Current transient quantity principal component cluster analysis direction protection method for power transmission line with static synchronous series compensator
A series compensation, static synchronization technology, applied in the fault location and other directions, can solve the problem of difficult identification of line faults with static synchronization series compensator equipment, and achieve the effect of high reliability and reliable identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
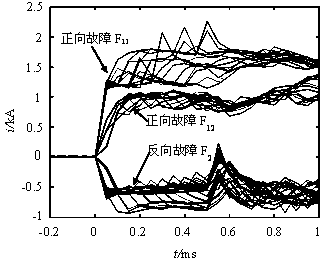
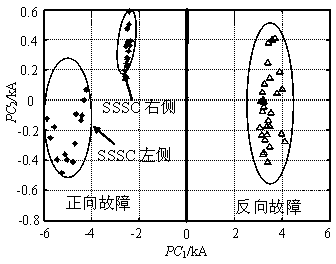
[0033] Embodiment 1: A current transient principal component clustering analysis direction protection method for a transmission line with a static synchronous series compensator. Principal component analysis is performed on the line-mode current data containing the fault phase in the time window. According to the sample data in the first principal component (PC 1 ) projection on the axis q 1 To distinguish the forward fault from the reverse fault: first estimate the fault initial angle, when the fault initial angle is between 0° and 90°, if the projected value q 1 The sign of is positive, it is judged as a positive fault, if the projection value q 1 If the sign of is negative, it is judged as a reverse fault; when the initial fault angle is between -90° and 0°, if the projection value q 1 The sign of is negative, it is judged as a positive fault, if the projection value q 1 If the sign of is positive, it is judged as a reverse fault.
[0034] The specific steps of the...
Embodiment 2
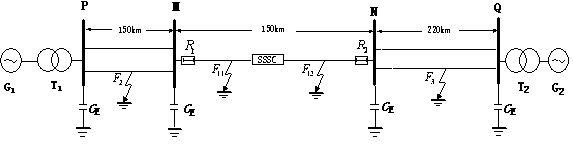
[0047] Example 2: 500kV line with static synchronous series compensator such as figure 1 shown. The line parameters are as follows: the total length of the line is 150km for the PM section, 150km for the MN section, and 220km for the NQ end. Fault location: A single-phase ground fault occurs 63km away from the M terminal on the MN section. The grounding impedance is 0Ω, the fault time is 0.474s, the initial fault angle is -90°, and the sampling rate is 20kHz.
[0048] (1) According to step 1 to step 3 in the manual, construct the principal component clustering analysis space with different initial fault angles, and obtain the principal component clustering formed by clustering the fault current sample data with initial fault angles of 90° and -90° respectively at the M terminal Analysis space such as 3, Figure 5 shown;
[0049] (2) Put the fault sample into the principal component clustering space that responds to the initial fault angle according to step 4 in the specifi...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3: 500kV line with static synchronous series compensator such as figure 1 shown. The line parameters are as follows: the total length of the line is 150km for the PM section, 150km for the MN section, and 220km for the NQ end. The grounding impedance is 10Ω, the fault time is 0.4715s, the initial fault angle is -30°, and the data sampling rate is 20kHz. A single-phase ground fault occurs at a distance of 97km from the M terminal on the MN section.
[0052] (1) According to step 1 to step 3 in the manual, construct the principal component clustering analysis space with different initial fault angles, and obtain the principal component clustering formed by clustering the fault current sample data with initial fault angles of 90° and -90° respectively at the M terminal Analysis space such as 3, Figure 5 shown;
[0053] (2) Put the fault sample into the principal component clustering space that responds to the initial fault angle according to step 4 in the spec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com