Dynamic resource allocating method and apparatus, base station, terminal
A dynamic resource and allocation method technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of high control signaling overhead, LTE control channel scheduling high-frequency carriers, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
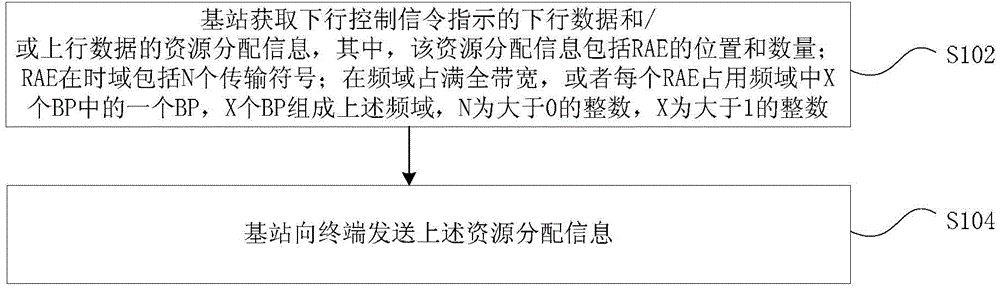
[0197] Assuming that there are at least two carrier elements linked to a terminal UE1, the two carrier elements can be located at the same node TP0 or at two different nodes TP1 and TP2, and TP1 and TP2 have ideal backhaul links (smaller backhaul delay). It is assumed that the LTE carrier element is CC0, and the high-frequency carrier element is CC1. When the base station wants to send downlink data to UE1 on CC1 and expects UE1 to receive it correctly, the base station sends corresponding downlink control indication signaling on CC0 to indicate the time domain resource position of the downlink data corresponding to UE1 on CC1. Such as Figure 5 shown. Wherein, it is assumed that CC0 is a 4GLTE carrier, and CC1 is a high-frequency carrier. DR means that UE1 receives downlink data on CC1. HARQ means that UE1 feeds back the HARQ information for downlink data on the uplink carrier corresponding to CC0. RR means that UE1 receives and retransmits downlink data on the high-frequen...
Embodiment 2
[0214] The base station indicates the number of corresponding downlink data resource allocation time units by using the downlink control indication signaling in a predetermined manner. The RAE is composed of N (N>0) transmission symbols in the time domain, and the N value base station and the terminal can be defined in a predefined manner, wherein, there is a one-to-one correspondence between the N value and the 4GLTE carrier element bandwidth, or N There is a corresponding relationship between the value and the bandwidth of the high-frequency carrier element, as shown in Table 2. Wherein Zn (1-4) is an integer greater than zero.
[0215] Table 2
[0216] System Bandwidth (MHz)
N value selection
≤X1
Z1
X1+1~X2
Z2
X2+1~X3
Z3
X3+1~X4
Z4
[0217] The base station schedules UE1 to receive downlink data on corresponding one or more RAEs on the downlink carrier corresponding to CC1 through the DL Grant signaling on th...
Embodiment 3
[0231] The base station indicates the number of corresponding downlink data resource allocation time units by using the downlink control indication signaling in a predetermined manner. The RAE is composed of N (N>0) transmission symbols in the time domain, and the N-value base station can be configured to the terminal through high-layer signaling. Preferably, the predefined N value is one of the following values: 24, 28, 30, 32, 40, 42.
[0232] The base station schedules UE1 to receive downlink data on one or more corresponding RAEs on CC1 through DL Grant signaling on the 4G carrier CC0.
[0233] When the maximum time window scheduled by DLGrant is when, and includes Y RAEs, then the base station instructs UE1 to receive downlink data in one or more RAEs of the Y RAEs. Preferably, the value of Y is 10, or the value of Y is the number of RAEs included in the time domain within 1 ms.
[0234]Preferably, when the first resource allocation mode is adopted in the DLGrant (s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com