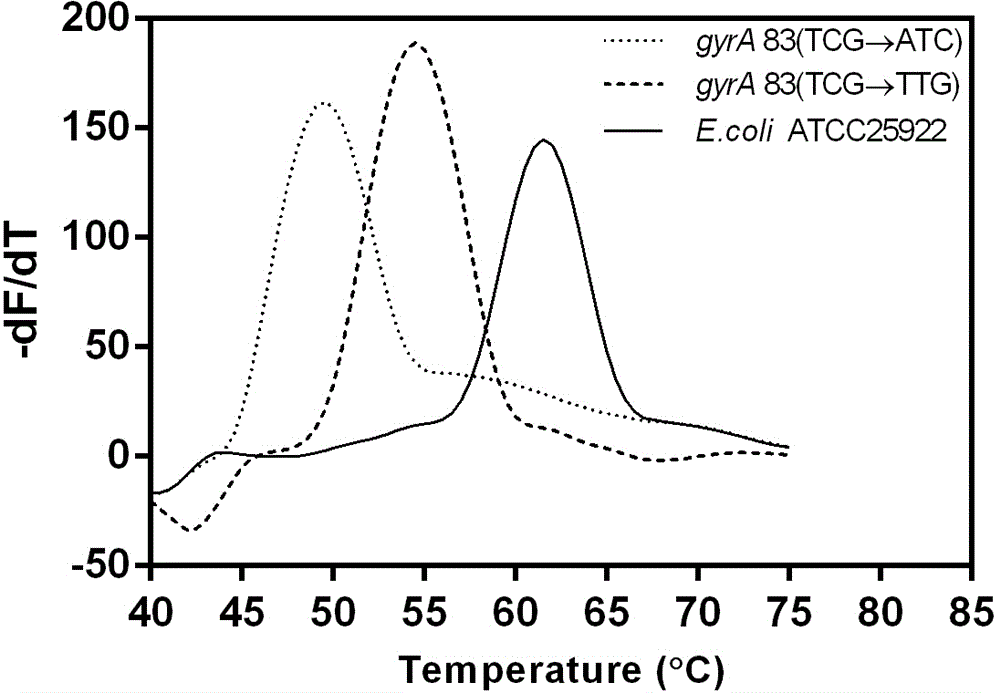
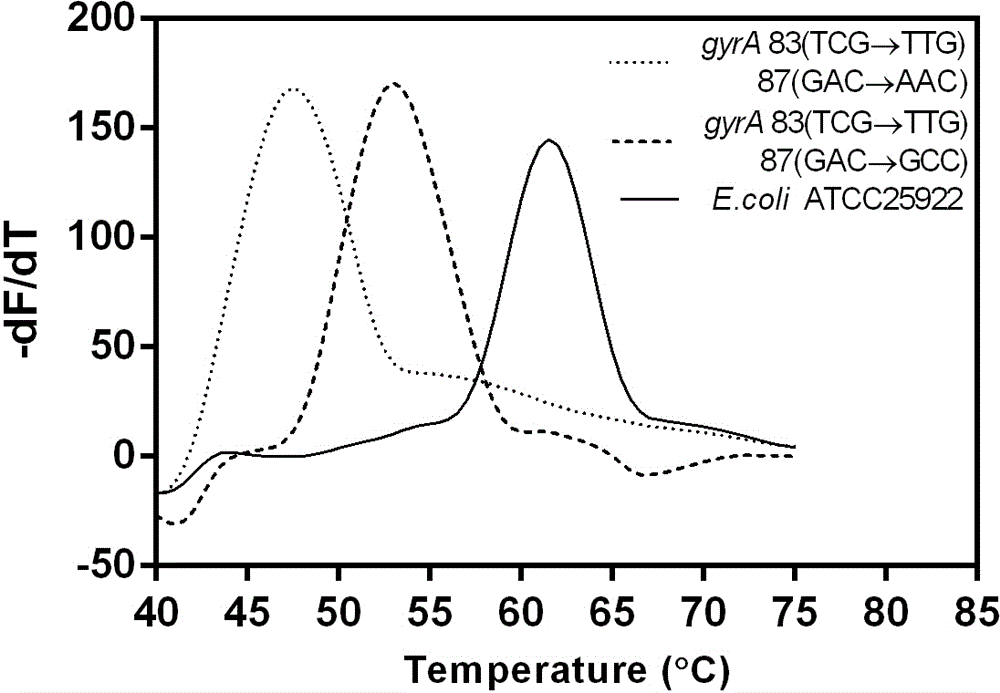
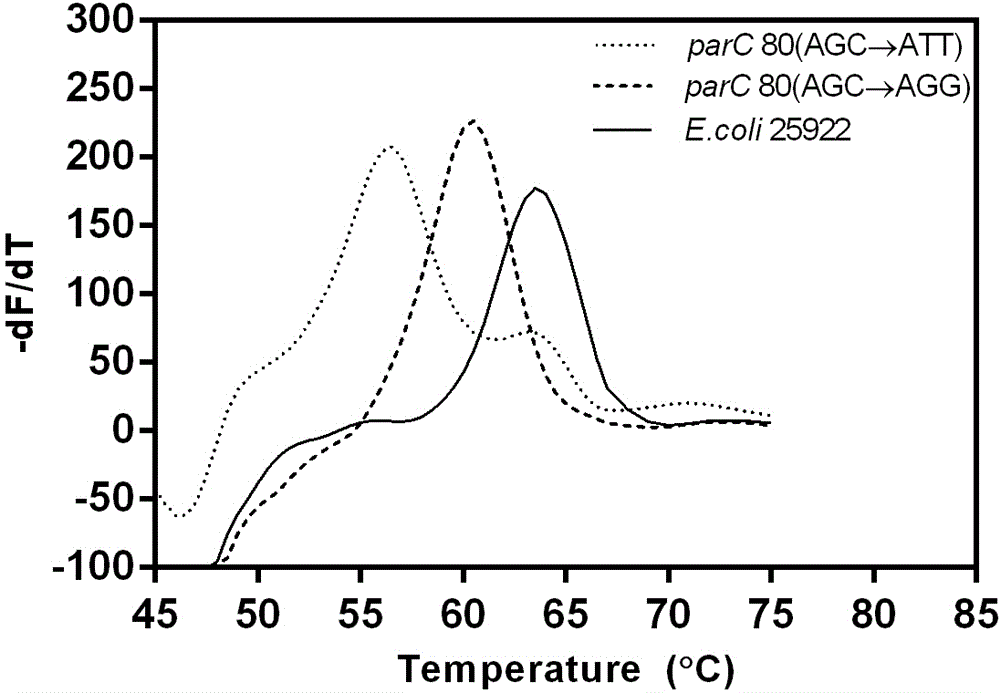
Method for detecting escherichia coli fluoroquinolone-resisting gyrA/parC gene point mutation
A technology of Escherichia coli and quinolones, which is applied in the point mutation of parC gene to detect the fluoroquinolone resistance of Escherichia coli gyrA, and achieves the effects of low cost, favorable popularization and favorable method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: Escherichia coli to be tested and standard bacterial strains E. coli Genomic DNA Extraction of ATCC25922
[0033] Use conventional bacterial genomic DNA extraction methods, or bacterial genomic DNA extraction commercial kits (product number: SK8225, Sangon Biotech) to extract the genomic DNA of Escherichia coli to be tested and the standard strain Escherichia coli ATCC25922, and the concentration of the final DNA sample is about 150ng / μL.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Design of specific primer pairs for two single-plex PCR amplifications
[0035] Using the primer design software primer premier 6, the wild-type standard strain E. coli ATCC25922 gyrA gene and parC The gene is used as a template to design two primers for single-plex PCR amplification, and the designed amplification includes gyrA (Ser codon 83 and Asp codon 87) nucleotide sequences including pairs of primers, and parC Multiple pairs of primers including the nucleotide sequence of (Ser codon 80 and Glu codon 84), after verification of each pair of primers, the specific PCR primer pair was obtained gyrA-FR (The upstream primer is the single-stranded DNA shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the downstream primer is the single-stranded DNA shown in SEQ ID No.2) and parC-FR (The upstream primer is the single-stranded DNA shown in SEQ ID No.3, and the downstream primer is the single-stranded DNA shown in SEQ ID No.4).
[0036] The primers were synthesized by a profe...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Design of dual fluorescent-labeled probes gyrP and parP
[0038] Use the probe design software Xpression primer 3.1 to design the nucleotide sequences of the dual fluorescently labeled probes gyrP (shown in SEQ ID No.5) and parP (shown in SEQ ID No.6), and entrust the designed probes to Modified and synthesized by a professional company, purified by HPLC.
[0039] The specific design of the probe is: connect the HEX fluorescent group at the 5' end of the fluorescent labeling probe gyrP, connect the BHQ2 fluorescence quenching gene at the 3' end; connect the FAM fluorescent group at the 5' end of the fluorescent labeling probe ParP, and connect the fluorescent group at the 3' end. The 'end is connected to the BHQ2 fluorescence quencher gene; the probe gyrP includes 25 nucleotides, covering the gyrA Gene encoding nucleotide sequence from Gly 81 to Ile 89 for detection gyrA (Ser codon 83 and Asp codon 87) base point mutation; probe ParP Consists of 29 nucleo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com