Method for producing epothilone B based on coupling of microbial fermentation and membrane separation techniques
A microbial fermentation and epothilone technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of stagnation or even decline in epothilone accumulation, decline in epothilone synthetase activity, and difficulty in further increasing production, so as to shorten production time , Operating conditions are mild, reducing the effect of inhibition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
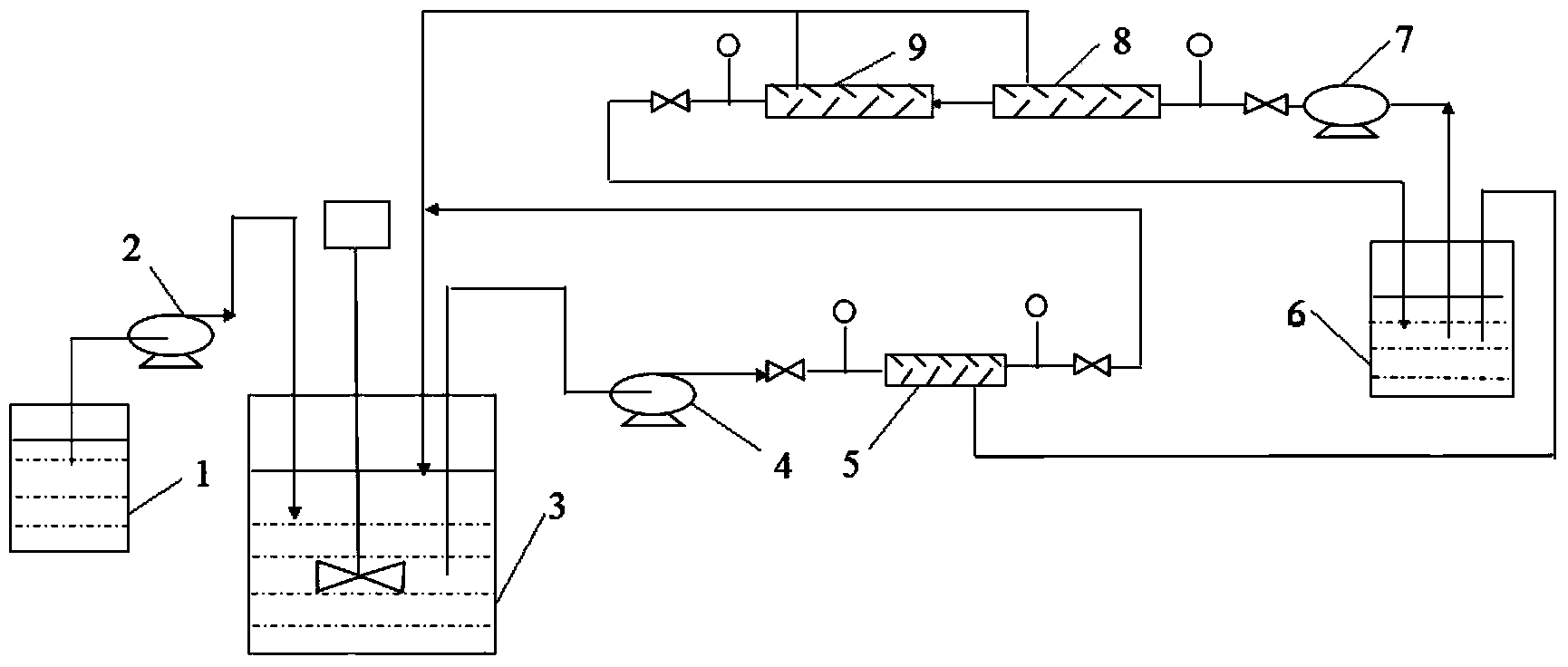
[0029] see figure 1 , the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0030] 1) Fermentation culture: Inoculate 1 L of 100 mg of bacterial species, inoculate Cystobacter celluli ATCC25532 in a 5 L fermenter, and the liquid filling amount is 60%. The fermentation medium is composed of yeast powder 20g / L, corn starch 5g / L, sodium dihydrogen phosphate 1g / L, disodium hydrogen phosphate 1g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O2g / L, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.1g / L, CaCl 2 2g / L, MnCl 2 0.1g / L and glucose 10g / L. The pH of the fermentation medium was 7.2, and it was sterilized at 115 °C for 30 min. The fermentation conditions in the fermenter 3 were as follows: the temperature was 30° C., the stirring speed was 100 r / min, and the ventilation rate was 0.3 vvm.
[0031] 2) Microfiltration membrane filtration: After the fermentation started, epothilone B continued to accumulate, and the concentration of the fermentation broth continued to increase. When the output of epothilone B reached 0.1 mg / L, the se...
Embodiment 2
[0037] see figure 1 , the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0038] 1) Same as Example 1.
[0039] 2) Microfiltration membrane filtration: After the fermentation started, epothilone B continued to accumulate, and the concentration of the fermentation broth continued to increase. When the output of epothilone B reached 0.1 mg / L, the second pump 4 was started, and the concentration was 10 mL / min. The flow rate of the partial fermentation culture liquid is pumped into the filter device 5 with microfiltration membrane for filtration, the retained fermentation liquid is returned to the fermentation tank 3, and the filtrate enters the concentration tank 6, and the sterilization rate reaches 96%; Among them, the microfiltration membrane is a polyethersulfone membrane with a pore size of 1.0 μm, the microfiltration membrane component is a plate-type flat membrane, the filtration temperature is 37° C., and the pressure is 0.5 MPa.
[0040] 3) with embodiment 1;
[00...
Embodiment 3
[0045] 1) with embodiment 1;
[0046] 2) with embodiment 1;
[0047] 3) ultrafiltration membrane and nanofiltration membrane filtration and concentration: when the filtrate volume after the sterilization in the concentration tank reaches 55% of the fermentor volume, the third pump 7 is opened, and the filtrate pump is pumped with the flow velocity of 10mL / min Enter into the ultrafiltration apparatus 8 with ultrafiltration membrane, and its retentate is returned to the fermentor 3, the filtrate continues to be filtered through the nanofiltration apparatus 9 with nanofiltration membrane, and the retentate after filtration returns to the concentration tank 6. The filtrate without macromolecules is returned to the fermentation tank 3; wherein, the ultrafiltration membrane is a hollow fiber membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 150KD, the ultrafiltration membrane module is a tubular type, the filtration temperature is 37°C, and the pressure is 0.5MPa. The nanofiltration memb...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com