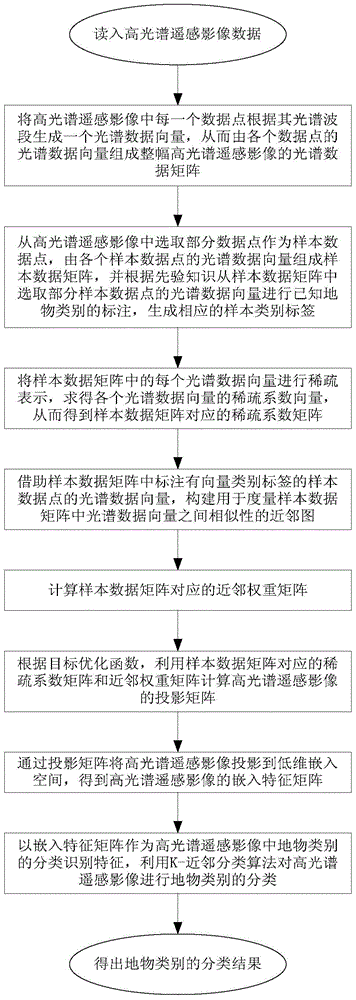
Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method based on semi-supervised sparse discriminative embedding
A sparse discriminative embedding, hyperspectral remote sensing technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instrumentation, computing, etc., can solve the problem of not effectively utilizing discriminative information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0136] The Washington DC Mall hyperspectral remote sensing image dataset used in this experiment is a local area of the National Mall in Washington DC. The dataset has 191 bands with a band spacing of 10nm and a spatial resolution of 3m. The known categories of ground features include seven categories: "building", "forest", "(stone path) path", "road", "lawn", "lake" and "shadow". In the experiment, four classification experiments were carried out for each classification method involved in the comparison. The four classification experiments randomly selected 2, 4, 6, and 8 data points from each type of ground object as classified points, and obtained from the remaining training samples. Randomly select 60 unlabeled data as unlabeled samples to form a training sample set, and all the remaining data points are used as test samples. The four classification experiments are recorded as 2-lab, 4-lab, 6-lab, 8-lab, respectively. lab, for each classification method involved in the ...
Embodiment 2
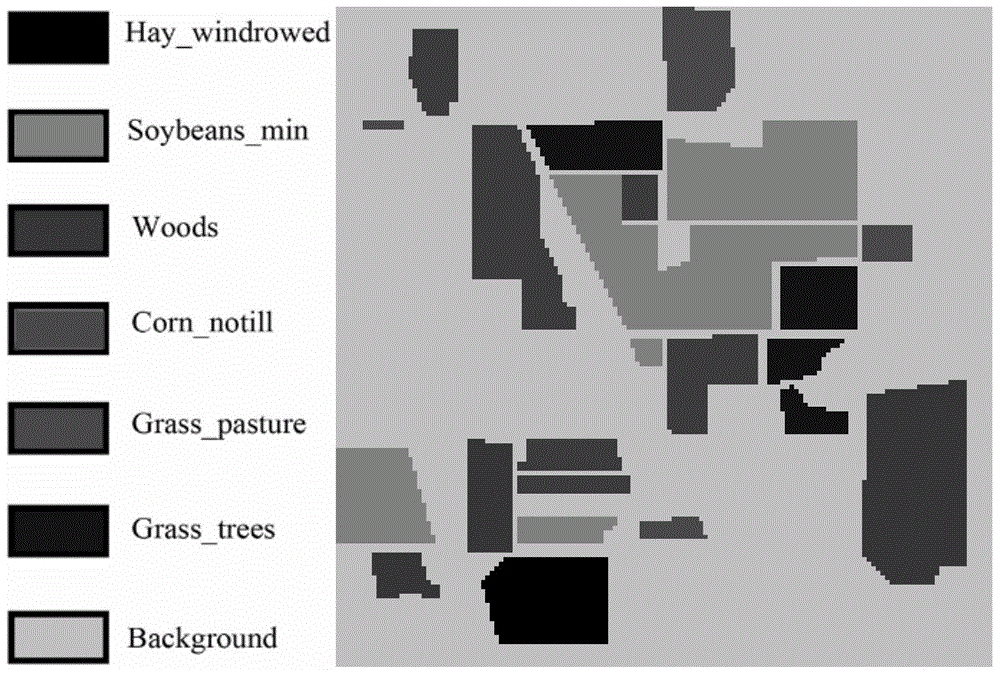
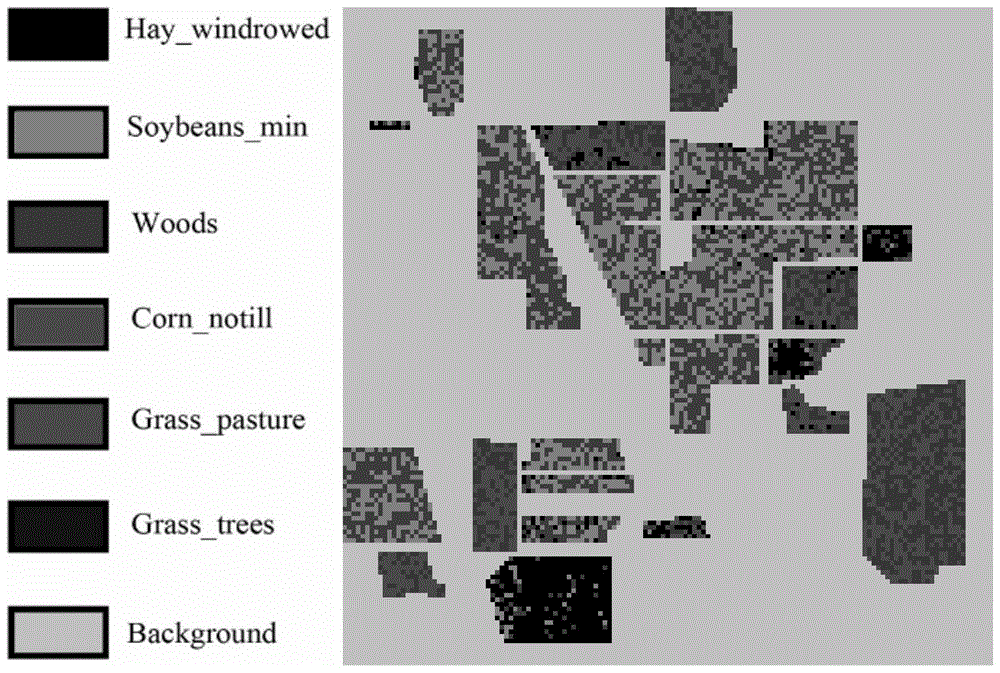
[0141] The Indian Pine hyperspectral remote sensing image dataset used in the experiment covers an agricultural area in the northwest of Indiana, USA. The data point space size of this dataset is 145×145, and there are 220 bands and 17 known object categories. Considering the influence of noise, this experiment selects 200 bands and selects 6 categories from the ground object categories with more data points for experiments. The fifth categories of the 6 categories are "Hay_windrowed", "Soybeans_min", "Woods", "Corn_notill", "Grass_pasture", "Grass_trees". In the experiment, four kinds of classification experiments were carried out for each classification method participating in the comparison. The four classification experiments randomly selected 2, 4, 6, and 8 data points with category labels from each type of ground object, and selected data points from the remaining training samples. Randomly select 60 unlabeled data as unlabeled samples to form a training sample set, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com