A Method for Evaluating the Thickness of Material Subsurface Machining Damaged Layer
A subsurface damage and damage layer technology, which is applied in the field of evaluation of the thickness of the subsurface damage layer of materials, can solve the problem of the difficulty of non-destructive detection of the thickness of the subsurface damage layer, and achieve the effect of wide applicability and reduction of the number of tests.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
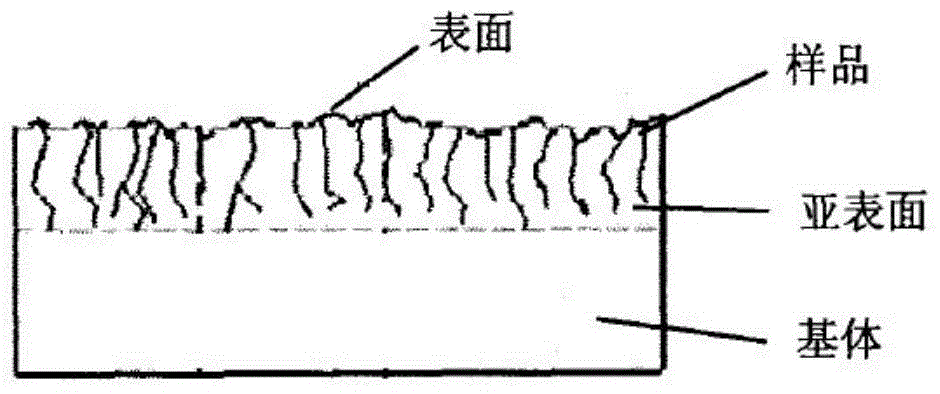
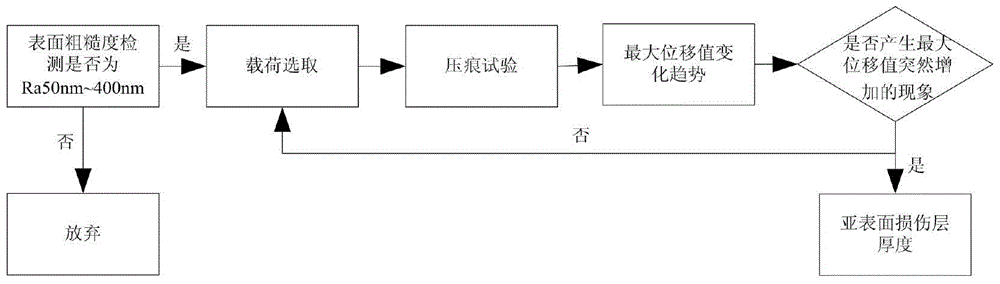
[0029] The evaluation method of the present invention first detects the surface roughness of the material sample: if the range of the surface roughness of the material sample is not within 50nm to 400nm, the test is abandoned; if the range of the surface roughness of the material sample is 50nm to 400nm; then the material sample is tested indentation test;
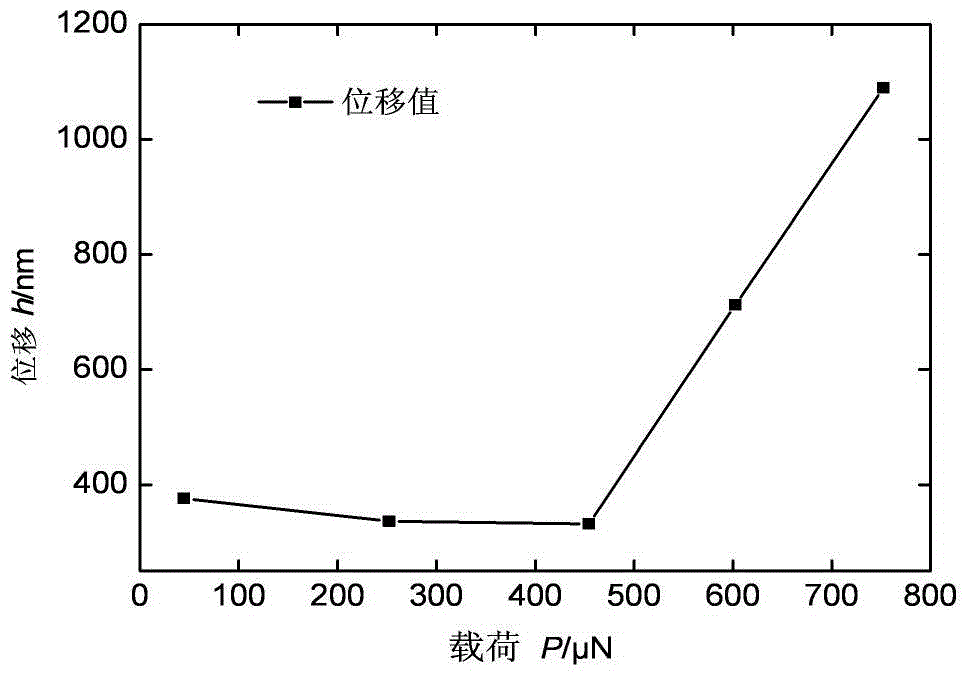
[0030] The process is as follows: first set the load, with 45μN as the initial load, and 50-200μN as the increment, set the load in turn, and the end load is 1500μN; the increment between every two adjacent set loads can be the same or can be different; then carry out the indentation test on the material sample, carry out the loading-unloading test in sequence according to the set load from small to large and record the maximum displacement value of the indenter in each load loading-unloading test; When the increase rate of the maximum displacement value produced by the selected load loading-unloading test is greater than ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com