Synthetic aperture laser imaging radar optical processor based on band-pass filter
A synthetic aperture laser and imaging radar technology, applied in the field of optical processors, can solve the problems of small optical imaging results, complex imaging process, and no involvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments, but the protection scope of the present invention should not be limited thereby.
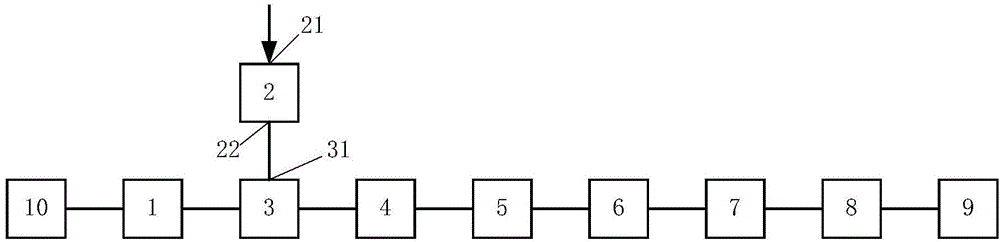
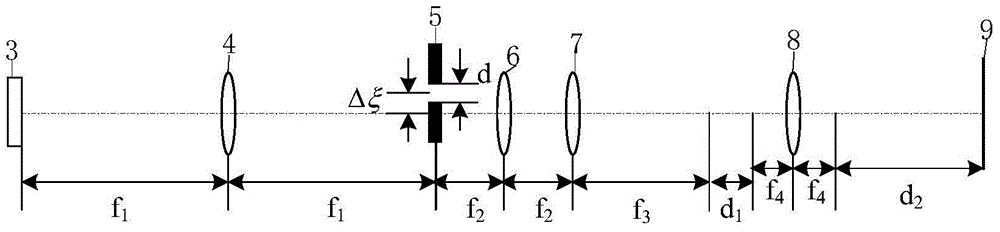
[0016] see first figure 1 , figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of the optical processor of the band-pass filter-based synthetic aperture laser imaging radar of the present invention. As can be seen from the figure, the present invention is based on the optical processor of the band-pass filtered synthetic aperture laser imaging radar, which consists of a laser 10, a collimating beam expander unit 1, a synthetic aperture laser imaging radar data receiving unit 2, and a transmissive intensity type liquid crystal space A light modulator 3, a first spherical lens 4, a slit 5, a second spherical lens 6, a cylindrical lens 7, a third spherical lens 8, and a light screen 9, sequentially along the direction of the optical axis of the laser light emitted by the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com