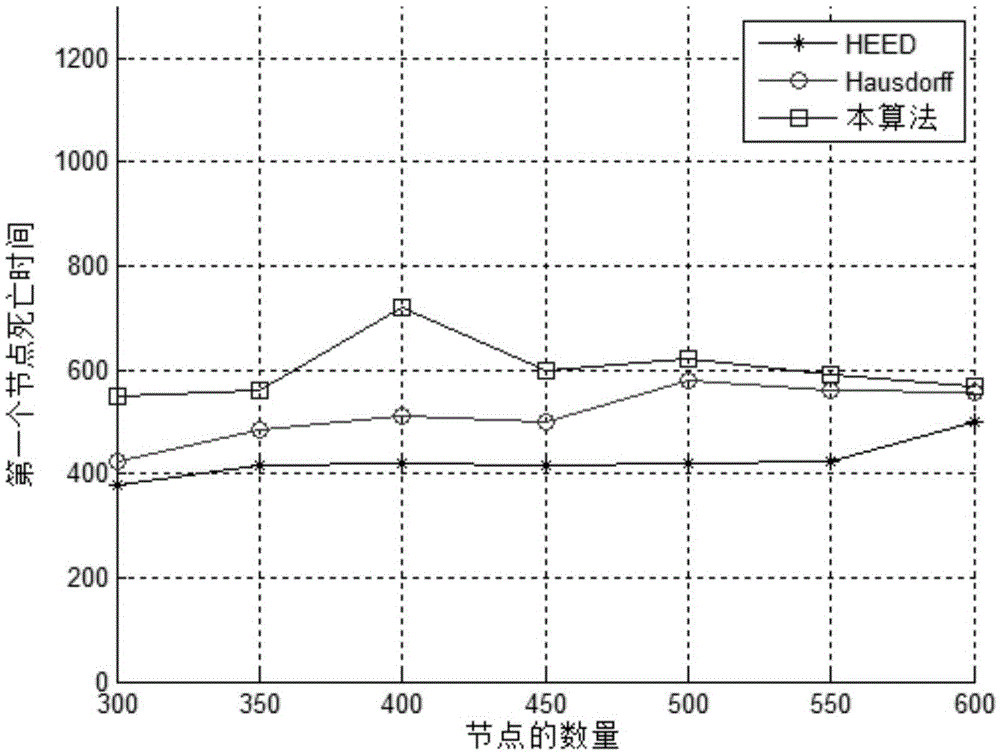
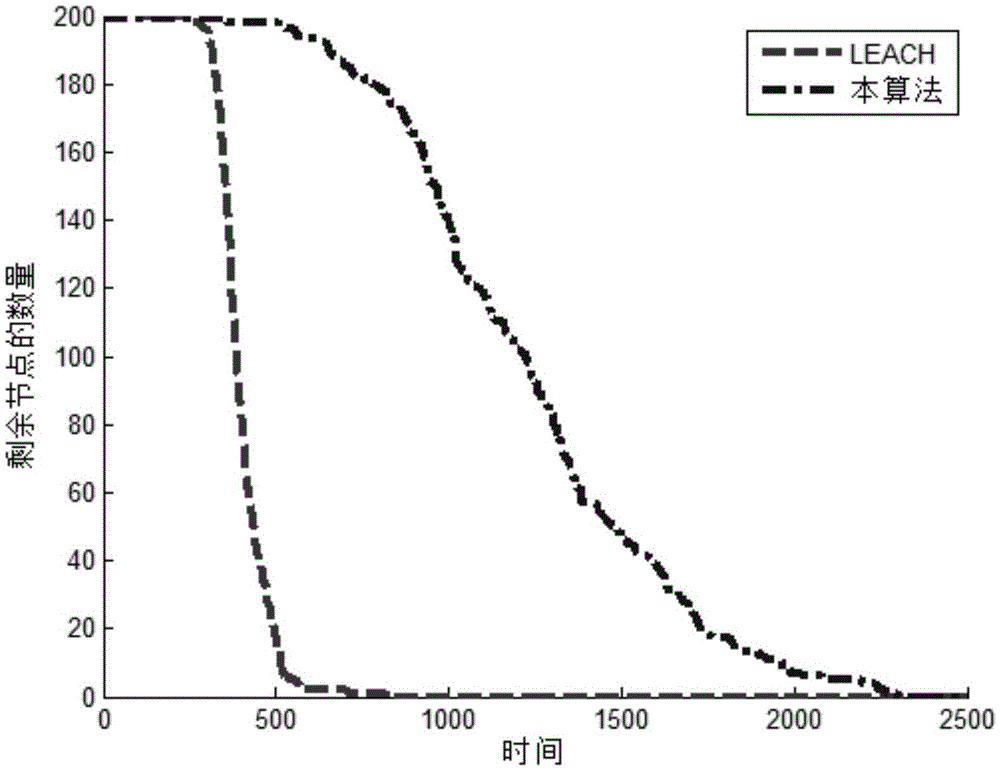
[0087] Combined with Table 1 below, figure 2 and image 3 The scheme in embodiment 1 and 2 is carried out feasibility verification, see the following description for details:
[0088] The particle swarm-based wireless sensor network routing method proposed in the embodiment of the present invention is verified below. Simultaneously, a simulation experiment is compared with an existing routing method to prove that the method can effectively prolong the life cycle of the network.
[0089] Next, use MATLAB software for simulation. First, set the parameters. The simulation parameter table is as follows:
[0090]
[0091]
[0092] First with the existing HEED algorithm [5] and Hausdoff algorithm [6] Comparing the initial node death time, the result is as follows figure 2 shown. The abscissa is the number of different wireless sensor nodes defined in the simulation, and the ordinate is the death time of the first wireless sensor node. figure 2 It can be seen from the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com