Brand-new photovoltaic grid-connected inverter multi-wave-crest MPPT algorithm
An inverter and photovoltaic technology, applied in photovoltaic power generation, instruments, adjusting electrical variables, etc., can solve the problem that the fixed-cycle scanning method does not realize the judgment of shadows and no shadows, and the full-cycle scanning method cannot be performed or done. To real-time and other issues, to achieve the effect of improving dynamic tracking efficiency, suitable for popularization, stability and power generation improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
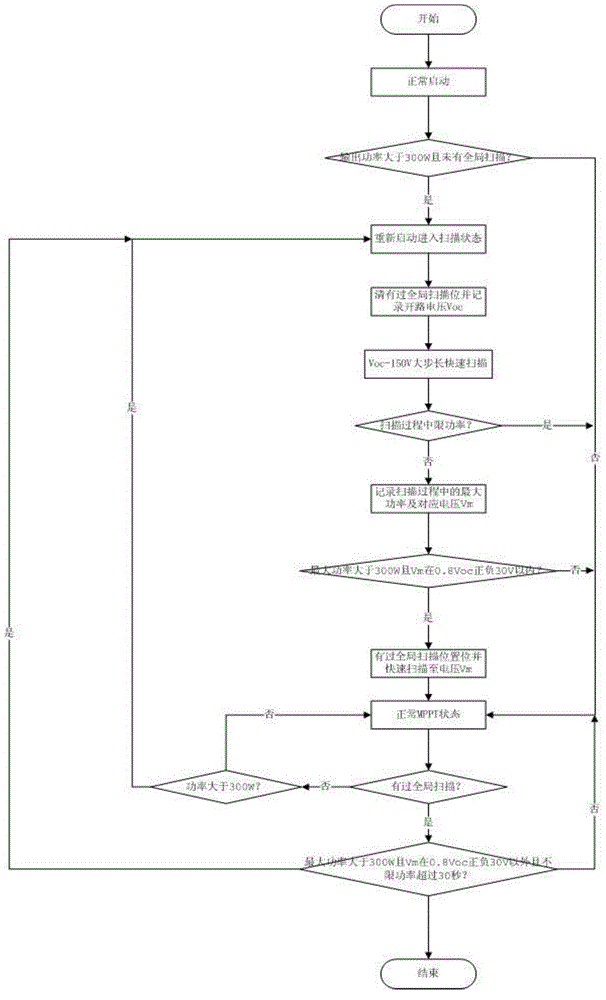
[0024] A new multi-peak MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic grid-connected inverters, including the determination of the operating voltage of the photovoltaic system, the determination of the shadow judgment formula, and the shadow scanning. The specific methods are as follows:
[0025] Step 1. The working voltage of the photovoltaic system satisfies the determination of the formula. There are two characteristics of solar modules in practical applications. One is that when the light intensity changes, it has little influence on the optimum working voltage point of the photovoltaic system and has little influence on the current. Very large, when the light intensity of a certain module is particularly low, triggering the bypass diode to work will cause the voltage and current mismatch between the strings, and there will be multiple peaks. The other is when the temperature changes sharply, the best The working voltage changes greatly and satisfies the following formula: Vmppt=Vmppt0*(...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com