A Thermal Parameter Recognition Method Based on Affine Transformation Best Matching Image
A technology of thermal parameters and affine transformation, applied in the direction of thermal expansion coefficient of materials, testing the strength of materials by applying a stable bending force, etc. It can solve the problems of time-consuming and complicated calculation process, and achieve easy operation, eliminate errors, and reduce repetition. The effect of heating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
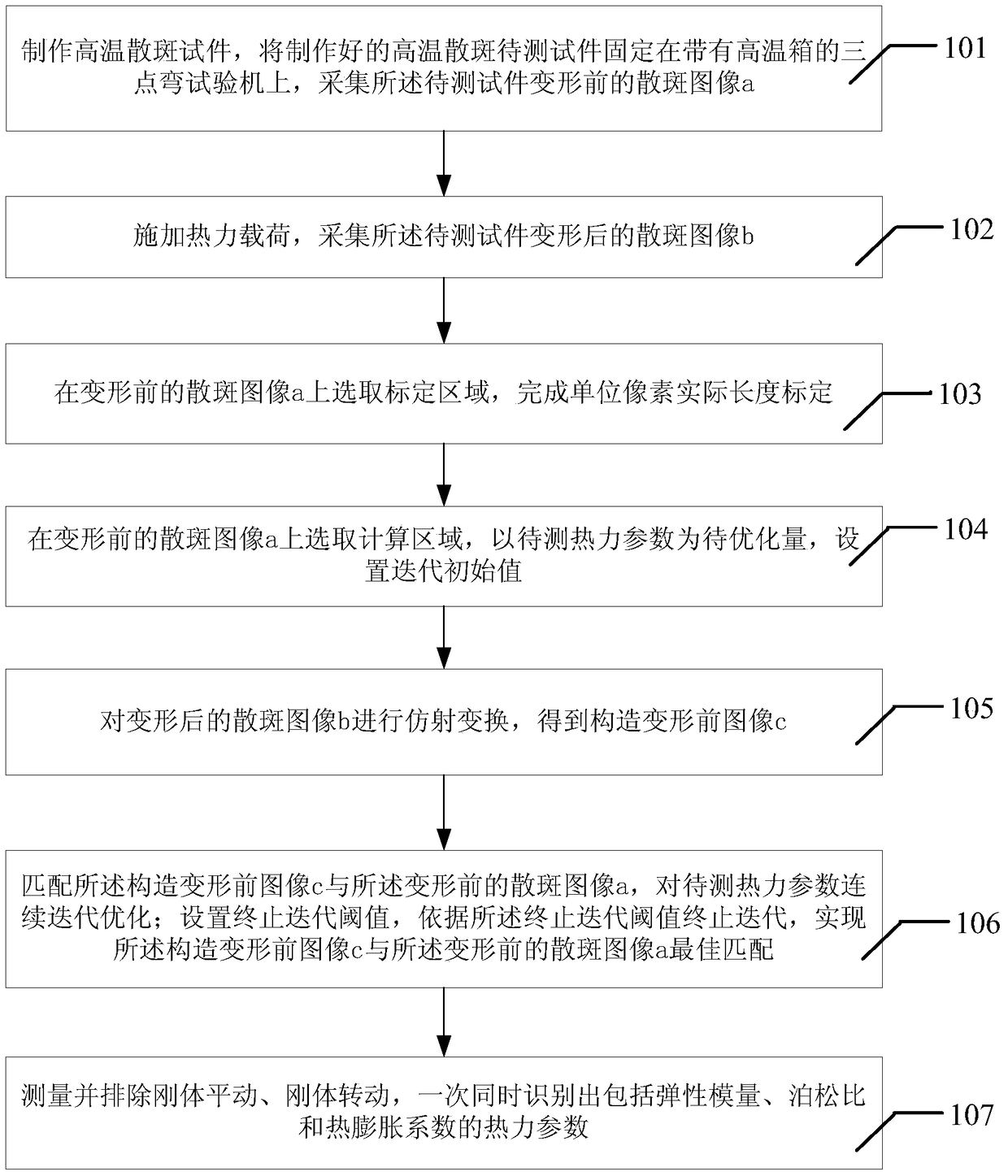
[0056] see figure 1 Shown is a specific embodiment of a thermal parameter identification method based on an affine transformation best matching image described in this application. The method described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0057] Step 101, making a high-temperature speckle test piece, fixing the prepared high-temperature speckle test piece on a three-point bending testing machine with a high-temperature box, and collecting a speckle image a of the test piece before deformation;
[0058] Step 102, apply a thermal load, and collect the deformed speckle image b of the test piece;
[0059] Step 103, select a calibration area on the speckle image a before deformation, and complete the calibration of the actual length of the unit pixel;
[0060] Step 104. Select the calculation area on the speckle image a before deformation, take the thermal parameter to be measured as the quantity to be optimized, and set the iteration initial value p 0 :
[0061] p...
Embodiment 3
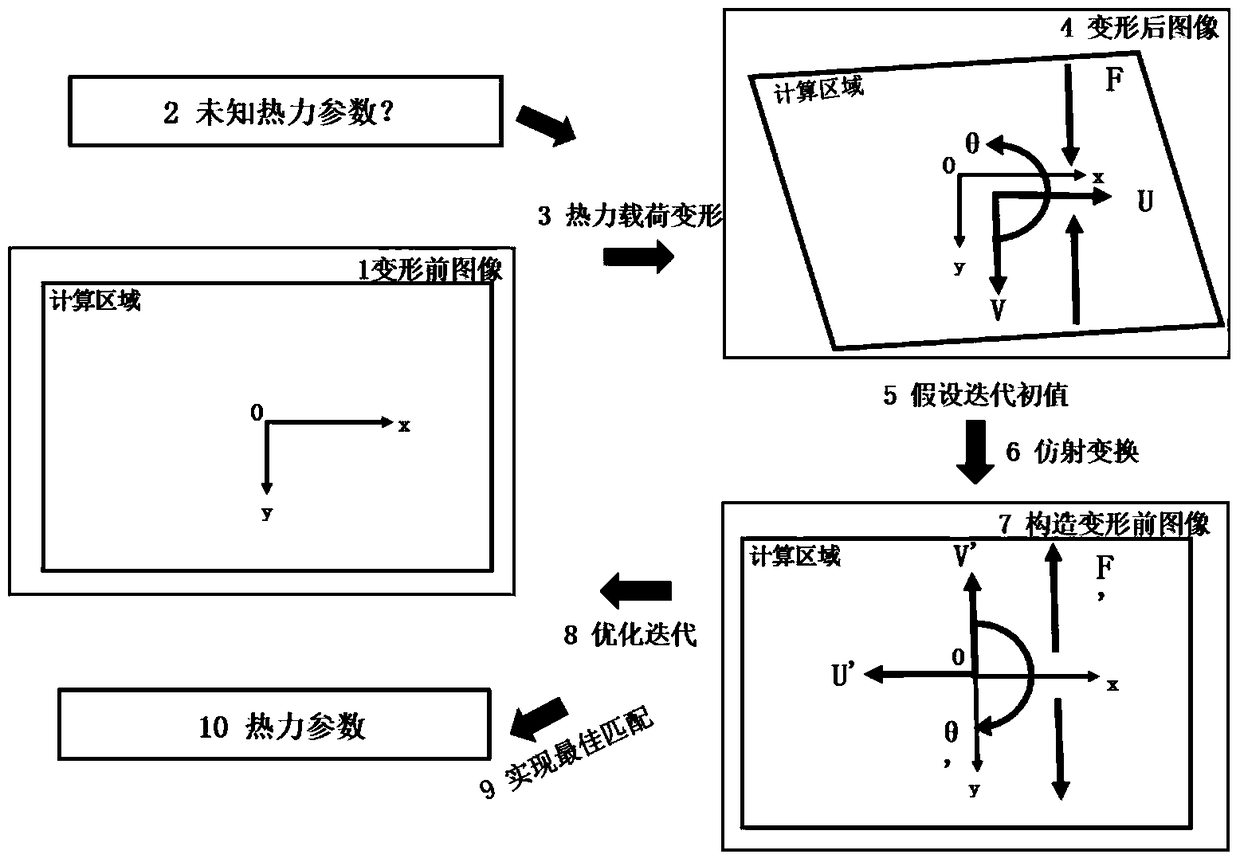
[0122] figure 2 Best fit image model for affine transformation. Use monochromatic light illumination and acquisition device to collect speckle image 1 before deformation (image a), apply thermal load, unknown material parameters 2 control thermal load deformation 3, and form deformed image 4 (image b). According to the thermal parameters to be optimized, the initial value of iteration is assumed to be 5. The affine transformation 6 is completed according to the iterative initial value, and an undeformed image 7 (image c) is obtained. Using the optimization iterative algorithm to construct the pre-deformed image, that is, construct the undeformed image 7 (image c) and the pre-deformed image 1 (image a), perform iterative optimization 8, and output the measurement results of thermal parameters 10 when the best matching 9 is achieved.
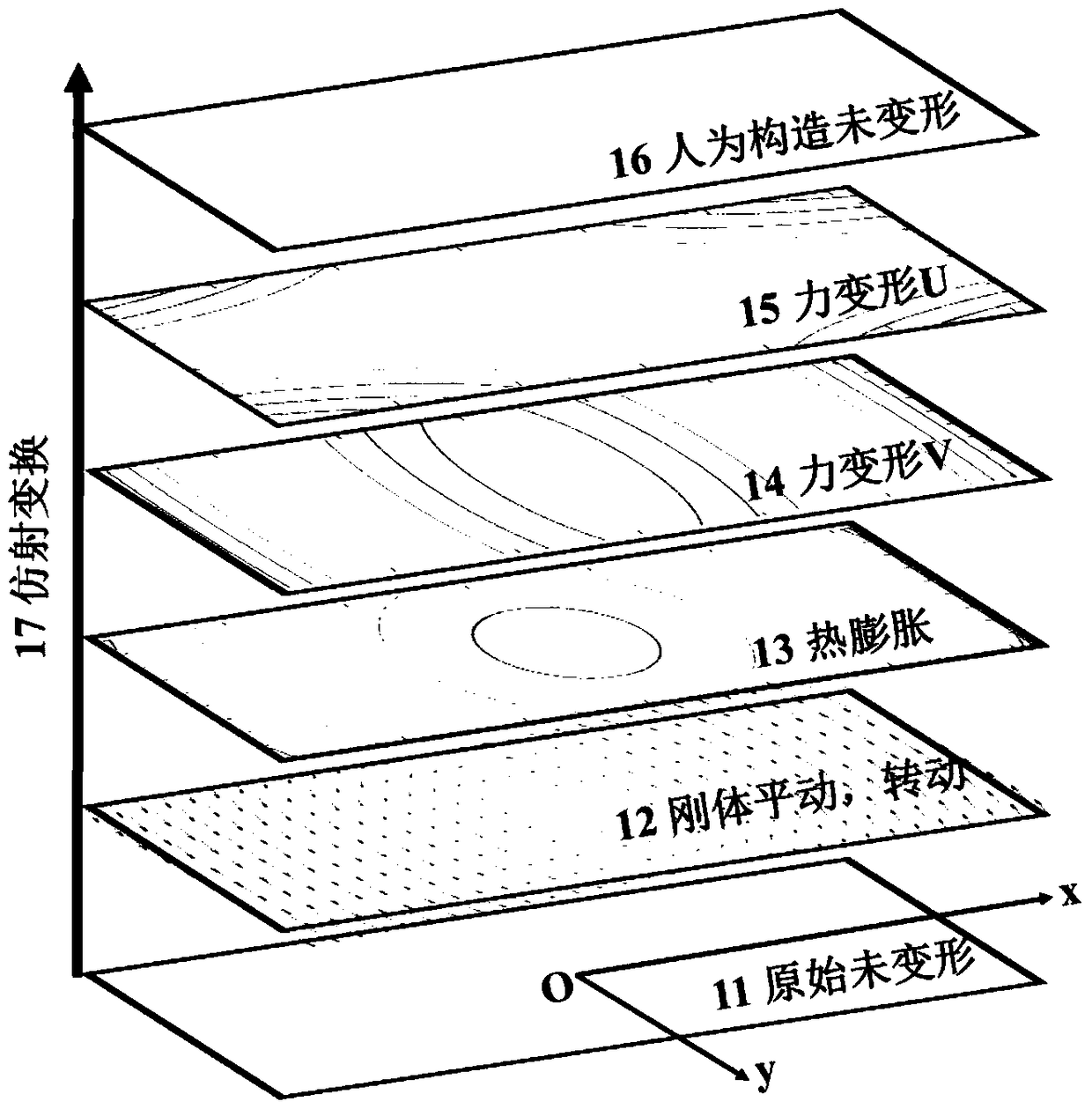
[0123] image 3 It is the schematic diagram of affine transformation. The affine transformation displacement is composed of rigid body trans...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com