Dynamic equivalence and modeling methods and systems for double-fed wind power plant
A doubly-fed wind farm, dynamic equivalent technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as large amount of calculation, increase in the number of equivalent wind turbines, complexity, etc., and achieve a small amount of calculation. , good adaptability, simple modeling effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
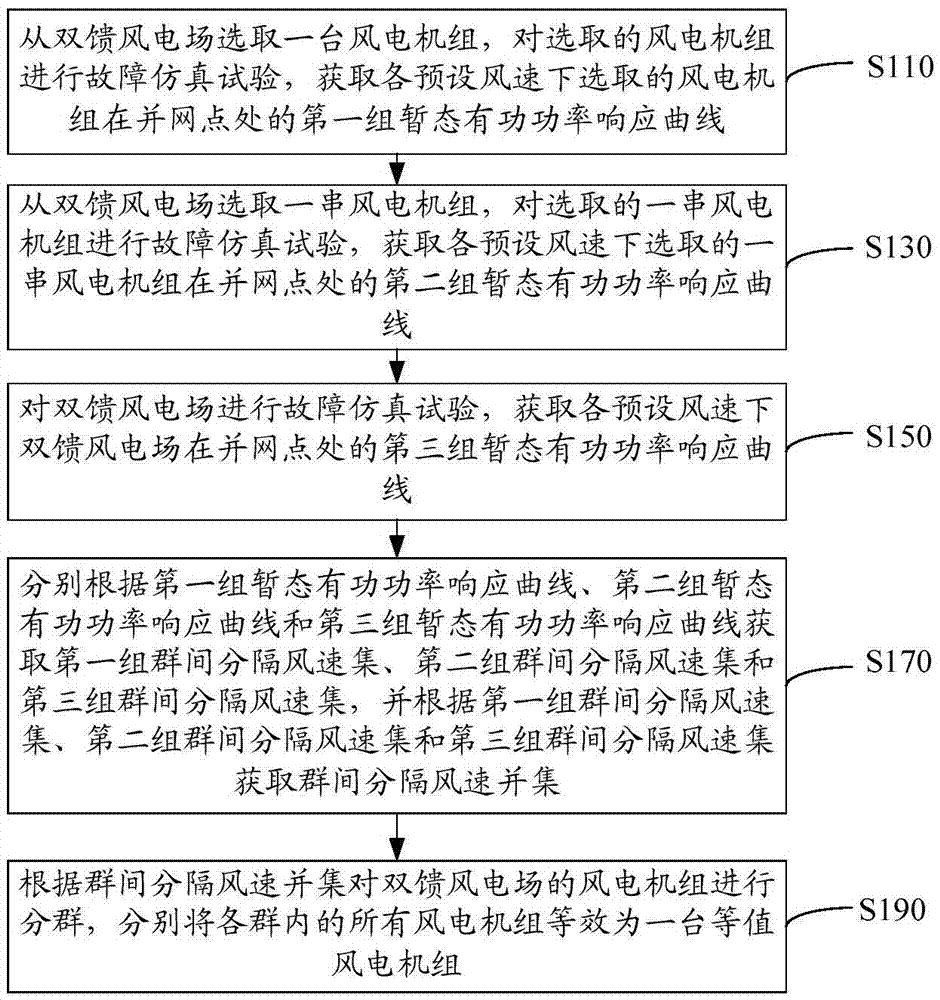
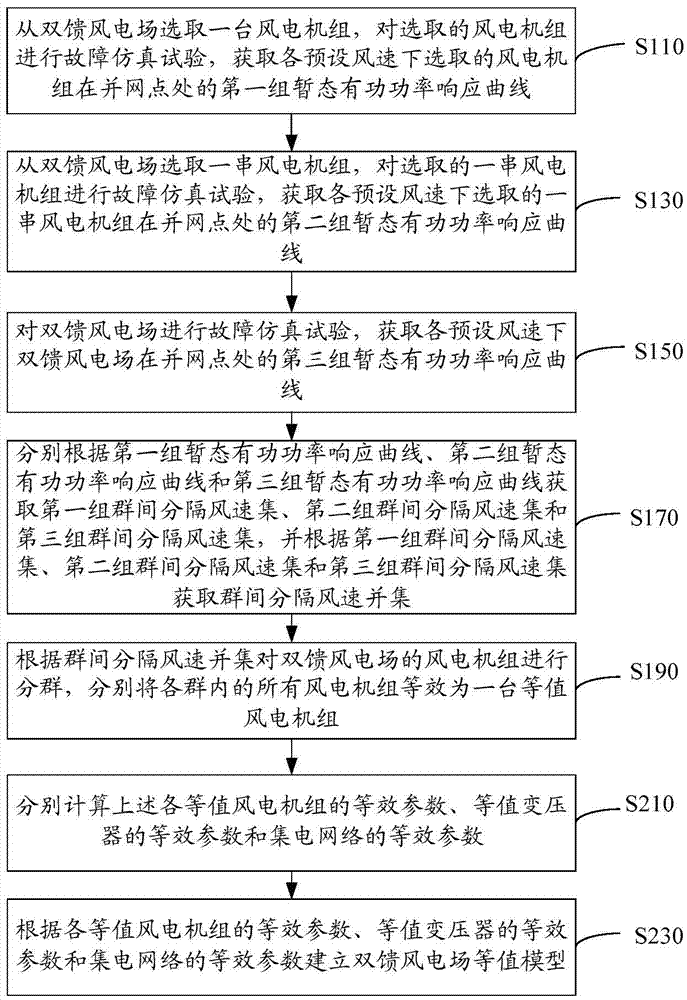
[0038] refer to figure 1 , the dynamic equivalence method of a doubly-fed wind farm in an embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps.
[0039] S110: Select a wind turbine from the doubly-fed wind farm, conduct a fault simulation test on the selected wind turbine, and obtain the first set of transient active power response curves of the selected wind turbine at the grid connection point under each preset wind speed.
[0040] Wherein, the doubly-fed wind farm in this embodiment is a wind farm in which all doubly-fed wind turbines have the same rated output value. The preset wind speed may be the wind speed within the full wind speed operation area (from the cut-in wind speed to the cut-out wind speed of the fan, the wind speed interval is 0.1m / s). The grid connection point is the connection point where the generator of the wind turbine is connected to the power grid.
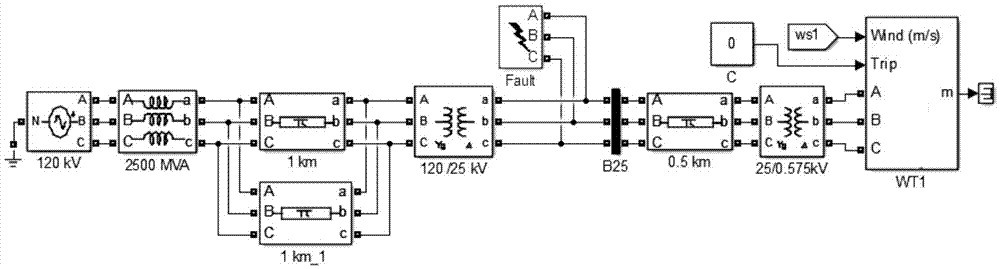
[0041] Carry out a fault simulation test on a selected wind turbine, specifically, sett...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com