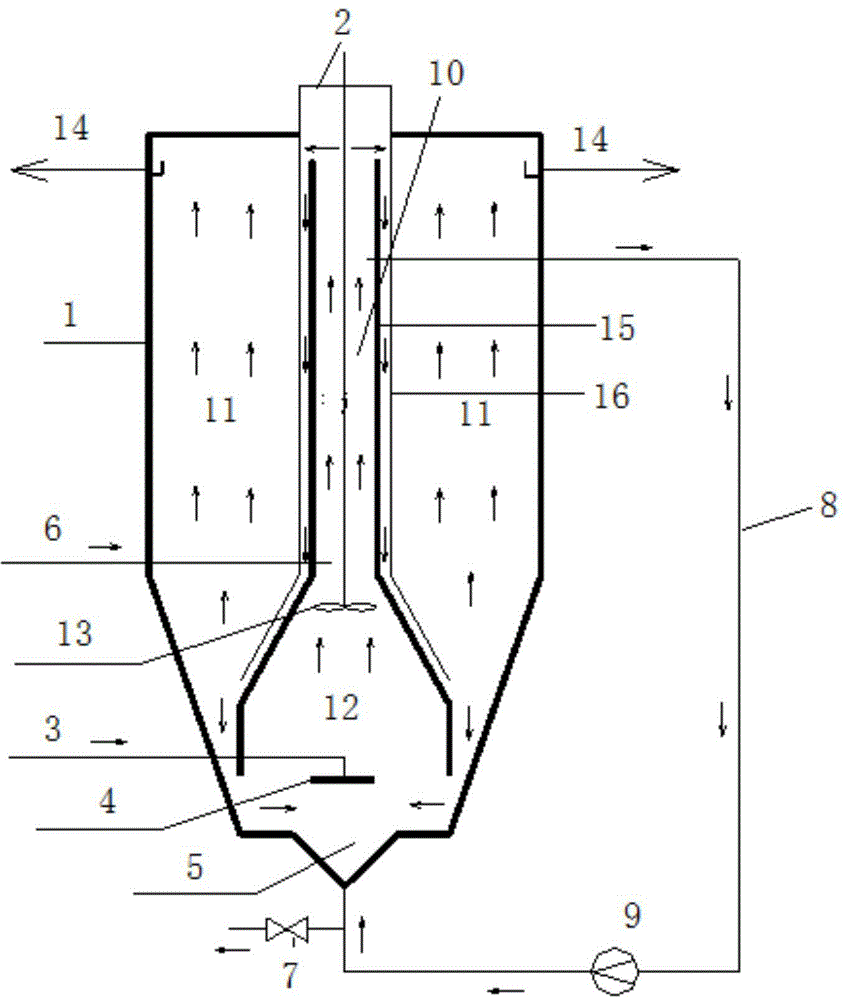
Device and method for synchronous denitrification and dephosphorization of slightly polluted water
A technology for simultaneous denitrification and phosphorus removal, and micro-polluted water, applied in chemical instruments and methods, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. and other problems, to achieve the effect of small head loss, low pollutant load and small hydraulic loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
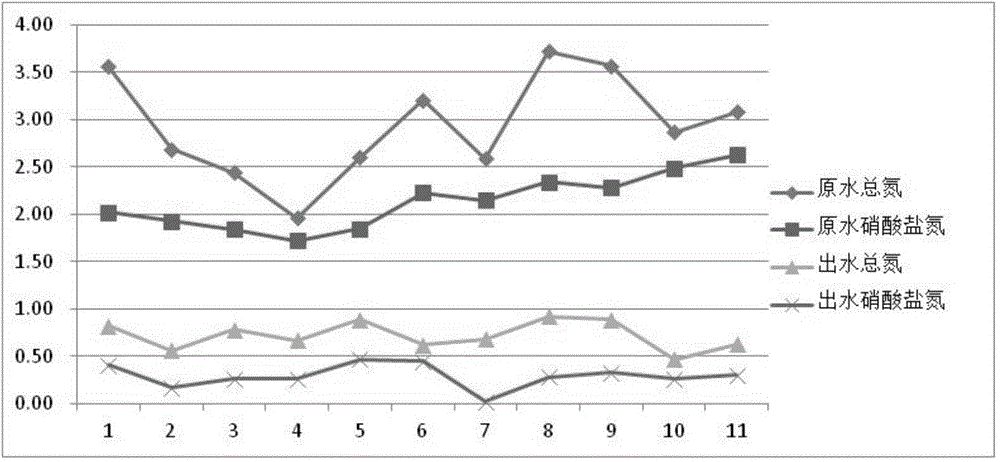
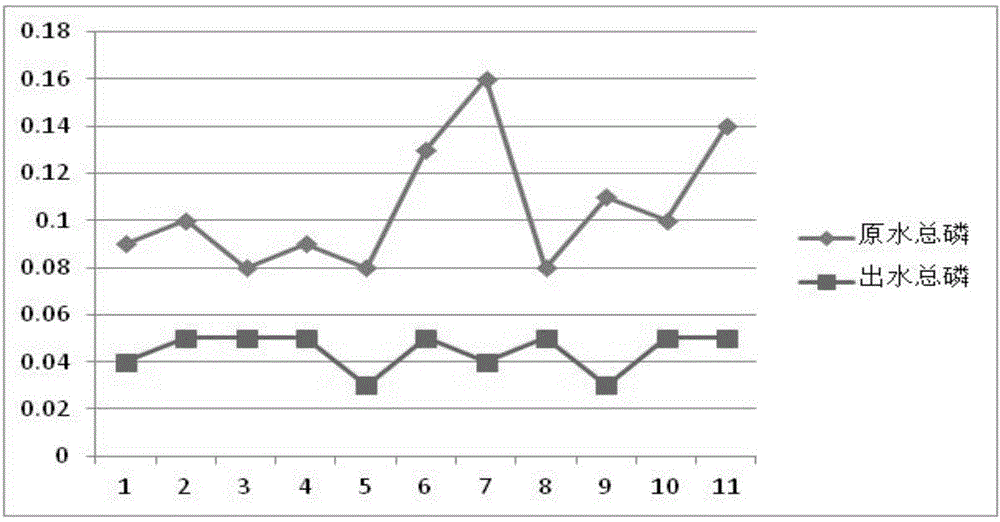
[0067] A pilot test was carried out on the water of Taihu Lake in Wuxi. During the test, the temperature of the lake water was 18-20°C, and the treated water volume was 1m 3 / h, the rising flow rate of the control reactor is 0.8m / h, the hydraulic retention time is 1.2h, the concentration of the sludge layer in the sedimentation zone is 6.6g / l, the average value of the total nitrogen concentration in the raw water is 2.94mg / l, and the concentration of nitrate nitrogen The average value is 2.13mg / l, and the average value of total phosphorus concentration is 0.11mg / l. After denitrification and phosphorus removal treatment, the average value of effluent total nitrogen concentration is 0.72mg / l, and the average value of nitrate nitrogen concentration is 0.29mg / l. The average total phosphorus concentration was 0.04 mg / l. The removal rate of total nitrogen reached 75.5%, the removal rate of nitrate nitrogen reached 86.4%, the removal rate of total phosphorus reached 63.6%, and the ind...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Experimental research was carried out on lake water in a park in Beijing. During the test period, the temperature of the lake water was 19-27°C, and the treated water volume was 0.8m 3 / h, the rising velocity of the reactor is controlled to be 0.64m / h, the hydraulic retention time is 1.2h, the concentration of the sludge layer in the sedimentation zone is 6g / l, the average concentration of total nitrogen in the raw water is 3.07mg / l, and the average concentration of nitrate nitrogen The value of total nitrogen concentration is 2.10mg / l, and the average value of total phosphorus concentration is 0.16mg / l. The average value of phosphorus concentration is 0.05 mg / l. The removal rate of total nitrogen reached 76.5%, the removal rate of nitrate nitrogen reached 95.2%, the removal rate of total phosphorus reached 68.8%, and the indicators such as total nitrogen and total phosphorus have reached the fourth type of water body in the "Environmental Quality Standards for Surface ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com