Common-mode signal filter
A common-mode signal and filter technology, applied in the field of thin-film common-mode signal filters, can solve the problems of increased manufacturing cost, complex structure, and many process variables, and achieves the effect of accurately controlling common-mode impedance and eliminating common-mode noise.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example 〕
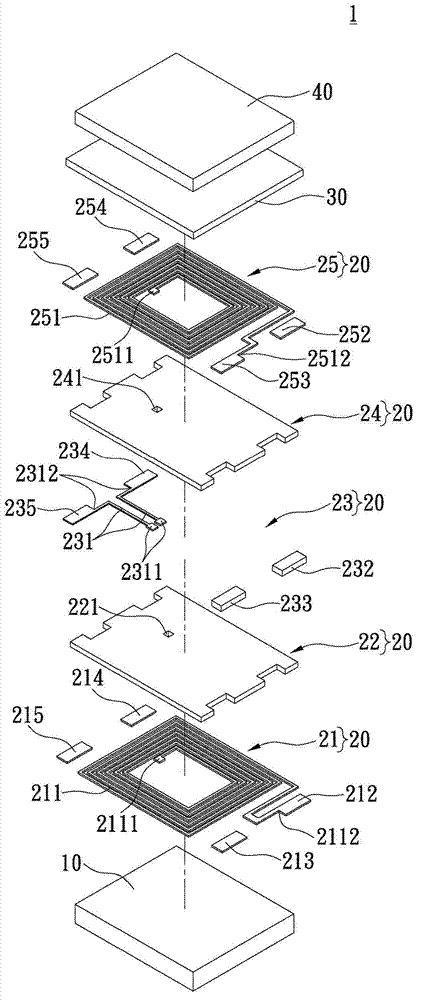
[0108] See figure 1 , Which shows an exploded view of the common mode signal filter 1 of the first embodiment of the present invention. The common mode signal filter 1 includes an insulating substrate 10 made of non-magnetic material, a coil laminated structure 20, an insulating layer 30 and a magnetic material layer 40.
[0109] Specifically, the coil laminate structure 20 is disposed on an insulating substrate 10 made of non-magnetic material, and the coil laminate structure 20 includes a first coil body layer 21, a first electrical insulating layer 22, and a coil lead-out layer 23 in sequence. , A second electrical insulation layer 24 and a second coil body layer 25. The insulating layer 30 is arranged between the coil laminated structure 20 and the magnetic material layer 40, so that the magnetic material layer 40 is covered on the coil laminated structure 20 to become the cover of the common mode signal filter 1, which can increase common mode signal filtering. The inductan...
no. 2 example
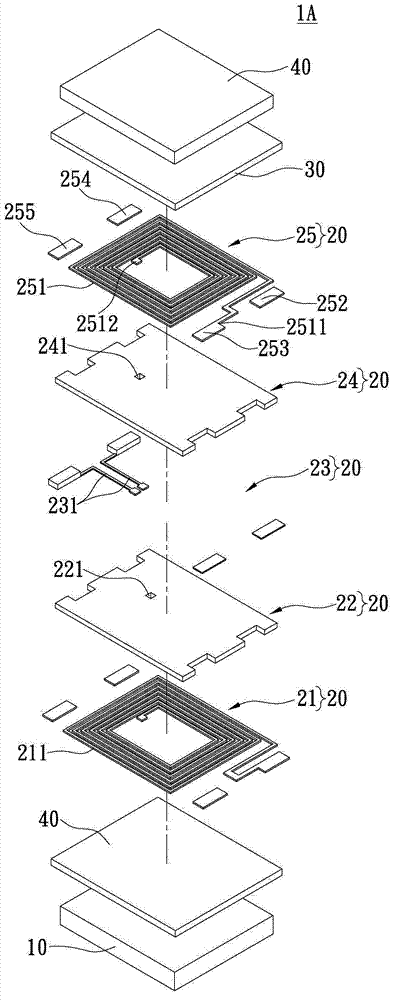
[0122] See Figure 3A , Which shows an exploded view of the common mode signal filter 1A of the second embodiment of the present invention. The difference from the first embodiment is that the common mode signal filter 1A further includes another magnetic material layer 40, and the other magnetic material layer 40 is disposed on the coil laminated structure 20 and the insulating substrate made of non-magnetic material. Between 10.
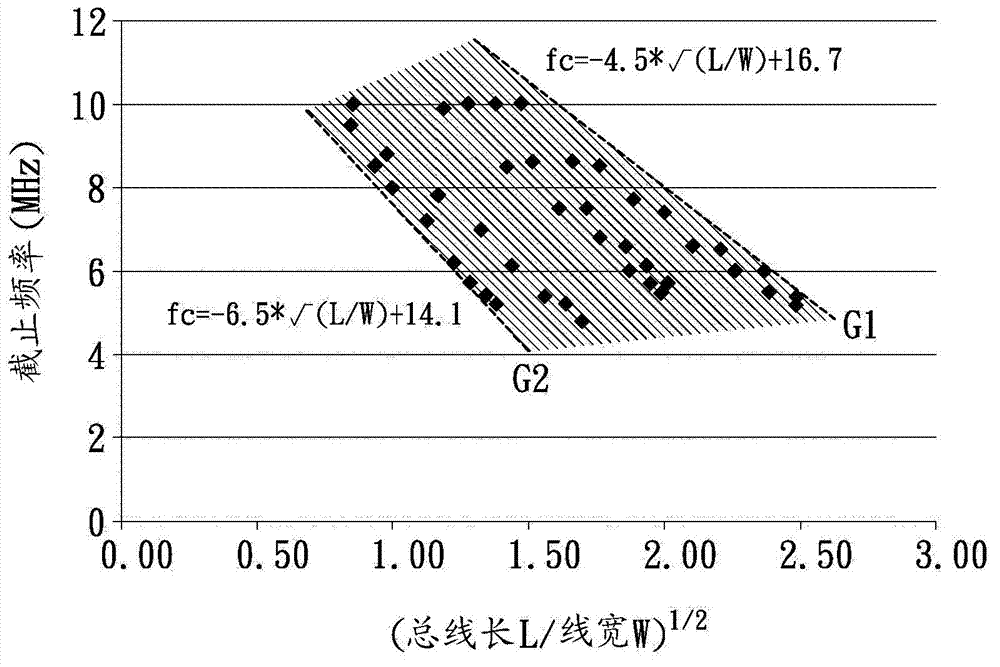
[0123] In more detail, the magnetic material layer 40 is sandwiched between the first coil body layer 21 and the insulating substrate 10 made of non-magnetic material to achieve a higher common mode noise filtering effect. Similarly, the bus length L (mm) and line width W (mm) of the first coil 211 and the second coil 251 can satisfy the following relational expressions:
[0124] [(14.1-fc) / 6.5] 2 2 , Where fc is the cutoff frequency of the differential mode signal, and the cutoff frequency is approximately between 4 to 10 MHz, which meets the requirem...
no. 3 example
[0126] See Figure 3B , Which shows an exploded view of the common mode signal filter 1B of the third embodiment of the present invention. The difference from the second embodiment is that the common mode signal filter 1B further includes a plurality of magnetic parts 50. Specifically, these magnetic parts 50 are ferrite cores, which have the advantages of high magnetic permeability, high resistance in a wide frequency range, and low eddy current loss.
[0127] In addition, the first electrical insulating layer 22 and the second electrical insulating layer 24 both have through holes 222 and 242, and the through holes 222 and the through holes 242 are adjacent to the first conductive structure 221 and the second conductive structure 241, respectively. Thereby, the magnetic parts 50 can be disposed on the inner side of the first coil 211, one end of the pair of L-shaped wires 231, and the inner side of the second coil 251 through the through holes 222 and 242 to increase the stabil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com