Rotating type rigidity-changing flexible joint
A technology of flexible joints and variable stiffness, which is applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems of not being able to adapt to fast motion and impact, the joint flexible deformation angle is limited, and the unfavorable application of joint robots, etc., to reduce the spring volume, realize flexible output, reduce The effect of small power requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] Further describe the present invention below in conjunction with embodiment and accompanying drawing thereof. However, the protection scope of the claims of the present application is not limited to the description scope of the embodiments.
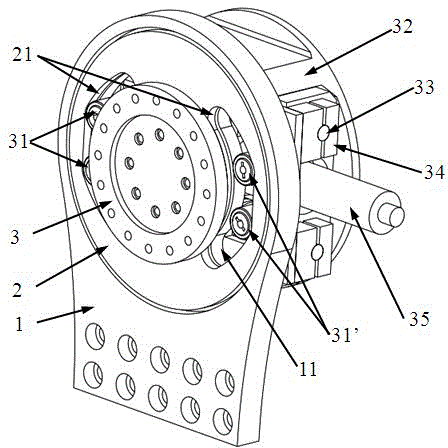
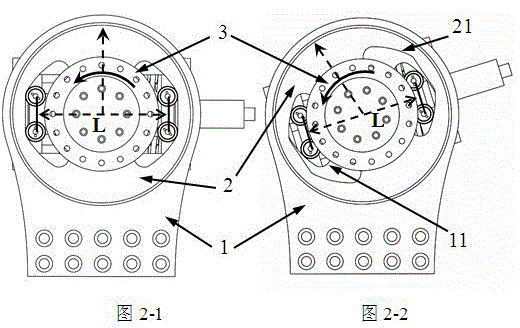
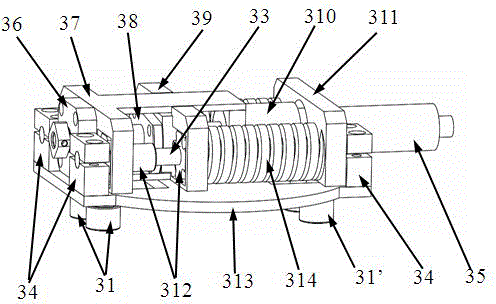
[0028] A kind of rotary variable stiffness flexible joint designed by the present invention (flexible joint for short, see Figure 1-5 ), including a passive variable stiffness mechanism and an active flexible drive mechanism, characterized in that the passive variable stiffness mechanism mainly includes: joint output disc 1, joint first drive disc 2, joint second drive disc 3, first cam group 31, The second cam group 31', the first cam group mounting seat 37, the second cam group mounting seat 311, the optical shaft 33, the optical shaft support seat 34, the stiffness adjustment mounting plate 313, the linear bearing 312 and the compression spring 314, the joint The first drive disc 2 is fixedly connected to the second drive disc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com