Method of fabricating solar cells with p-doped cdte layers of reduced thickness
A technology of solar cells and doped layers, applied in the direction of final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] In the following, the method according to the invention is explained in a first exemplary embodiment showing the production of a solar cell in a layer structure, without any limitation being meant for said embodiment.
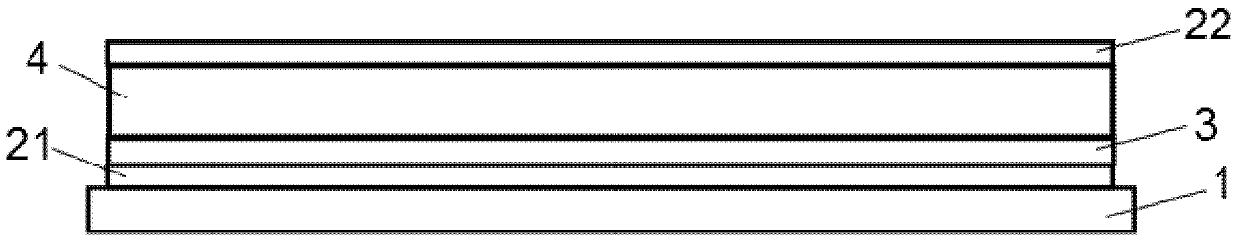
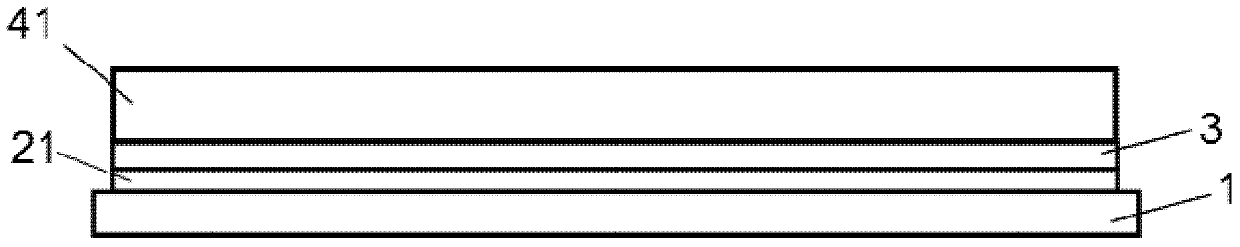
[0043] as in Figure 2a As shown in , the front contact (21) and the CdS layer (3) have been applied on the transparent substrate (1) by means of methods according to the prior art. As a front contact ( 21 ), a 450 nm thick transparent bilayer [fluorine-doped tin oxide (350 nm) as conductive layer and tin oxide (100 nm) as high-resistance buffer layer] was applied (as TCO). The CdS layer (3) reaches a thickness of 90nm and is deposited using the CSS technique. On it, a first CdTe layer ( 41 ) according to the invention is deposited with a thickness of 1.6 μm. The deposition process was carried out as a CSS process at a substrate temperature of 530°C, resulting in large grains of the deposited layer.
[0044] Figure 2b A sacrificial doped layer (5) a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com