Magnetic-resonance imaging method for synchronous measurement of fluid speed and temperature in porous medium
A porous medium and internal fluid technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to measure large speeds and generating artifacts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and with the best embodiment.
[0032] A method for simultaneously and quickly measuring the velocity and temperature of a homogeneous fluid containing hydrogen protons, the operation steps of which are as follows:
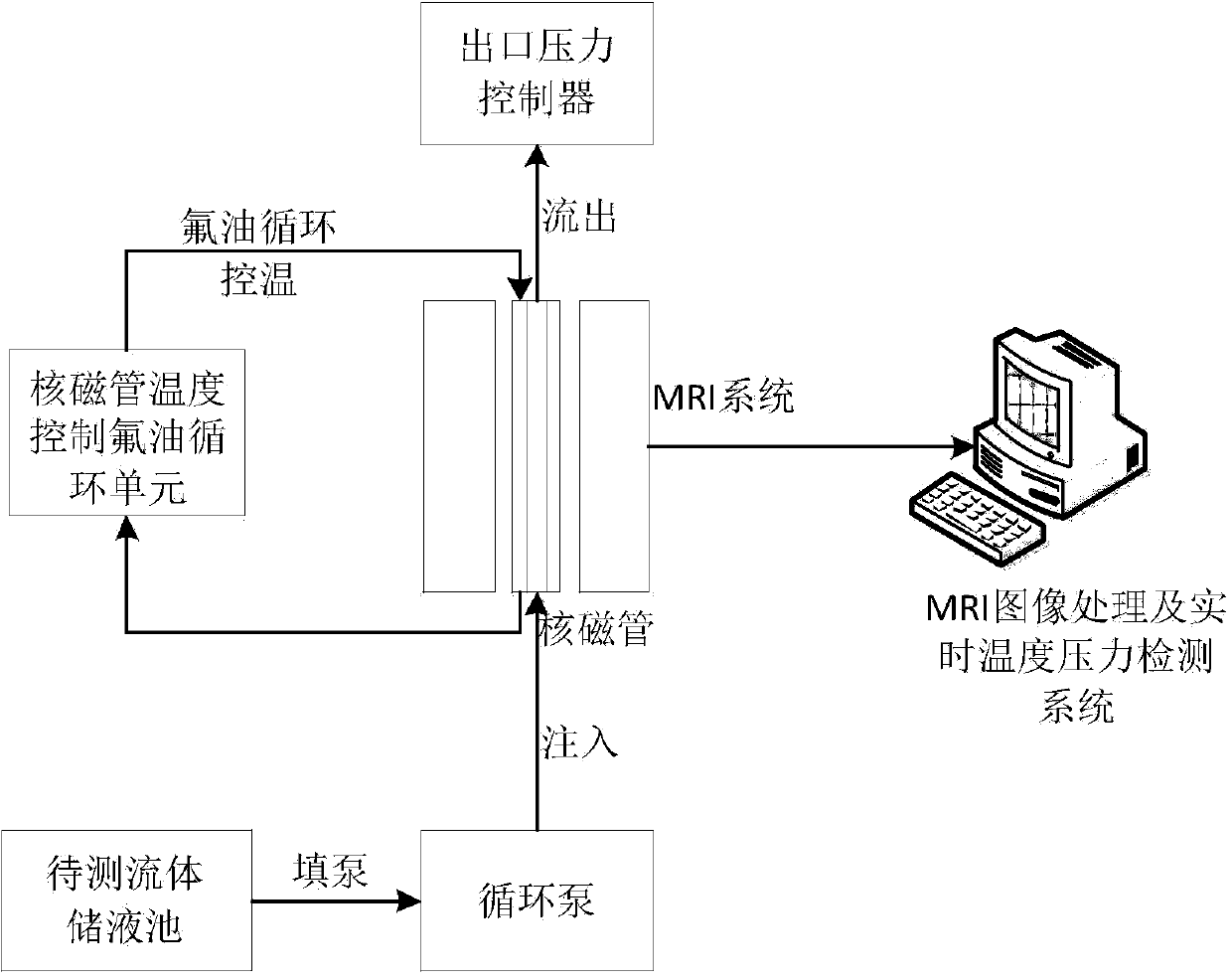
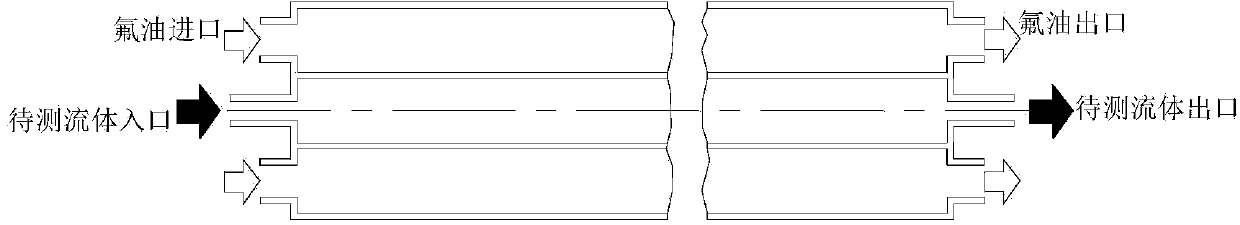
[0033] (1) First use figure 1 The circulation pump shown goes to the NMR tube ( figure 2 ) into the test fluid containing hydrogen protons from the bottom up, stop the injection after the NMR tube is full, adjust the temperature to control the temperature of the fluorine oil circulation unit, and wait for a long enough time for the temperature of the liquid in the NMR tube to stabilize. set a TR 1 value, image acquisition of the static liquid with a multi-layer spin-echo sequence, and then set another TR 2 The values were collected for the second time with a multi-slice spin echo sequence, and all the parameters of the two measurement sequences were ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com