Hybrid optical amplifier with optimized noise figure
A hybrid amplifier and noise figure technology, applied in semiconductor amplifier structures, lasers, phonon exciters, etc., can solve problems that do not consider NF optimization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
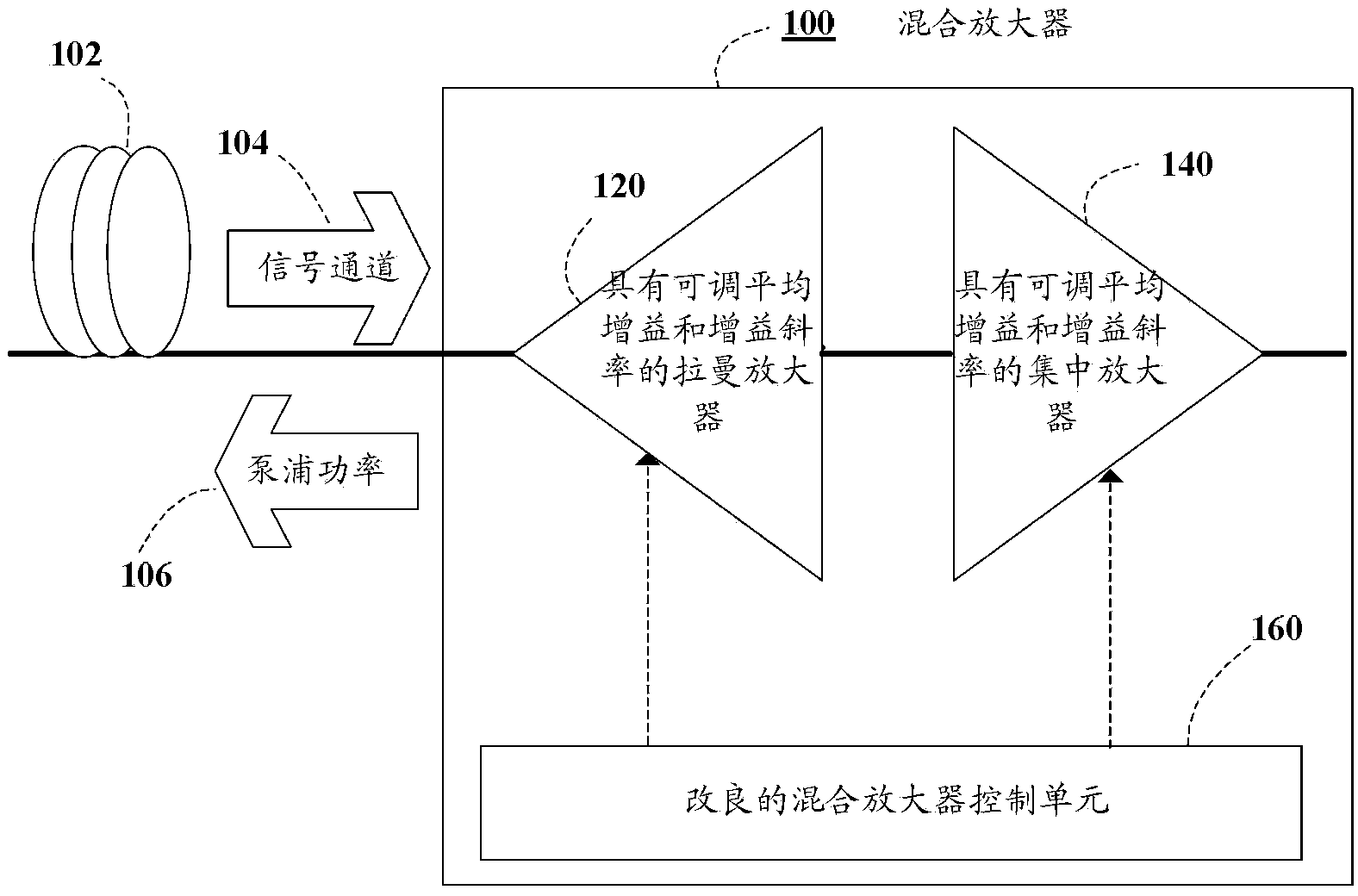
[0028] figure 1 A schematic diagram of a variable gain hybrid amplifier 100 according to an embodiment disclosed herein is shown. The hybrid amplifier 100 is connected to the fiber segment 102 and is designed to amplify the WDM signal channel 104 . The hybrid amplifier 100 includes two amplifier sections: a variable-gain Raman amplifier (RA) 120 and a variable-gain focusing amplifier (LA) 140 . Each amplifier features adjustable average gain and gain slope functions. Raman amplifier 120 injects pump power 106 into fiber segment 102 in a backward pump configuration, thereby amplifying WDM signal path 104 as it propagates through the fiber segment. WDM signal path 104 then enters HA100 and is further amplified by LA140. The hybrid amplifier 100 is controlled by a "modified" control unit 160 .
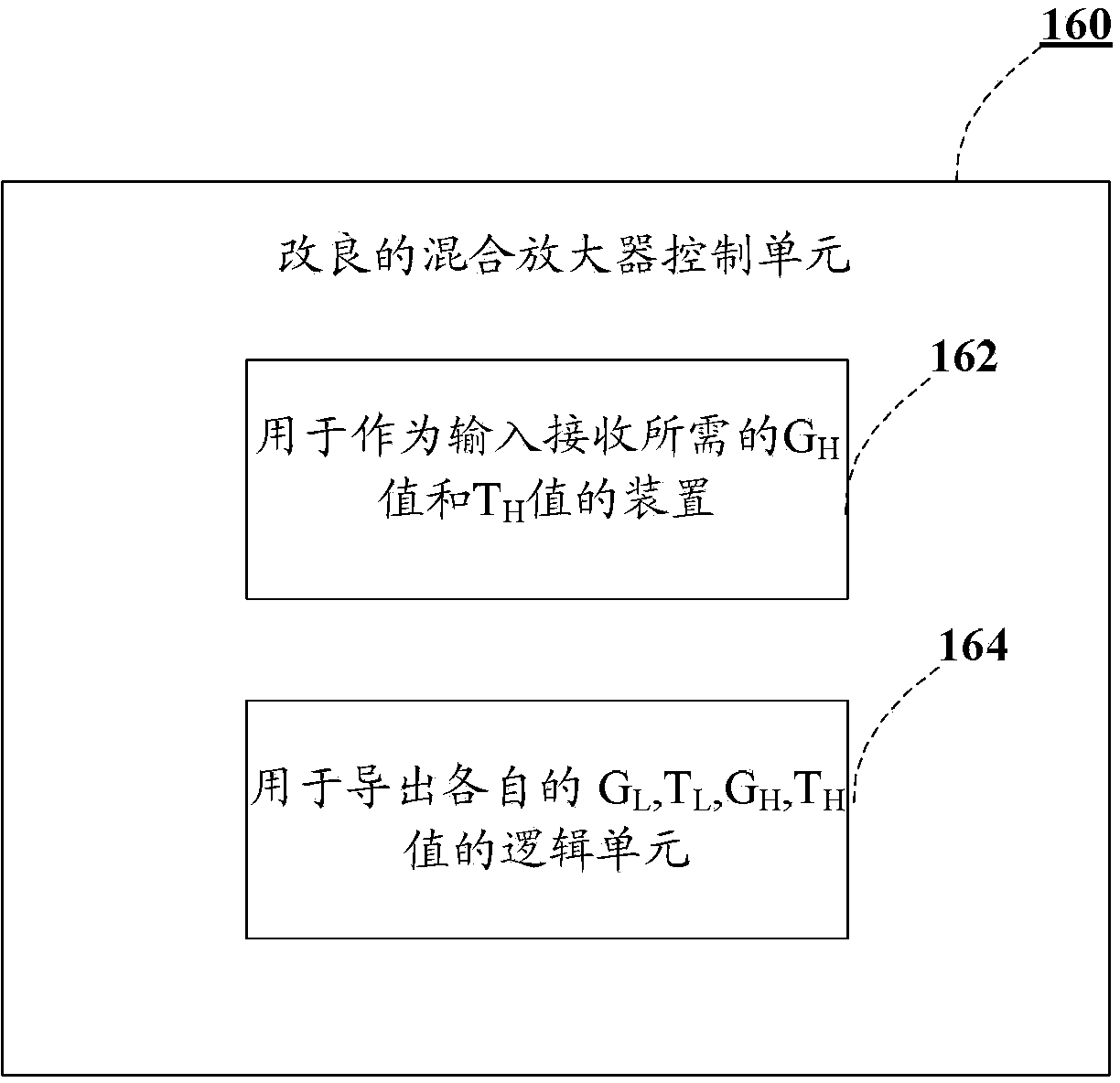
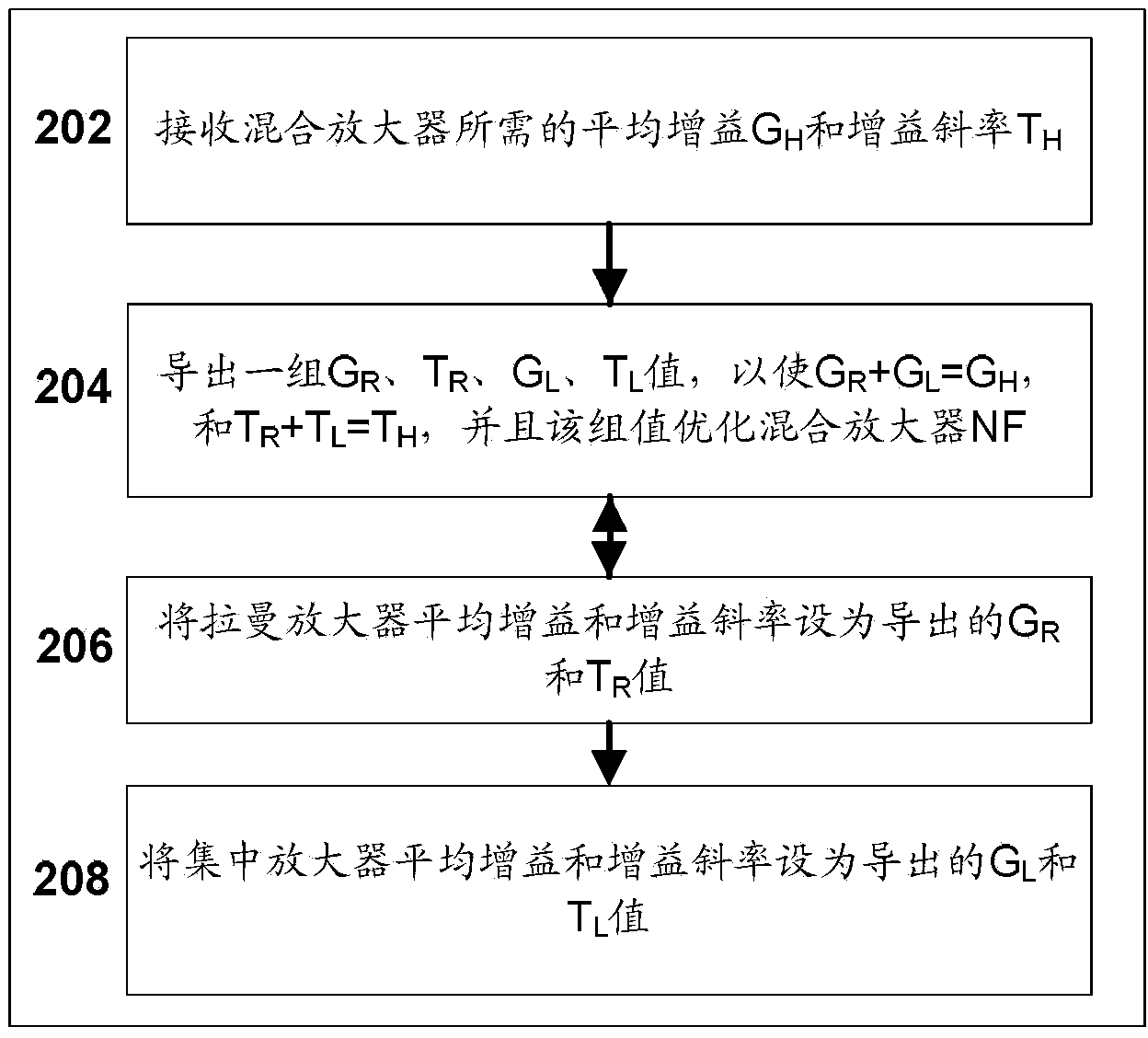
[0029] Details of an embodiment of the modified control unit 160 are in Figure 1a is schematically shown in the diagram, and its operation consists of figure 2 The flowchart illus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com