Opportunistic decoding of transmissions on a forward link in a machine-to-machine wireless wide area network
A technology of wireless wide area network and forward link, which is applied in the field of communication in the machine-to-machine wireless wide area network, and can solve the problems of inefficient use of power supplies of M2M devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
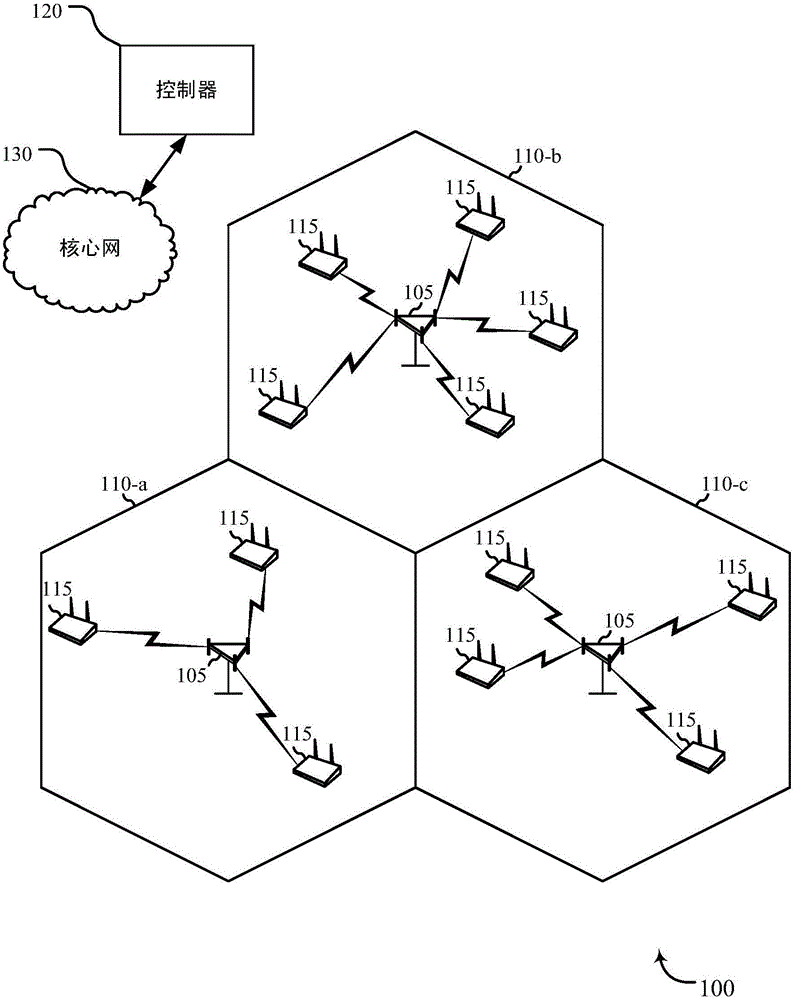
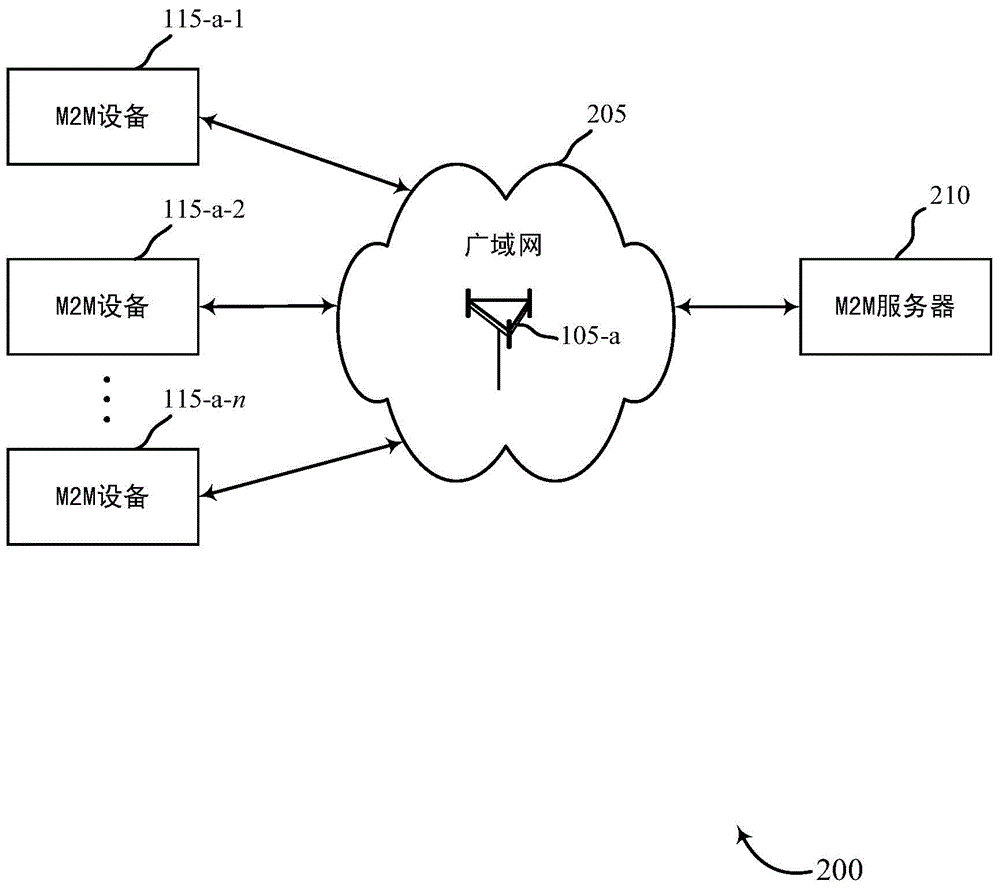
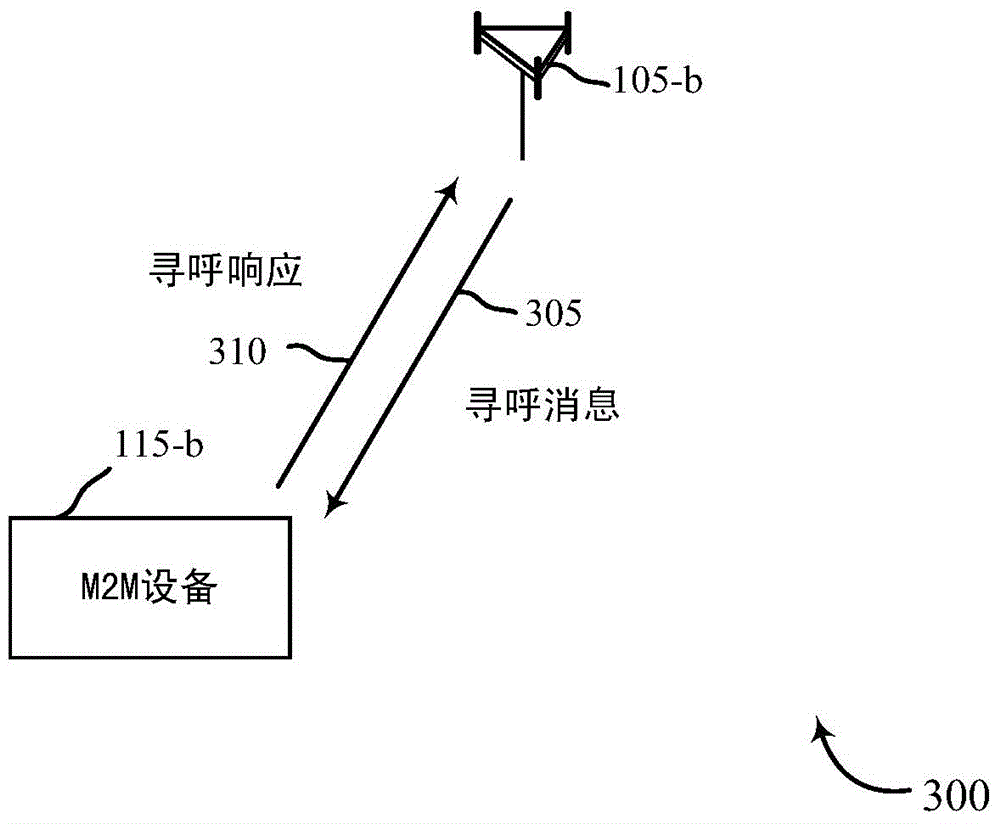
[0032] Methods, systems and devices are described herein for conserving power of M2M devices by providing an opportunistic decoding scheme for packets received by M2M devices on the forward link of an M2M wireless WAN. Conventional cellular systems can employ additional physical layer channels to facilitate reverse link communication between M2M devices and base stations. For example, a reverse link control channel may be established between the M2M device and the base station to carry a physical layer ACK message. However, establishing these channels and sending physical layer ACK messages requires bandwidth on the reverse link and power of the M2M device. In M2M wireless WAN, it is desirable to save power of M2M devices. Therefore, the traditional cellular system approach presents significant drawbacks for M2M wireless WANs.
[0033] To improve power efficiency, M2M devices may minimize the amount of transmissions they make on the reverse link. In addition, the device can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com