Method of analysing iron melt
一种熔体、热分析的技术,应用在制造蠕墨铸铁领域
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
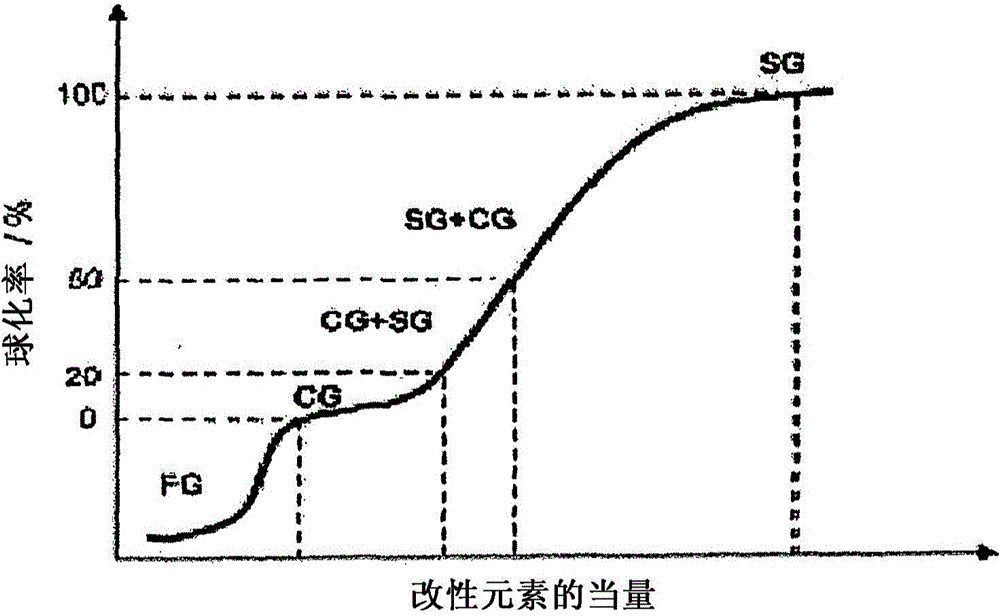
[0069] According to an embodiment of the invention, the above analysis and prediction of the nodularity ratio for a particular melt forms part of a method for manufacturing compacted graphite iron. According to one embodiment of the invention, the method comprises the steps of: providing a melt comprising predetermined amounts of carbon, magnesium, balance iron and unavoidable impurities; casting at least a portion of the melt in a mould; and Thermal analysis of a casting melt during cooling of the casting melt and prediction of the nodularity of the casting melt are taught. Thereafter, according to the foregoing teachings (wherein the nodularity is preferably estimated according to ISO16112:2006 Appendix B), as a test for the nodularity within a predetermined range (the range is preferably 0 to 30%, and more preferably 0 to 20%) % nodularity) in response to the predicted nodularity, changing the content of the nodularity influencing agent in the remainder of the melt that has...
Embodiment
[0075] A melt having a composition (in mass %) according to Table 1 was prepared in an induction furnace of the intermediate frequency type with a melting capacity of 4 tons. The melt was incubated with 0.1% Inobar and 0.02% RE (rare earth). The composition of the respective melts was measured by means of a spectrometer. Cekv is the carbon equivalent of the corresponding melt, expressed as CE=%C+%Si / 4+%P / 2.
[0076] Table 1
[0077] Test No.
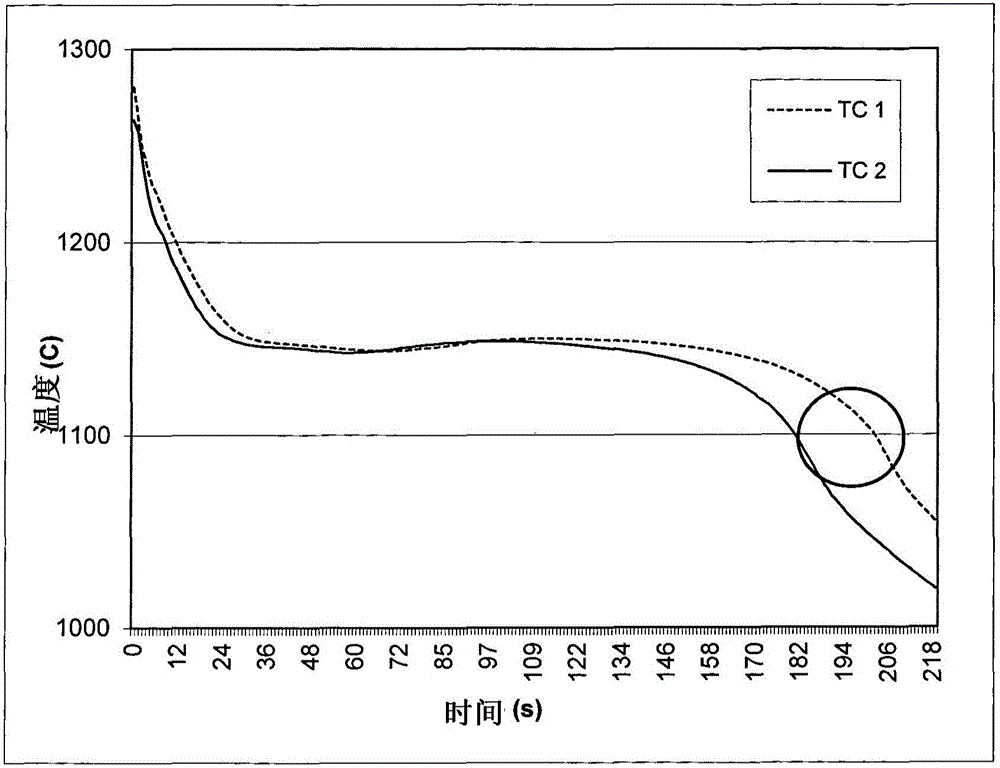
[0078] Samples of the test melts presented in Table 1 were fabricated by casting the corresponding melts in molds having cavities that produced structures with stepped geometries (eg Figure 7 presented), with a thickness in the range of 8 mm to 70 mm (from the thinnest to the thickest rung).
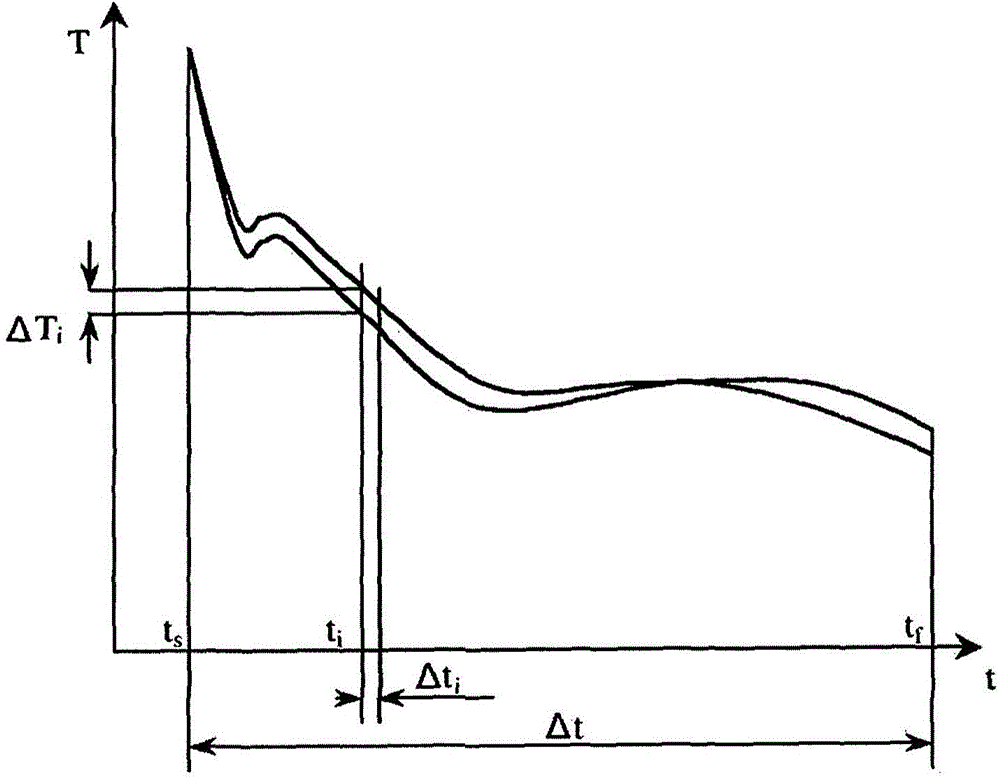
[0079] During the cooling of the cast melt, the temperature of the melt was measured versus time by means of a K-type thermocouple (QuiK-Cup (manufacturer: Heraeus Electro-Nite)) and plotted. The sampling rate was 1 Hz and the obtain...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| spheroidization ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com