Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial strain and application thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and strains, applied in the direction of application, bacteria, microorganisms, etc., to achieve the effect of preventing cardiovascular diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
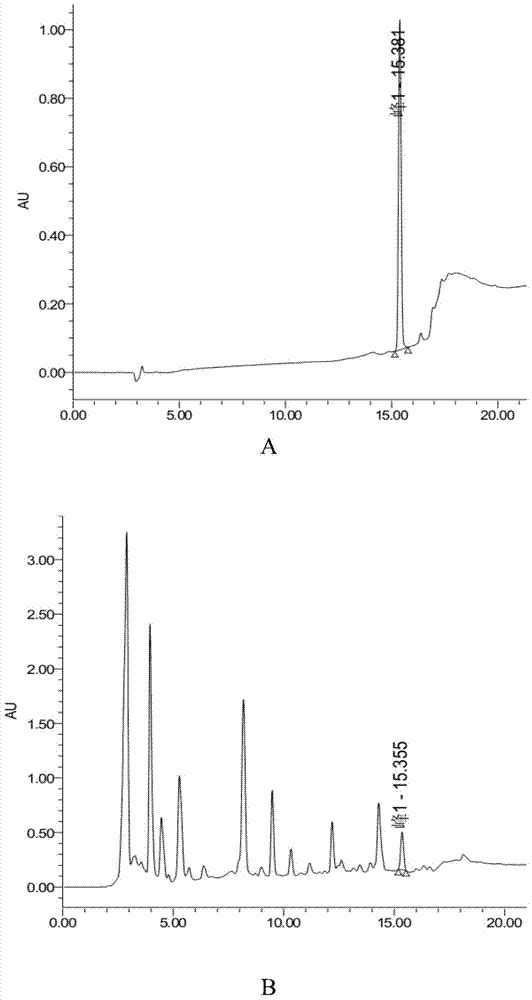
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] This example is used to illustrate the research of vegetable species on phenyllactic acid in kimchi fermented by lactic acid bacteria.
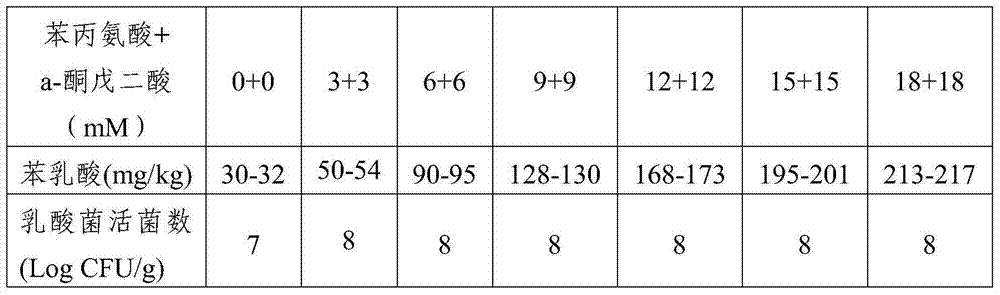
[0061] Select 1000g each of fresh beans, mustard greens and cabbage, wash, cut, drain and put them in a kimchi jar, add sterilized vegetable pickling solution according to the mass ratio of material to liquid at 1:1, and marinate at 25°C for 24 hours. The activated Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC No.8744 of the 2nd generation was pressed by 1×10 5 The inoculum amount of CFU / g (relative to the quality of vegetable raw materials) is inoculated, and the liquid seal is cultured statically at 30° C., and fermented for 5 days to obtain a kimchi product. The phenyllactic acid in kimchi and the viable count of lactic acid bacteria were measured. The results are shown in Table 1. Different vegetable types have a significant impact on the concentration of phenyllactic acid in kimchi. The content of phenyllactic acid in beans is the highest, follow...
Embodiment 2
[0065] This example is used to illustrate the effect of salt water pre-pickle on the enrichment of phenyllactic acid in kimchi fermented by lactic acid bacteria.
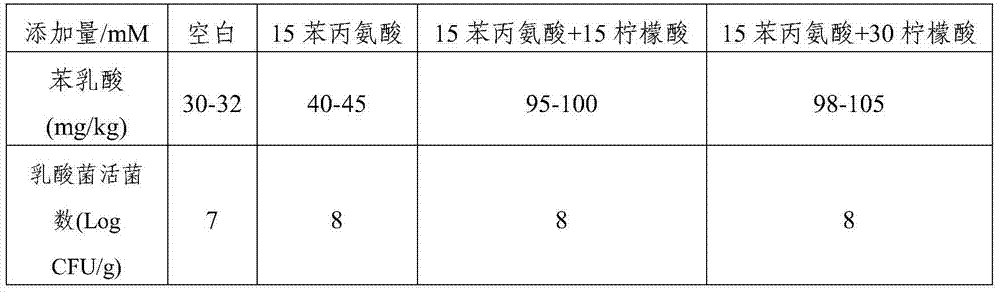
[0066] Select 1000g of fresh beans, wash, cut, drain and place in a kimchi jar, add sterilized vegetable pickling solution according to the mass ratio of solid to liquid at 1:1, and pickle at 25°C according to the time given in Table 2. The activated Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC No.8744 of the 2nd generation was pressed by 1×10 5 The inoculum amount of CFU / g (relative to the quality of vegetable raw materials) is inoculated, and the liquid seal is cultured statically at 30° C., and fermented for 5 days to obtain a kimchi product. Determination of phenyllactic acid in pickled vegetables and the viable count of lactic acid bacteria, the results are shown in Table 2, salt water pre-pickled time has a significant impact on the concentration of phenyllactic acid in pickled vegetables, the phenyllactic acid content of 24...
Embodiment 3
[0070] This example is used to illustrate the effect of fermentation temperature on the enrichment of phenyllactic acid in kimchi fermented by lactic acid bacteria.
[0071] Select 1000g of fresh beans, wash, cut, drain and place in a kimchi jar, add sterilized vegetable pickling solution according to the mass ratio of material to liquid at 1:1, and marinate at 25°C for 24 hours. The activated Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC No.8744 of the 2nd generation was pressed by 1×10 5 The inoculum amount of CFU / g (relative to the quality of vegetable raw materials) is inoculated, liquid-sealed, cultured according to the fermentation temperature in Table 3, and fermented for 5 days to obtain the kimchi product. The phenyllactic acid in kimchi and the viable count of lactic acid bacteria were measured. The results are shown in Table 3. Fermentation temperature has a significant effect on the concentration of phenyllactic acid in kimchi. The content of phenyllactic acid is the highest when ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com