Nucleic acid synthesis method based on bidirectional isothermal extension
A synthetic method and isothermal technology, applied in DNA preparation, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as difficult high-throughput synthesis, wrong hybridization, and inability to splice
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
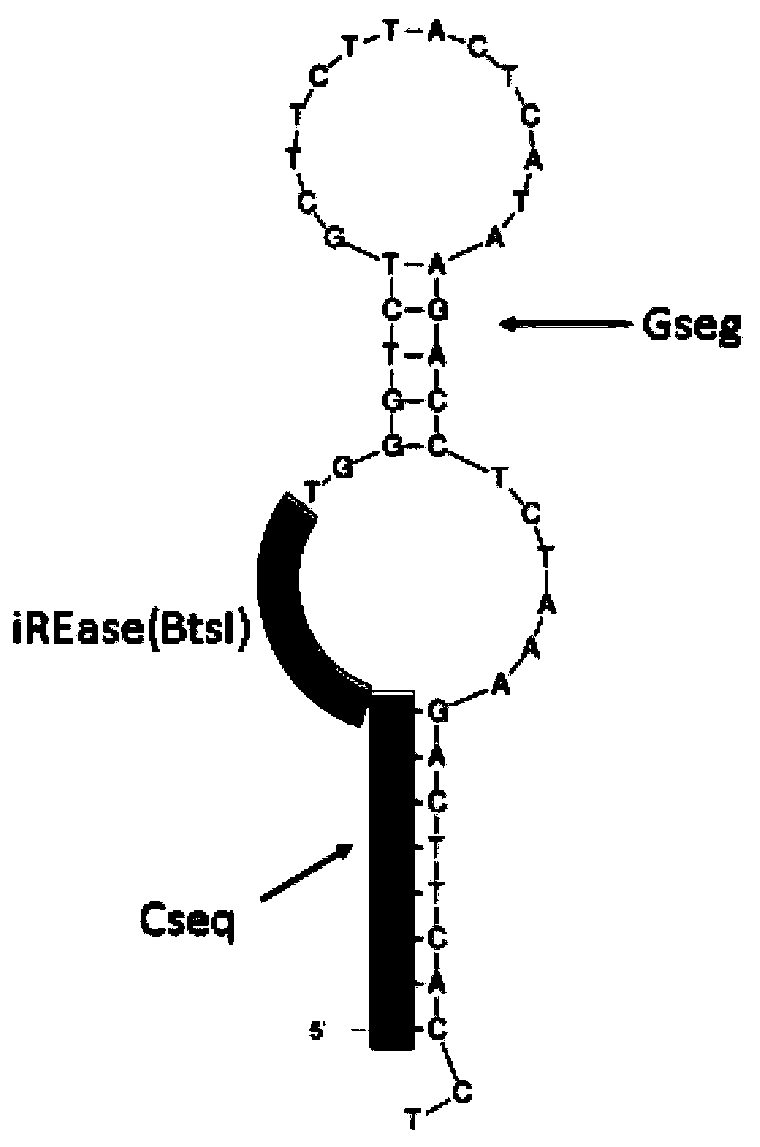
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1: Synthesizing a 412-base sequence using inside-out mode, which is a part of the lambda exonuclease gene
[0083] The sequence is as follows (SEQ ID NO.1):
[0084] 5’-TCACAACGTGATAGCAAAACCCCGCTCCGGAAAGAAGTGGCCTGA
[0085] CATGAAAATGTCCTACTTCCACACCCTGCTTGCTGAGGTTTGC
[0086] ACCGGTGTGGCTCCGGAAGTTAACGCTAAAGCACTGGCC
[0087] TGGGGAAAACAGTACGAGAACGACGCCAGAACCCTGTTTG
[0088] AATTCACTTCCGGCGTGAATGTTACTGAATCCCCGATCATC
[0089] TATCGCGACGAAAGTATGCGTACCGCCTGCT
[0090] CTCCCGATGGTTTATGCAGCGACGGCAACGGCCTTGAACTGAA
[0091] ATGCCCGTTTACCTCCCGGGATTTCATGAAGTTCCGGCTCGGT
[0092] GGTTTCGAGGCCATAAAGTCAGCTTACATGGCCCAGGTGCAGTA
[0093] CAGCATGTGGGTGACGCGAAAAAATGCCTGGTACTTTGCCAAC-3'
[0094] The splicing process is as follows:
[0095] step 1
[0096] Segment the target sequence into 10 short DNA fragments (Table 2).
[0097] Table 2.
[0098]
[0099] step 2
[0100] These short DNA fragments L1-L5, R1-R5 were assembled into hairpins HL1-HL1, HR1-HR5 (Table 3), ...
Embodiment 2
[0119] Embodiment 2: the phospholipase gene of a section of 366 bases is synthesized with inside-out pattern
[0120] Its sequence is as follows (SEQ ID NO.12):
[0121] 5’AGCCTGCTGGAATTTGGGCGTATGATCAAGGAGGAGACGGGGAAAAACCCTCTTTCCTCCTACATCTCTTACGGATGCTACTGTGGCTGGGGGGGCCAAGGCGAGCCAAAGGACGACACCGACCGTTGCTGCTTTGTGCACGACTGCTGTTACGGAAAACTGTGGGGCTGCAGCCCAAAAACGGACATTTACTTCTACTTCCGTAAGAACGGGGCTATCGTCTGCGGACGTGGCACCTGGTGTGAGAAGCAGATTTGTGAGTGTGACAAGGCCGCCGCAATCTGCTTCCGTGAGAATCTGGCCACGTACAAAGAAGAATATCACTCTTACGGGAAGTCTGGTTGCACGGAGAAGTCACCGAAATGC3’
[0122] The starting double strand is a pJW vector digested by BglI, the pJW vector is a modified pUC19 vector, the BtsI and BglI sites on it have been removed through mutation treatment, and two BglI sites have been introduced into the multi-cloning site, After digestion with BglI, the two ends of this linear vector are the 3' hanging sticky ends of 'AGG' and 'GGT' respectively.
[0123] The designed oligonucleotides are listed in Table 4.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com