Image processing device, image processing method, and image processing program
An image processing device and an image-in-image technology, which are applied in image data processing, image data processing, image enhancement, etc., can solve problems such as inability to accurately distinguish fine structures, inability to calculate feature quantities, poor resolution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
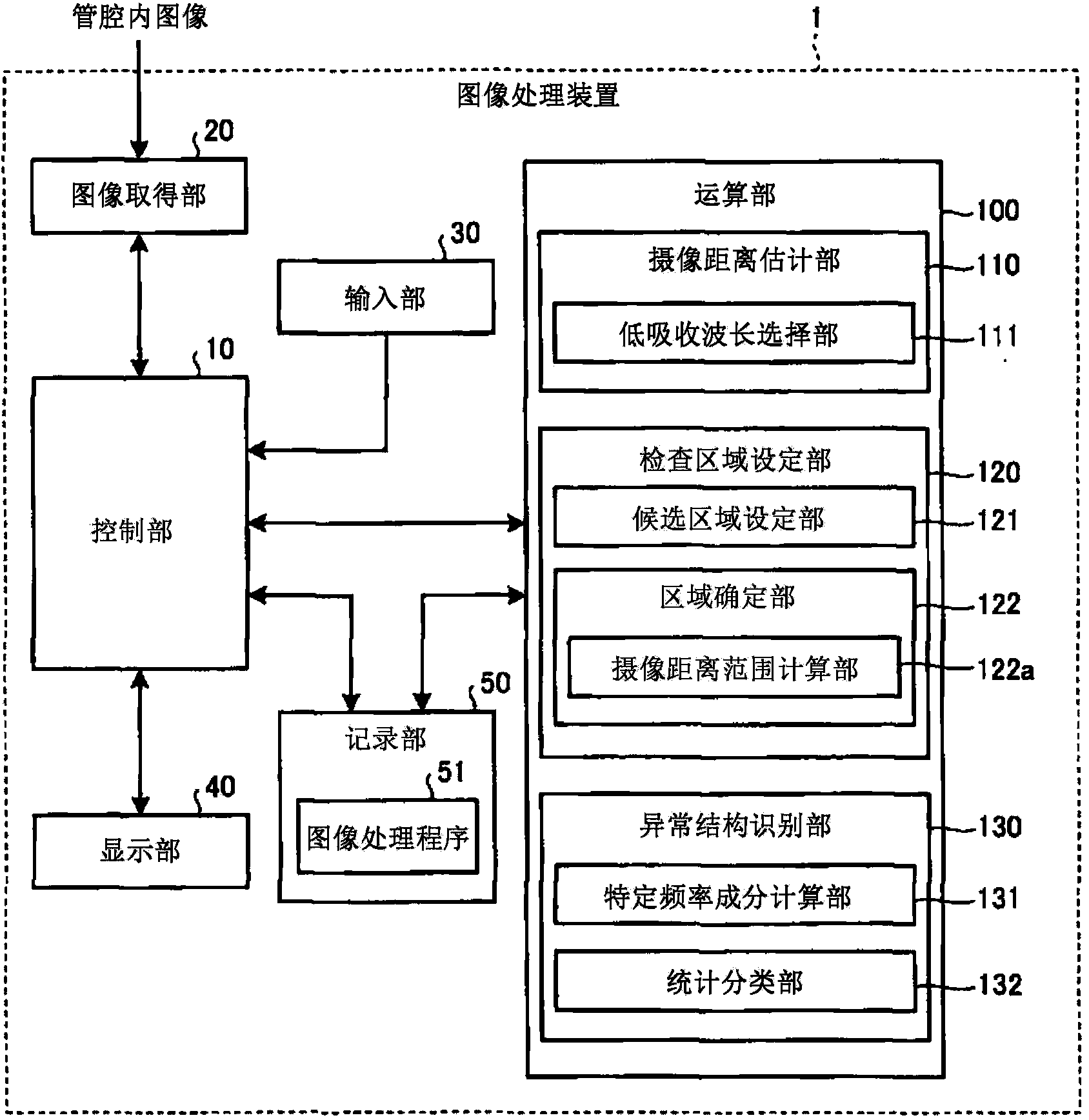
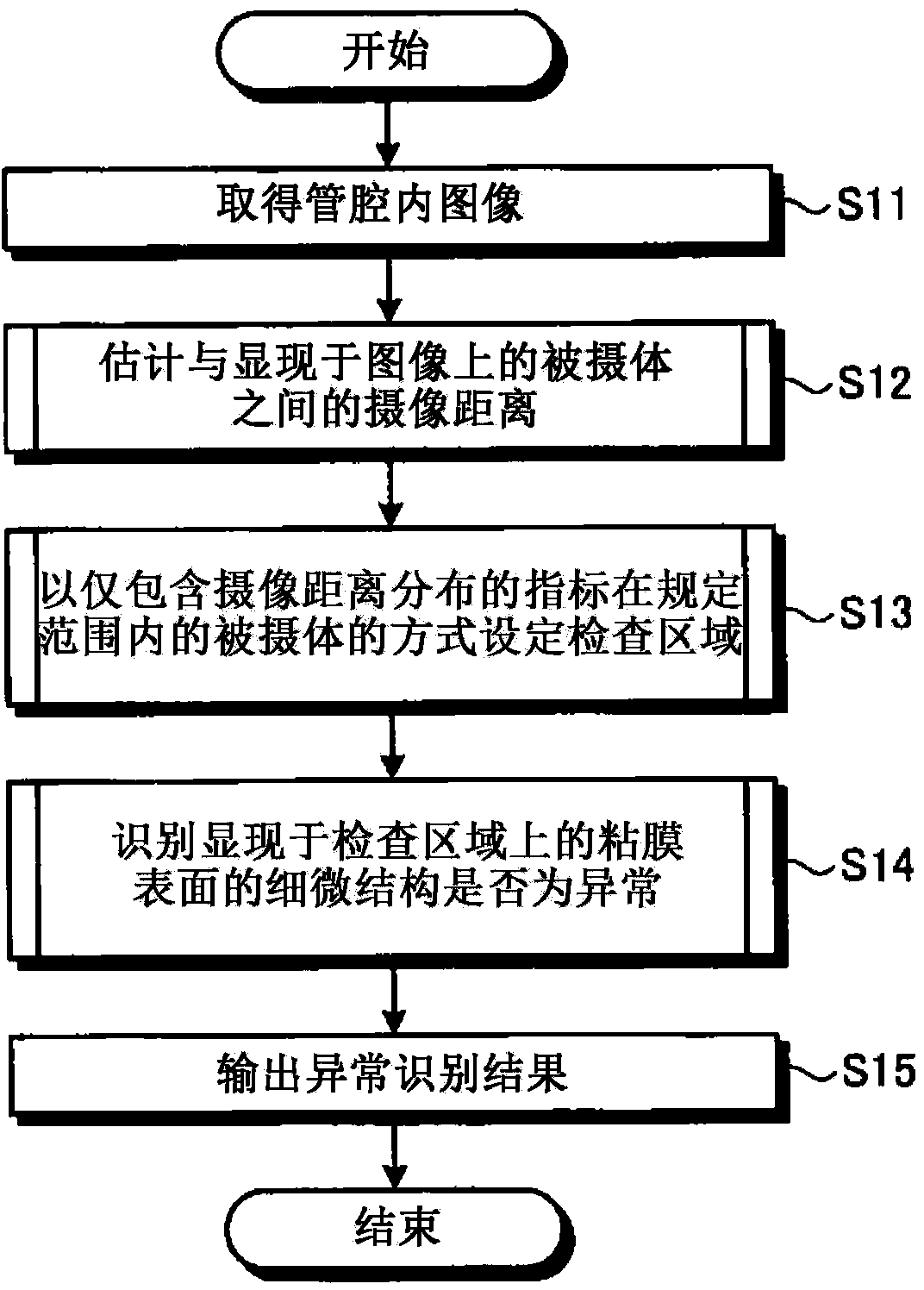
[0053] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of the image processing device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The image processing device 1 of the first embodiment is, for example, a device for imaging the inside of a living body's lumen with an endoscope or a capsule endoscope (hereinafter, they are collectively referred to simply as an endoscope). On the other hand, the acquired intraluminal image (hereinafter, may be simply referred to as image) is subjected to image processing for identifying abnormalities in the microstructure of the mucosal surface. The intraluminal image usually has a color with predetermined (for example, 256 gradation) pixel levels (pixel values) for R (red), G (green), and B (blue) wavelength components (color components) at each pixel position. image.
[0054] Such as figure 1 As shown, the image processing device 1 has a control unit 10 for controlling the overall operation of the image processing dev...
Deformed example 1-1
[0093] Next, Modification 1-1 of the first embodiment will be described.
[0094] Figure 8 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of the computing unit included in the image processing device according to Modification 1-1. Such as Figure 8 As shown, the calculating unit 100 - 1 of the modification 1-1 includes an imaging distance estimating unit 110 , an inspection region setting unit 140 , and an abnormal structure identifying unit 150 . In addition, the configuration and operation of the imaging distance estimation unit 110 are the same as those of the first embodiment. In addition, the overall structure and operation of the image processing device other than the computing unit 100-1 are also the same as those of the first embodiment.
[0095] The inspection region setting unit 140 has a candidate region setting unit 141 and a region specifying unit 142 . Among them, the candidate area setting unit 141 has a representative imaging distance acquisition unit 141...
Deformed example 1-2
[0112] Next, Modification 1-2 of the first embodiment will be described.
[0113] Figure 12 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of the computing unit included in the image processing device of Modification 1-2. Such as Figure 12 As shown, the computing unit 100 - 2 of Modification 1-2 includes an imaging distance estimating unit 110 , an inspection region setting unit 160 , and an abnormal structure identifying unit 170 . In addition, the configuration and operation of the imaging distance estimation unit 110 are the same as those of the first embodiment. In addition, the overall configuration and operation of the image processing device other than the calculation unit 100-2 are also the same as those of the first embodiment.
[0114] The inspection region setting unit 160 has a candidate region setting unit 161 and a region specifying unit 142 . The candidate region setting unit 161 has a representative imaging distance gradient calculation unit 161a that ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com