Improved and simplified plant chromosome fluorescence in-situ hybridization method
A fluorescence in situ hybridization and chromosome technology, which is applied in the fields of molecular cytogenetics and chromosome engineering, can solve the problems of physical health threats of experimental operators, complicated operation of hybridization procedures, ecological environment hazards, etc., so as to reduce non-specific hybridization reactions and methods. Simple operation, safe effect of denatured raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Identification of exogenous chromosomes in plants
[0027] The test materials used are rye and rye-wheat additional line seeds, which come from the germplasm resources preserved by the Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Jiangsu Province;
[0028] 1.1 Root tip culture: Put the seeds in a petri dish with wet filter paper on the bottom, and germinate them in a dark incubator at 23°C for 14-24h. After the seeds turn white, transfer them to a refrigerator at 4°C for 1-3 days. Then continue to put it back into the dark incubator at 23°C to continue germination until the root system is about 2-3cm long;
[0029] 1.2 Preparation of specimens: a. Material collection: Cut ~1cm root tips of germinated seeds in 1), and quickly put them in a container containing 1×10 -6In a vial of M8-hydroxyquinoline (placed in an ice-water mixture in advance), pre-treat in a refrigerator at 0°C for 14-20h. b. Fixation: transfer the root system to Carnot's fixative (V ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 Detection and analysis of plant chromosome structure variation
[0035] The wheat seeds used as the test material come from the germplasm resources preserved by the Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Jiangsu Province;
[0036] 2.1 root tip culture: same as Example 1.1;
[0037] 2.2 Specimen making: same as Example 1.2;
[0038] 2.3 Probe labeling: same as Example 1.3;
[0039] 2.4 Fluorescence in situ hybridization: same as Example 1.4;
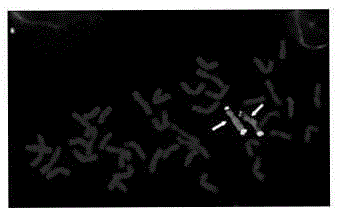
[0040] see attached result figure 2 ;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com