Motor vehicle and cam-type pushing force brake apparatus of electric vehicle
A technology of braking device and electric vehicle, which is applied to mechanical drive drum brakes, hydraulic drum brakes, brake actuators, etc., can solve the problems of low utilization rate of brake pads and inability to adjust the effective arm of the brake arm, etc. Achieve the effect of avoiding rainwater corrosion and rust, increasing the length and improving the utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
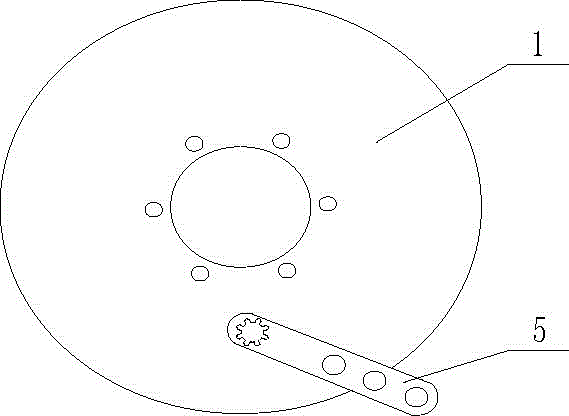
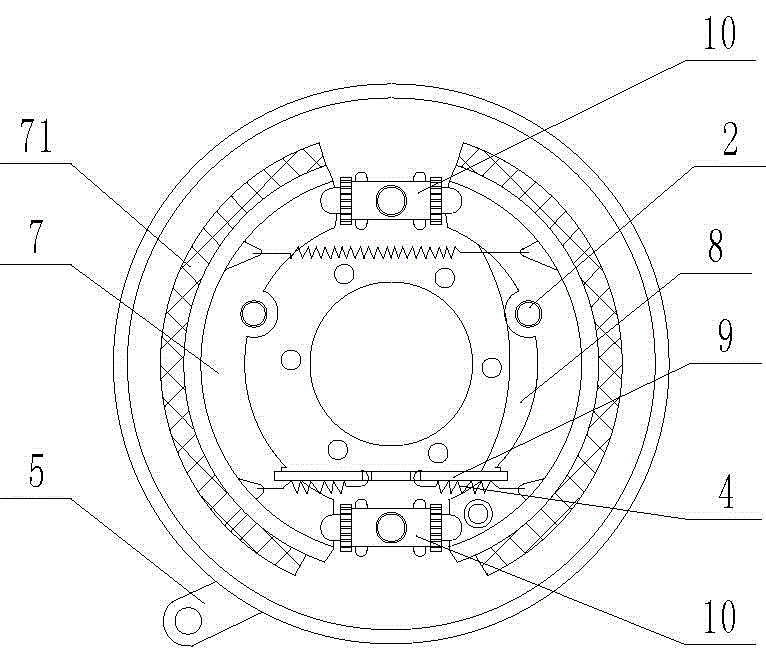
[0036] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 As shown, the cam-type thrust braking device for motor vehicles and electric vehicles includes a brake base plate 1, two positioning mechanisms 2, two first return springs 3, two second return springs 4, a brake arm 5, and a cam Axle 6, two arc-shaped brake shoes 7, a hand brake lever 8, a support plate 9, a brake cylinder 10, two adjusting push rods 11 and an adjusting device. The adjustment device, the brake cylinder body 10 and the support plate 9 are all located between the two arc-shaped brake shoes 7 . The handbrake lever 8 is connected to the brake bottom plate 1 through a pin shaft, and the end of the handbrake lever 8 is in contact with the support plate 9 . The adjusting device comprises an adjusting tube 14, two screw rods 141 are installed in the adjusting tube 14, nuts are arranged on the screw rods 141, grooves are arranged at the ends of the screw rods 141, and a plurality of grooves are...
Embodiment 2
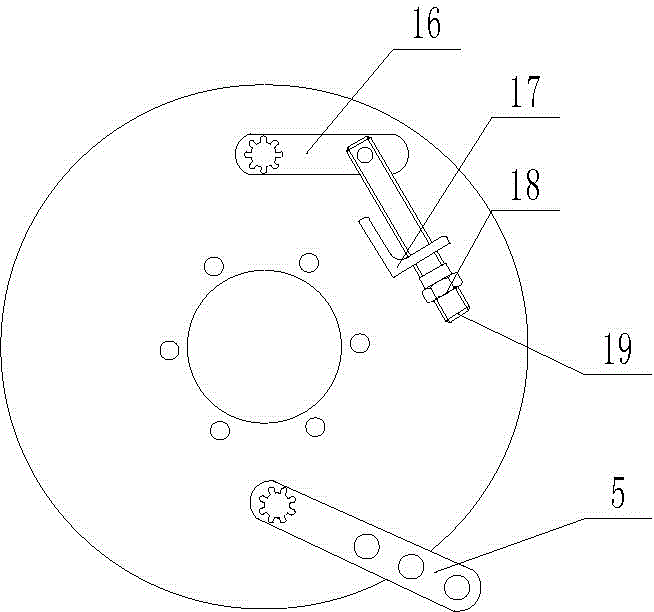
[0039] The difference between embodiment two and embodiment one is: as Figure 10 , Figure 11 As shown, the adjustment device is replaced by a cam type device.
[0040] The cam type device includes a brake cylinder block 10 , a camshaft 6 , an adjusting push rod 11 , a rotating arm 16 , a support base 17 , an adjusting pull rod 19 and a locking nut 18 . The rotating arm 16 is splined connected with the camshaft 6 , the rotating arm 16 is hinged with the adjusting pull rod 19 through a pin shaft, and the adjusting pull rod 19 is threadedly connected with the locking nut 18 . The support seat 17 is welded on the back side of the brake bottom plate 1 . The support base 17 is provided with a through hole for the adjustment rod 19 to pass through. Support seat 17 selects angle steel for use.
[0041] In the specific implementation process, the locking nut 18 is rotated, so that the adjusting rod 19 drives the rotating arm 16 to rotate, and the rotating arm 16 drives the camsha...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The difference between embodiment three and embodiment two is: as Figure 12 , Figure 13 , Figure 14 As shown, the second through hole in the brake cylinder is replaced by the first blind hole 22, and the positioning plate 20 is provided on the brake base plate 1, and the positioning plate 20 and the brake base plate 1 are connected by screws. The camshaft 6 is replaced by a double fulcrum camshaft 21 . The double fulcrum camshaft 21 is sequentially composed of a first rotating part, a second rotating part of the camshaft and a connecting part from top to bottom. The connecting part is a spline shaft. The positioning plate 20 is provided with a rotating hole matched with the second rotating part, and the first rotating part of the double fulcrum camshaft 21 is connected with the first blind hole 22 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com