Method and device for monitoring network node
A technology of network nodes and monitoring devices, applied in the computer field, can solve the problems of inability to distinguish and reduce the number of access requests, and achieve the effect of ensuring normal operation and improving the ability to defend against attacks.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
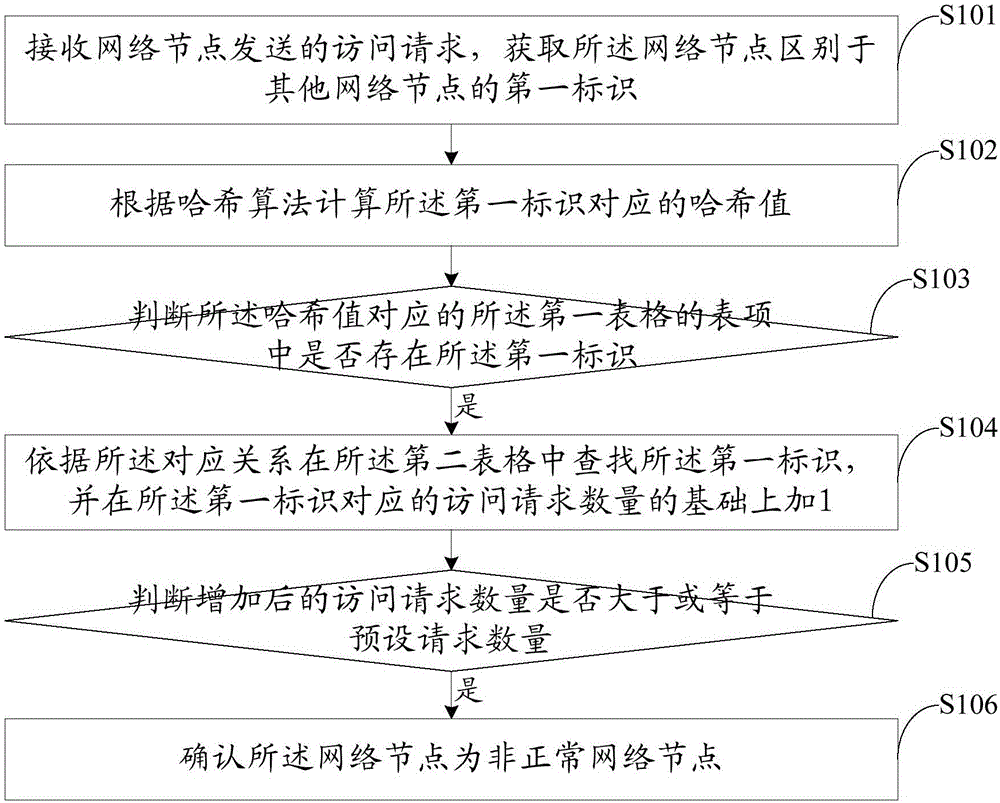
[0074] see figure 1 , which is a flow chart of Embodiment 1 of a network node monitoring method provided by the present invention.
[0075] The network node monitoring method provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0076] Step S101: Receive an access request sent by a network node, and obtain a first identifier that distinguishes the network node from other network nodes.
[0077] In the present invention, the first identifier is an identifier that distinguishes the network node from other network nodes, such as an IP (International Protocol, a protocol for interconnection between networks) address, a website cookie, a unique identifier of a network node physical device, etc. , or a combination of at least two of the above identifiers. Among them, the use of IP address as the first identifier is suitable for network nodes in non-local area networks; the use of website cookies as the first identifier requires the website to have the function of generating ...
Embodiment 2
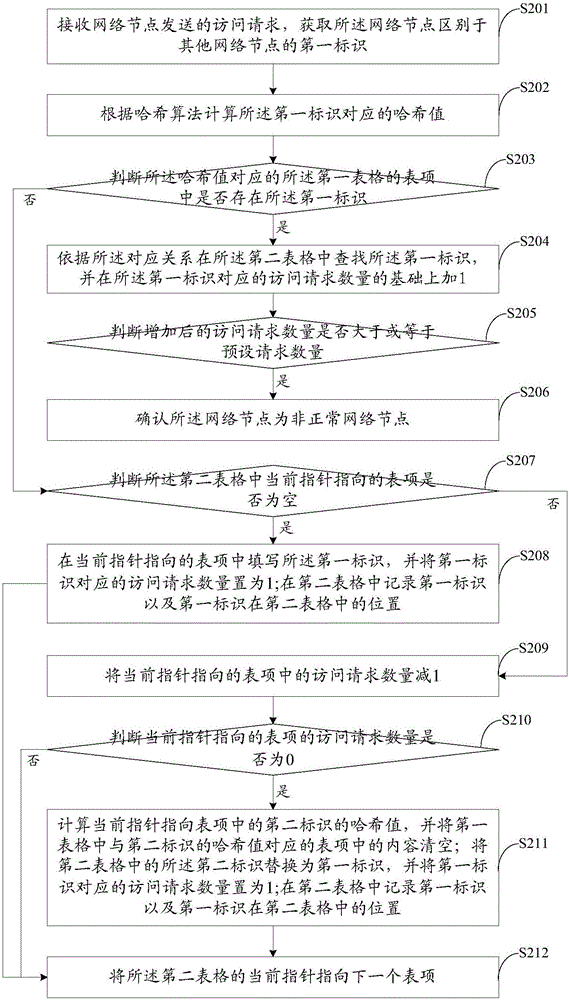
[0099] see figure 2 , which is a flow chart of Embodiment 2 of a network node monitoring method provided by the present invention.
[0100] The network node monitoring method provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0101] Step S201: Receive an access request sent by a network node, and obtain a first identifier that distinguishes the network node from other network nodes.
[0102] In the first method embodiment, the first identifier may include the IP address of the network node, a website cookie and / or a unique identifier of a physical device of the network node, and the like. However, since the first identification composed of the IP address, the website cookie and / or the unique identification of the physical device of the network node is often relatively complicated, it is time-consuming to find the first identification in the first table or the second table in the following steps In order to overcome this problem, in this embodiment, the IP address, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com