Electromagnetic drive variable-rigidity bionic swing propelling device
A propulsion device and electromagnetic drive technology, applied to non-rotating propulsion components, toys, entertainment, etc., can solve the problems of large temperature influence, complex control, large volume, etc., and achieve low mechanical loss, small volume, and good flexibility Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
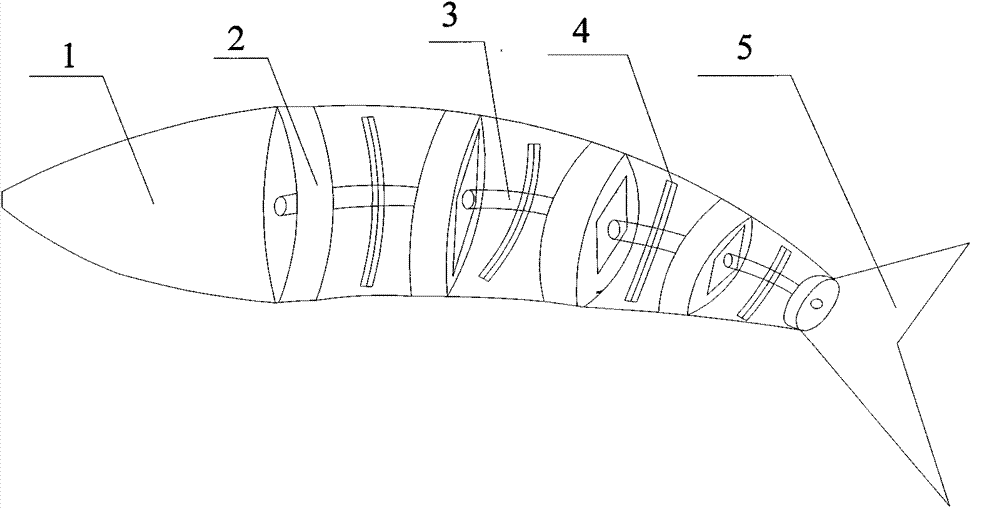
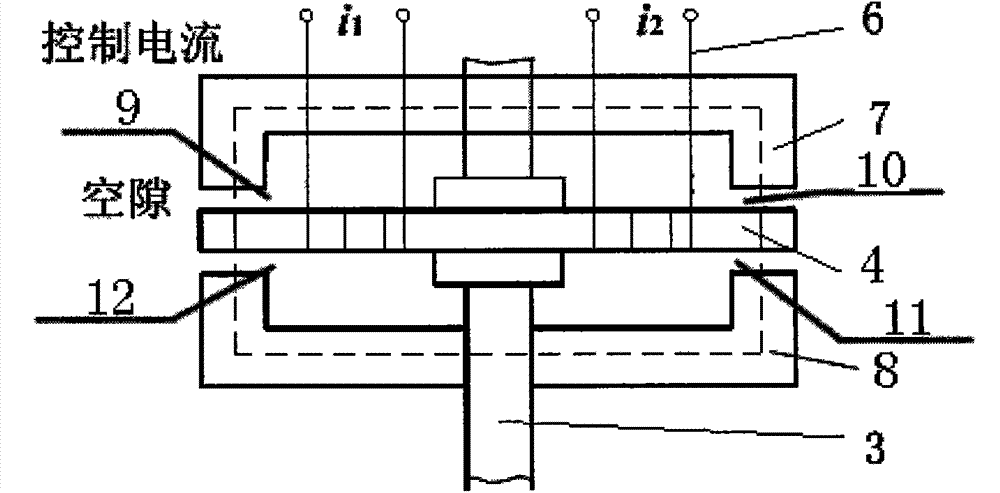
[0014] as attached figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides an electromagnetically driven variable stiffness bionic swing propulsion device, including a support 1, an electromagnetic swing unit with more than two sections and a tail fin 5, and all fish body shapes are sealed by the fish body skin. The electromagnetic oscillating unit of one section is connected with the head of the fish body, and the electromagnetic oscillating units of other levels are all connected with the flexible spine 3, and the last single-section electromagnetic oscillating unit is connected with the tail fin 5, and the electromagnetic oscillating unit includes an upper magnetic conductor 7. The lower magnet guide 8, the control coil 6, the flexible spine 3 and the armature 4, the flexible spine 3 is hollow, and a coil for controlling current is embedded inside, and the upper and lower magnet guides 7, 8 are respectively fixed on the flexible spine 3 Above, the armature 4 is fixed at the middl...
Embodiment 2
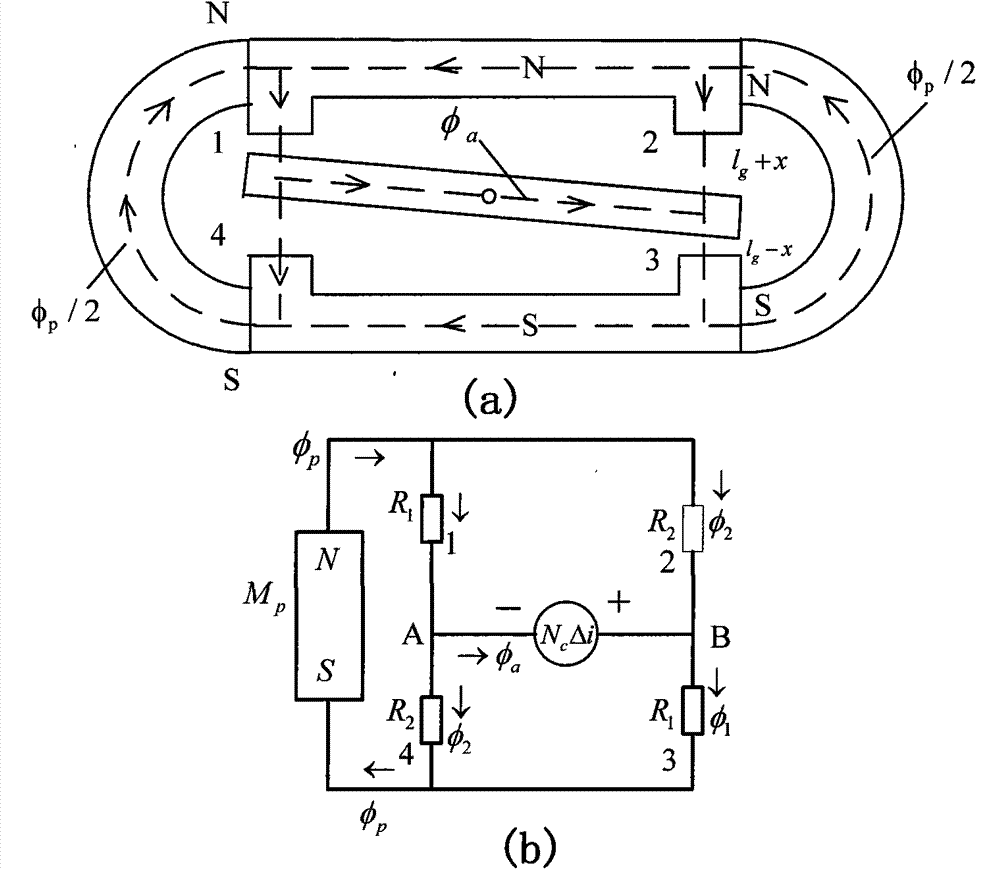
[0016] The specific principle of the drive control of the electromagnetic oscillating unit is as follows: the permanent magnet magnetizes the upper and lower magnetizers, one end is an N pole, and the other end is an S pole. When there is no signal current, the armature is in the middle of the upper and lower magnet conductors. Since the structure of the electromagnetic swing unit is symmetrical, the polarized magnetic flux generated by the permanent magnet in the air gap at both ends is the same, so that the two ends of the armature are affected It is the same as the electromagnetic suction, and there is no driving torque output. When the signal current passes through the coil, the control coil generates a control magnetic flux whose magnitude and direction depend on the magnitude and direction of the signal current. When the reaction moment generated by the elastic deformation of the flexible spine is balanced with the electromagnetic moment, the armature stops rotating. Ac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com