Driver circuit for power control
A driving circuit and power control technology, applied in the field of driving circuits for power control, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory working state of a controlled power control device, complicated control signal processing circuit, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
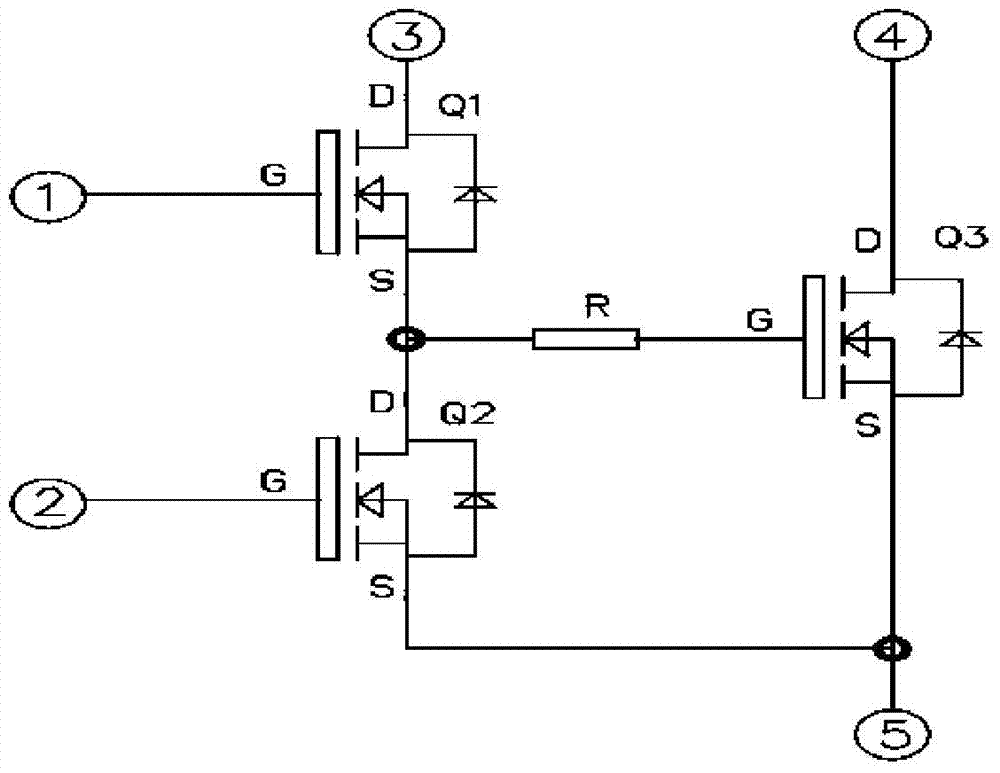
[0032] like figure 2 , the driving circuit for power control in this embodiment includes: the front stage of the driving circuit formed by the driving integrated circuit U1, which is used to control the output voltage of its voltage output terminal OUT according to the PWM signal (or logic signal) sent in from the outside; N- MOSFET (Q1), its gate G is connected to the voltage output terminal OUT of the driving integrated circuit; a first resistor R1 is set between the gate G of the N-MOSFET (Q1) and the original electrode S, and the N-MOSFET (Q1 )’s drain D is connected to the driving power supply; the gate G of the P-MOSFET (Q2) is connected to the voltage output terminal OUT of the driving integrated circuit; the source S of the N-MOSFET (Q1) is connected to the P-MOSFET (Q2 ) between the sources S of the second resistor R2; the controlled power control device Q3, the gate G of which is connected in series with the third resistor R3 and then connected to the source S of the...
Embodiment 2
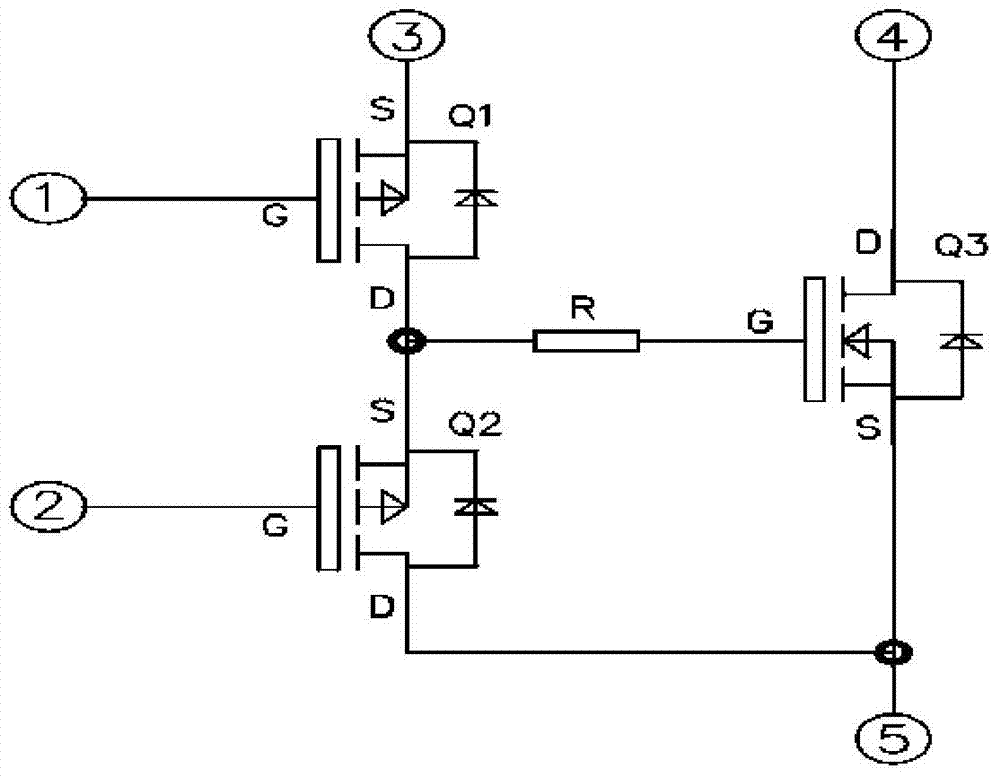
[0039] On the basis of Embodiment 1, the drive circuit for power control in this embodiment has the following modifications:
[0040] like image 3 , the voltage output terminal OUT of the driving integrated circuit is sequentially connected in series with the fourth resistor R4, the fifth resistor R5 and the first gate resistor RG1, and then connected to the gate G of the N-MOSFET (Q1); the fifth resistor R5 and The contact of the first gate resistor RG1 is connected in series with the first resistor R1 and then connected to the original electrode S of the N-MOSFET (Q1); the contacts of the fourth resistor R4 and the fifth resistor R5 are connected in series with the second gate resistor RG2 and then connected Gate G of the P-MOSFET (Q2).
[0041] Pin 3 is connected to the drive power. When the controlled power control device Q3 is used for the upper bridge, pin 4 is connected to the power supply positive of the power stage, and pin 5 is the output. When the controlled pow...
Embodiment 3
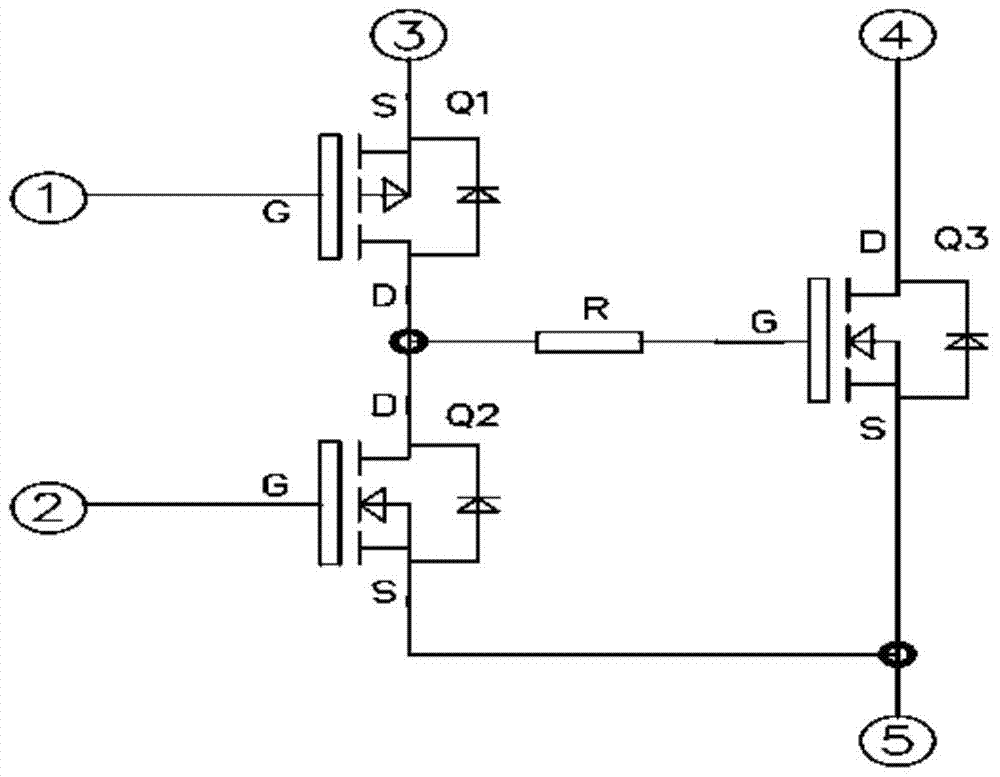
[0054] On the basis of Embodiment 1, the front stage of the driving circuit of this embodiment adopts Figure 8 The structure of the split devices shown is specifically adopted Figure 8 The front stage of the driving circuit is formed by the array devices on the left side of the dotted line.
[0055] Figure 8 Among them, pins 1 and 5 are connected to the drive power supply, generally 12V~15V.
[0056] Pin 2 is the input of the upper bridge control signal PWM (or logic signal).
[0057] Pin 7 is the input of the lower bridge control signal PWM (or logic signal).
[0058] Pin 6 is connected to the positive pole of the logic power supply, usually 3.3V or 5V.
[0059] Pin 8 is connected to the positive pole of the power supply.
[0060] Pin 10 is connected to the negative pole of the power supply.
[0061] Pin 9 is the power output.
[0062]D11 and C11 form a bootstrap boost circuit to provide drive power for the upper bridge.
[0063] The front stage of the drive circui...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com