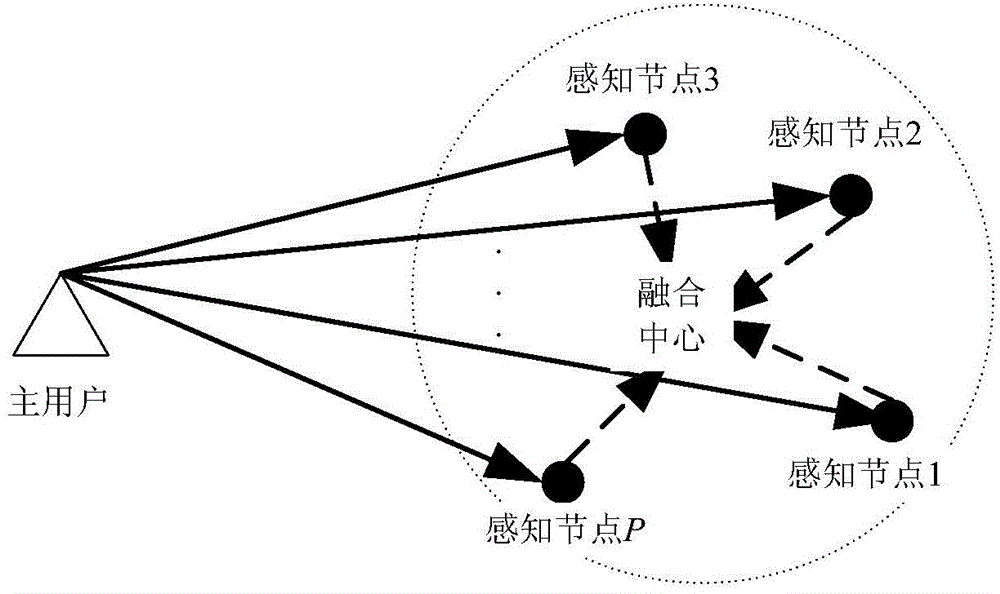
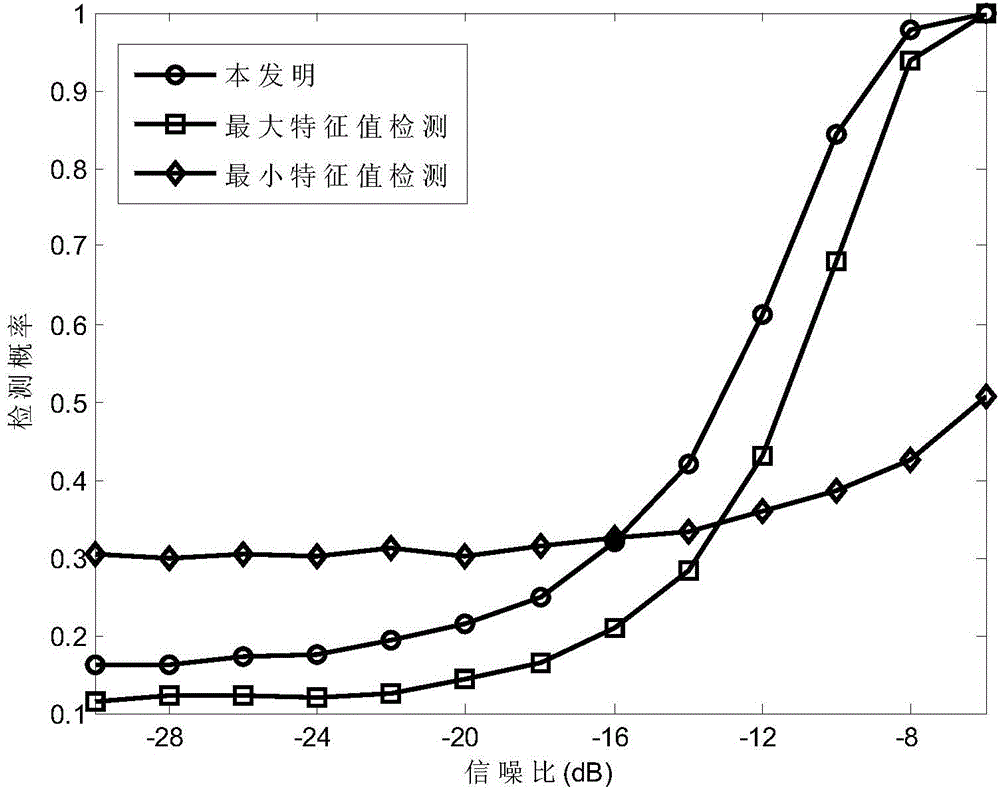
Half-blindness collaborative spectrum sensing method with reliable false-alarm performance
A collaborative and false alarm technology, applied in the field of spectrum sensing, can solve the problems of complex judgment threshold calculation, unstable false alarm performance, complex numerical calculation, etc., to achieve reliable false alarm performance, reduce implementation complexity, and low complexity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
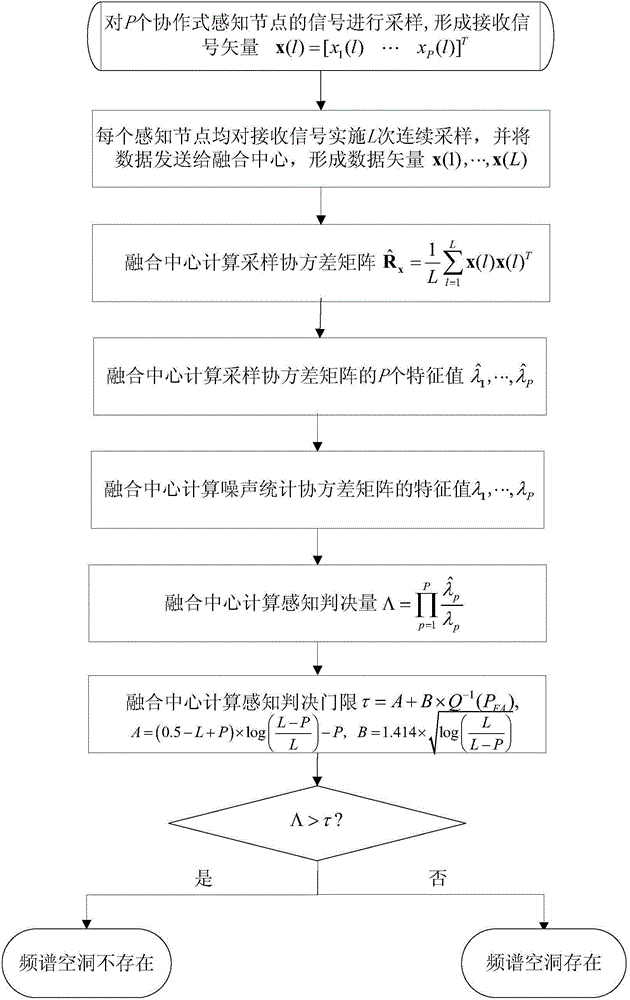
[0047] Define the sampling covariance matrix of the received signal data vector as:
[0048] R ^ x = 1 L Σ l = 1 L x ( l ) x ( l ) T - - - ( 2 )
[0049] Assume The P eigenvalues of At the same time, set the Gaussian background noise statistical covariance matrix R η The P eigenvalues of λ 1 , lambda 2 ..., λ P . Note that when the main user signal does not appear, it can be known from the theorem of large numbers that The P eigenvalues of will be numerically close to R η P eigenvalues of ; and when the primary user signal appears, d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com