led linear constant current drive circuit
A linear constant current drive, linear constant current technology, applied in the direction of lamp circuit layout, electric light source, lighting devices, etc., can solve the problems of reducing power factor, low efficiency, etc., to improve efficiency and power factor, improve efficiency, and ensure power Factor effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
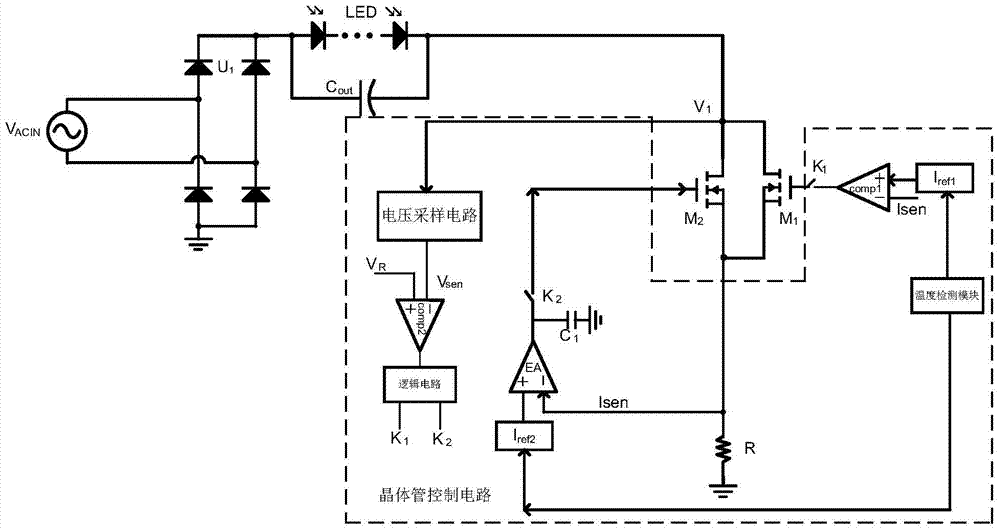
[0025] Embodiment 1: Reference figure 1 As shown, an embodiment of the present invention is illustrated, including a rectifier circuit U 1 and linear constant current control circuit, the input voltage V ACIN After the rectification circuit U 1 After rectification, it is input to the LED load, and the output capacitor C is connected in parallel with the LED load. out . The linear constant current control circuit is connected in series with the negative terminal of the LED load, and the linear constant current control circuit controls the average current flowing through the LED load to keep constant; at the same time, the other end of the linear constant current control circuit is connected to a resistor R, and the resistance R The other end is grounded.
[0026] The linear constant current control circuit includes a power transistor circuit and a transistor control circuit. In this embodiment, the power transistor circuit includes two parallel power transistors, respective...
Embodiment 2
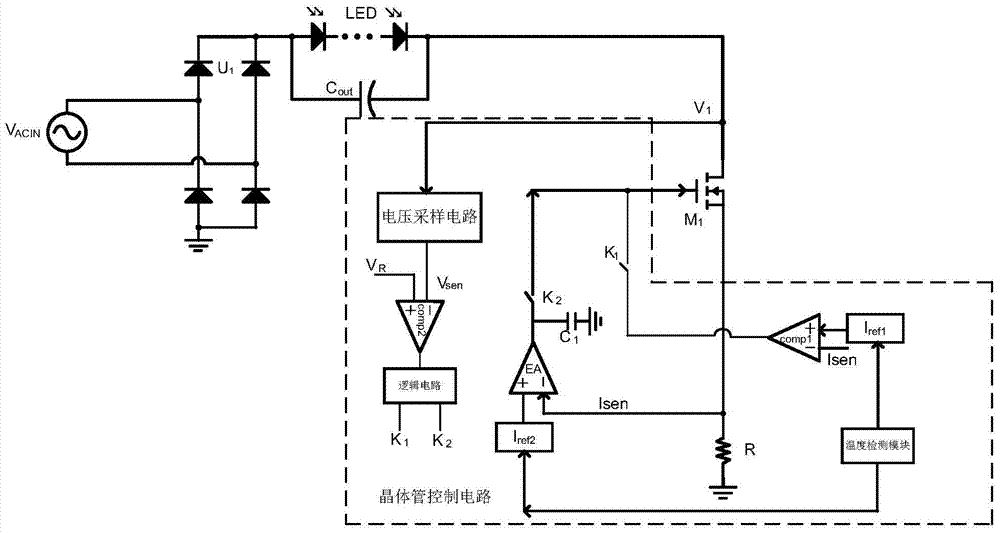
[0029] Embodiment two: reference figure 2As shown, another specific implementation manner of the present invention is illustrated. For the same parts as in the first embodiment, refer to the first embodiment, and details are not repeated here. The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that two power transistors are replaced by one transistor, and according to the sampling voltage signal V sen with V R (characterized by preset reference voltage V ref ) to determine which working range to work in. If V sen greater than V R is located in the second working interval T 2 , then the comparator COMP 1 The output terminal of the power transistor M 1 The control terminal is connected, if V sen less than V R is located in the first working interval T 1 and the third working interval T 3 , then the error amplifier EA 1 The output terminal (and there is a capacitor C at the output terminal 1 for error compensation) with the power transistor M 1 The ...
Embodiment 3
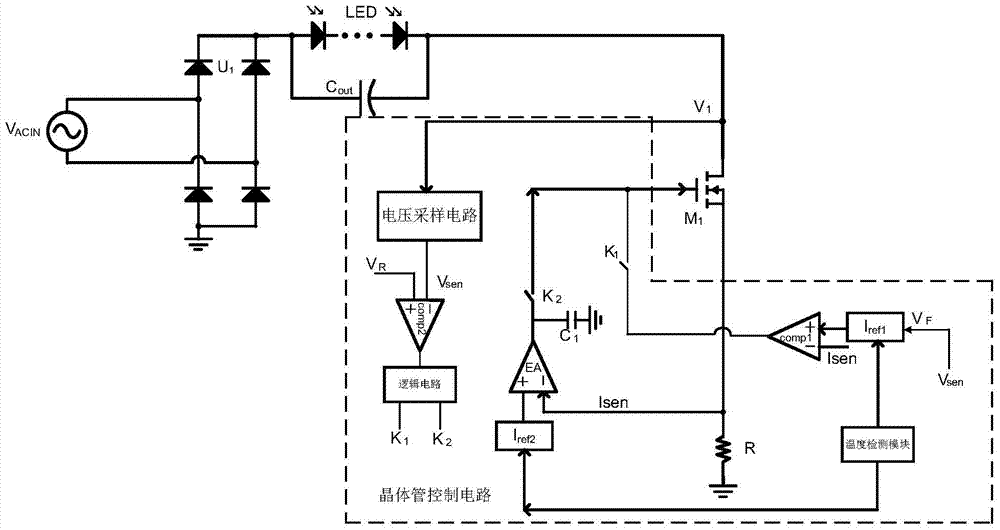
[0031] Embodiment three: reference image 3 As shown, an implementation mode of introducing voltage feedforward is illustrated. It can be seen from the figure that it is a further improvement scheme based on the second embodiment. In fact, introducing the voltage feedforward into the first embodiment can also be realized. Take the improvement of Example 2 as an example. Mainly the sampling voltage signal V sen Transformed into a feed-forward voltage signal V with the opposite trend F , using the feed-forward voltage signal as the first current reference value I ref1 .
[0032] For how to sample the voltage signal V sen transformed into a feed-forward voltage signal V F There are many implementations, so here is only an example: subtract the sampled voltage signal V from a constant voltage signal sen , the constant voltage signal can be optionally greater than the sampling voltage signal V sen peak signal.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com