A furnace start-up method for preparing elemental metal or alloy by molten salt electrolysis
A molten salt electrolysis and furnace start-up technology, applied in the field of electrolysis, can solve the problems of overweight electrolysis electrodes, inconvenient operation, heating of conductive cables, etc., and achieve the effects of stable performance, convenient removal, and avoiding sudden heating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A method for starting a furnace for preparing elemental metal or alloy by molten salt electrolysis, said method comprising the following steps:
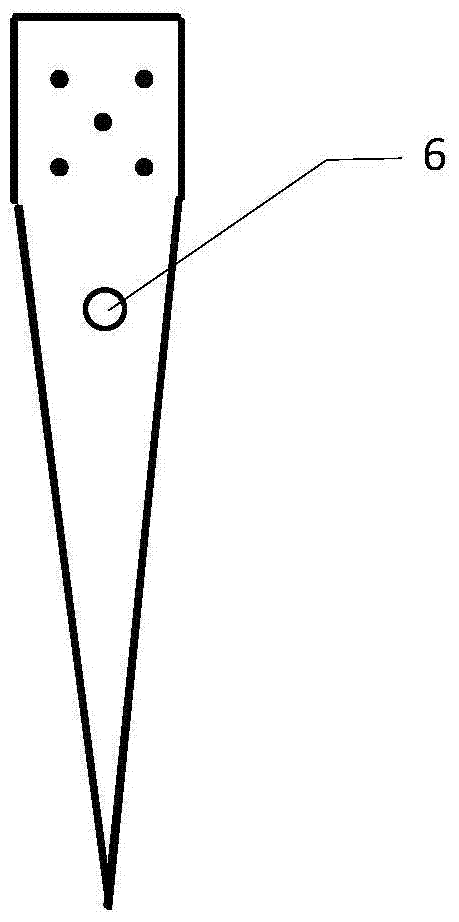
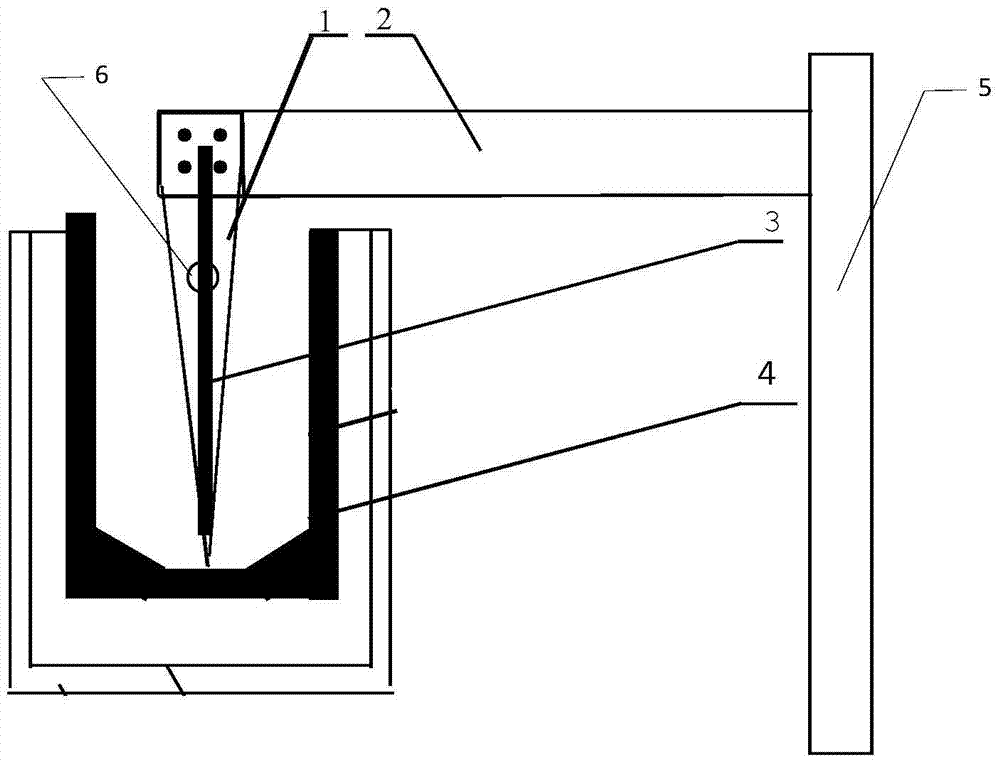
[0029] 1) if figure 2 As shown, at the same time, the starting electrode 1 and the electrolysis electrode 3 are fixed side by side on the conductive bar 2. After fixing, the distance between the electrolytic electrode 3 and the bottom of the graphite crucible 4 is greater than the distance between the starting electrode 1 and the bottom of the graphite crucible 4, and the conductive bar 2 is installed. On the electrode lifting device 5;
[0030] 2) Put the tip of the furnace starting electrode 1 in close contact with the bottom of the graphite crucible 4, but not in contact with the edge of the graphite crucible 4, and gradually add solid electrolytes into the graphite crucible;
[0031] 3) Turn on the AC stabilized power supply to heat the electrolyte, so that the electrolyte becomes completely liquid, and raise the furnace...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2 starts the furnace with potassium chloride as electrolyte
[0036] At the same time, the starting electrode 1 and the electrolysis electrode 3 are fixed side by side on the conductive bar 2. After fixing, the distance between the electrolytic electrode 3 and the bottom of the graphite crucible 4 is greater than the distance between the starting electrode 1 and the bottom of the graphite crucible 4, and the conductive bar 2 is installed on the electrode lift. on device 5. The electrolysis electrode is shorter than the start-up electrode, and an insulating high-temperature resistant metal collector is placed at the bottom. Add 5 kg of potassium chloride into the crucible, turn on the AC stabilized voltage power switch to the constant voltage position, the voltage is 7V, and the current is 1100A at this time. Continue to add 10kg of potassium chloride after energizing for 15 minutes, increase the current to 10V, 1550A, continue to add 30Kg of potassium chlori...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Embodiment 3 carries out furnace start with sodium chloride as electrolyte
[0038]At the same time, the starting electrode 1 and the electrolysis electrode 3 are fixed side by side on the conductive bar 2. After fixing, the distance between the electrolytic electrode 3 and the bottom of the graphite crucible 4 is greater than the distance between the starting electrode 1 and the bottom of the graphite crucible 4, and the conductive bar 2 is installed on the electrode lift. on device 5. The electrolysis electrode is shorter than the start-up electrode, and an insulating high-temperature resistant metal collector is placed at the bottom. Add 5kg of sodium chloride into the crucible, turn on the AC stabilized voltage power switch to the constant voltage position, the voltage is 7V, and the current is 1100A. After 15 minutes of electrification, continue to add 10kg of sodium chloride, increase the current to a voltage of 10.5V, 1600A, continue to add 30kg of sodium chlori...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com