Spectrum sharing method based on channel learning in mimo cognitive radio jamming network
A cognitive radio and spectrum sharing technology, applied in wireless communication, network planning, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems that algorithms cannot be directly applied, lack of control of secondary user interference power leakage, etc., so as to improve the efficiency of spectrum sharing and solve coexistence problems. problems, the effect of avoiding interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
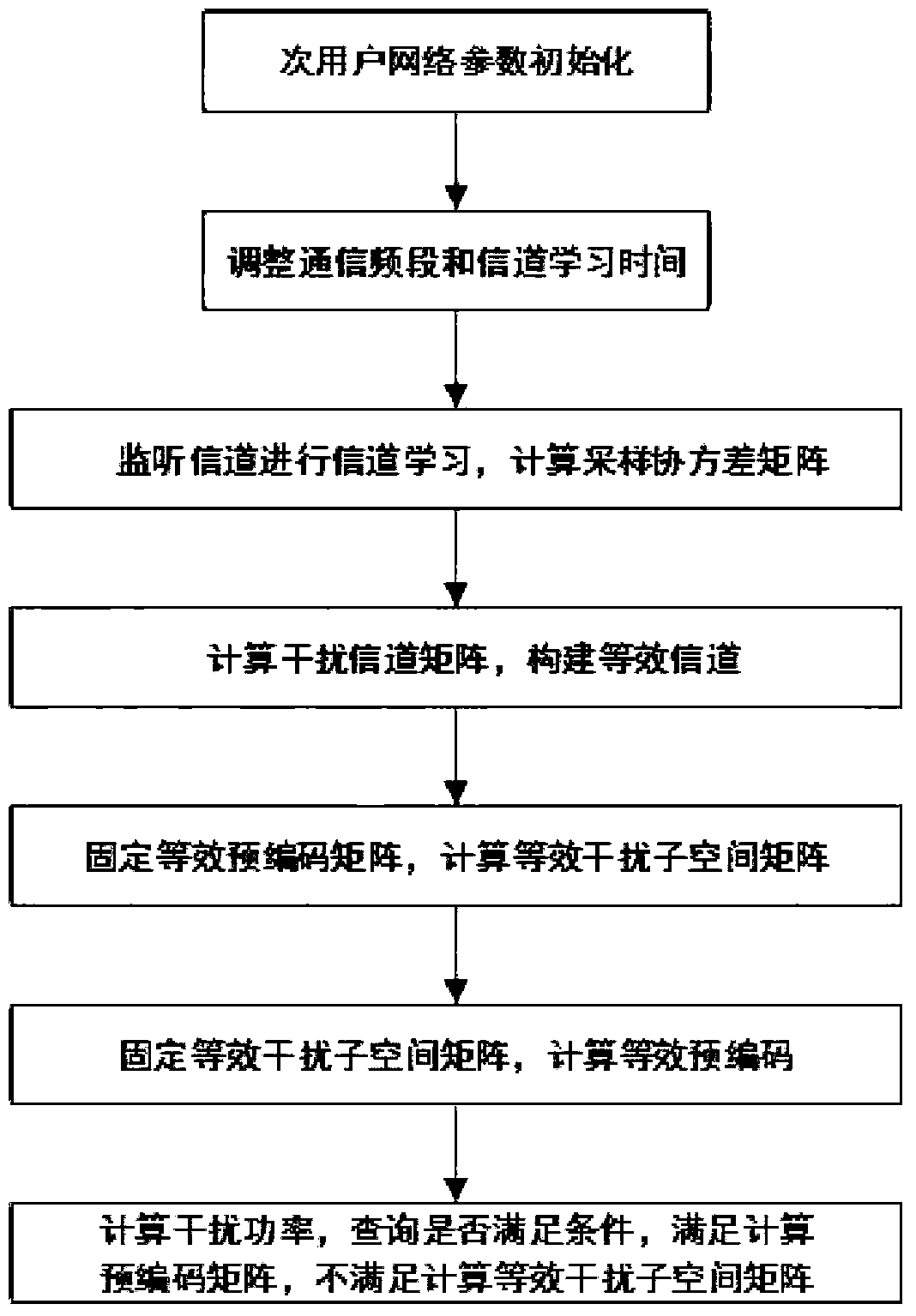
[0035] Embodiment one, see image 3 As shown, a spectrum sharing method based on channel learning in a MIMO cognitive radio interference network includes the following steps:
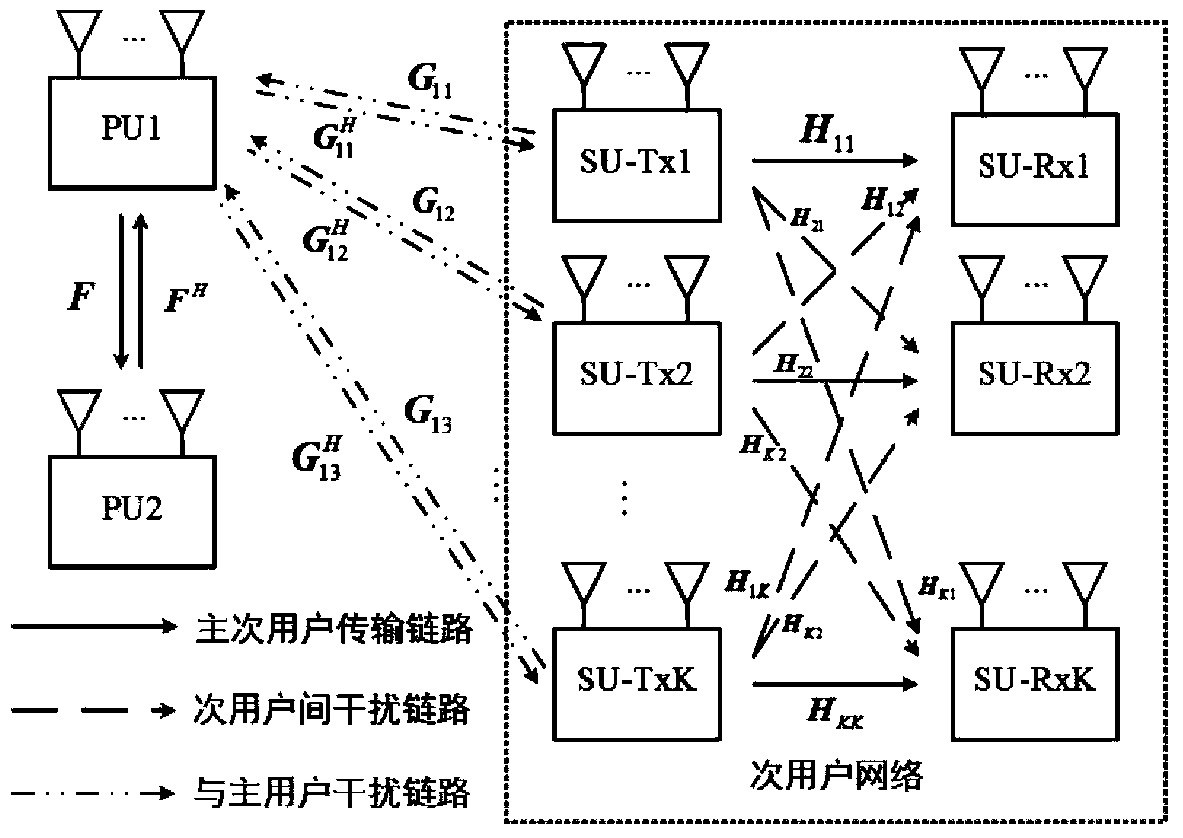
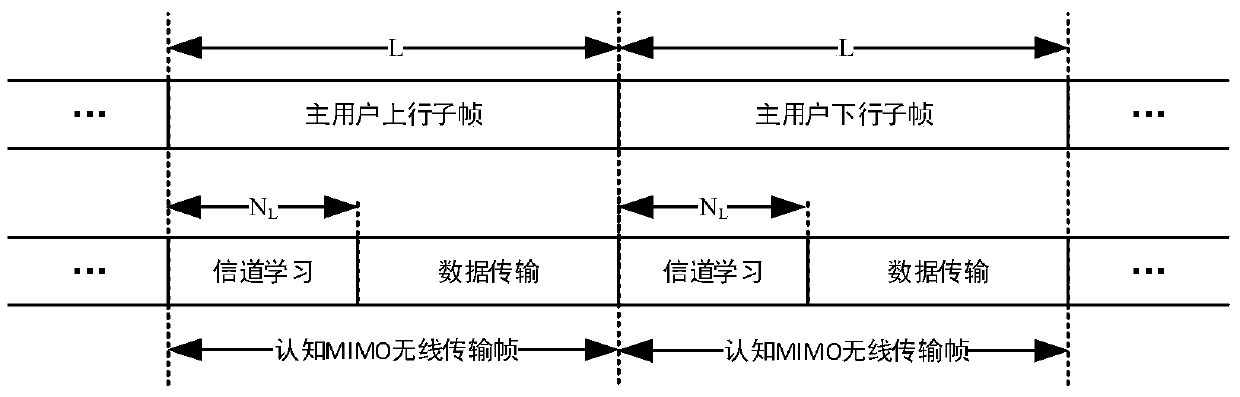
[0036] Step 1. According to the secondary user's communication requirements and antenna configuration, determine the degree of freedom d of each user's transmission k , set the sub-user internal interference threshold Г k , select the detection time length;
[0037] Step 2. The secondary user selects the communication frequency band and channel learning time, monitors the channel status in real time, and uses the received signal y 1k (n), calculate the sampling covariance matrix pair sampling covariance matrix Do eigenvalue decomposition get the eigenvalues and the orthogonal matrix of the interfering channel And adjust the selected frequency band according to the calculation results, so that the total number of sub-streams can meet in, m 0 The number of antennas for the primary user; ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2 is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that in step 4, the equivalent interference subspace matrix C is constructed l Specifically, according to the alternate minimization IA algorithm, the interference power leakage is described by the Frobenius norm of the matrix distance between the actual interference signal space and the preset interference space at the receiving end, and the spectrum problem is transformed into: where || || F Represents the matrix Frobenius norm; means B l Orthogonal complement space, that is, the equivalent interference subspace matrix C is obtained l ;Fix the equivalent precoding matrix A of each user k , transforming the problem into Among them, tr(A) represents the trace of matrix A, a is a fixed constant, and the optimal C l By N eq -d l The eigenvectors corresponding to the largest eigenvalues are formed, where get
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3 is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that in step 5, the equivalent interference subspace matrix C is used l Symmetry Calculation of Subscripts k and l It specifically includes: fixing the equivalent interference subspace matrix C of each user l , using the symmetry of the subscripts k and l, we get Transmitter equivalent precoding A of secondary user l k Depend on the d k The eigenvectors corresponding to the smallest eigenvalues are formed, that is, we get
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com