A process for the manufacture of products from cruciferous crops
A technology of cruciferous products, applied in the fields of application, food science, fat production, etc., which can solve the problems of not explicitly mentioning myrosinase, myrosinase-glucosinolate problem not being clearly solved, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
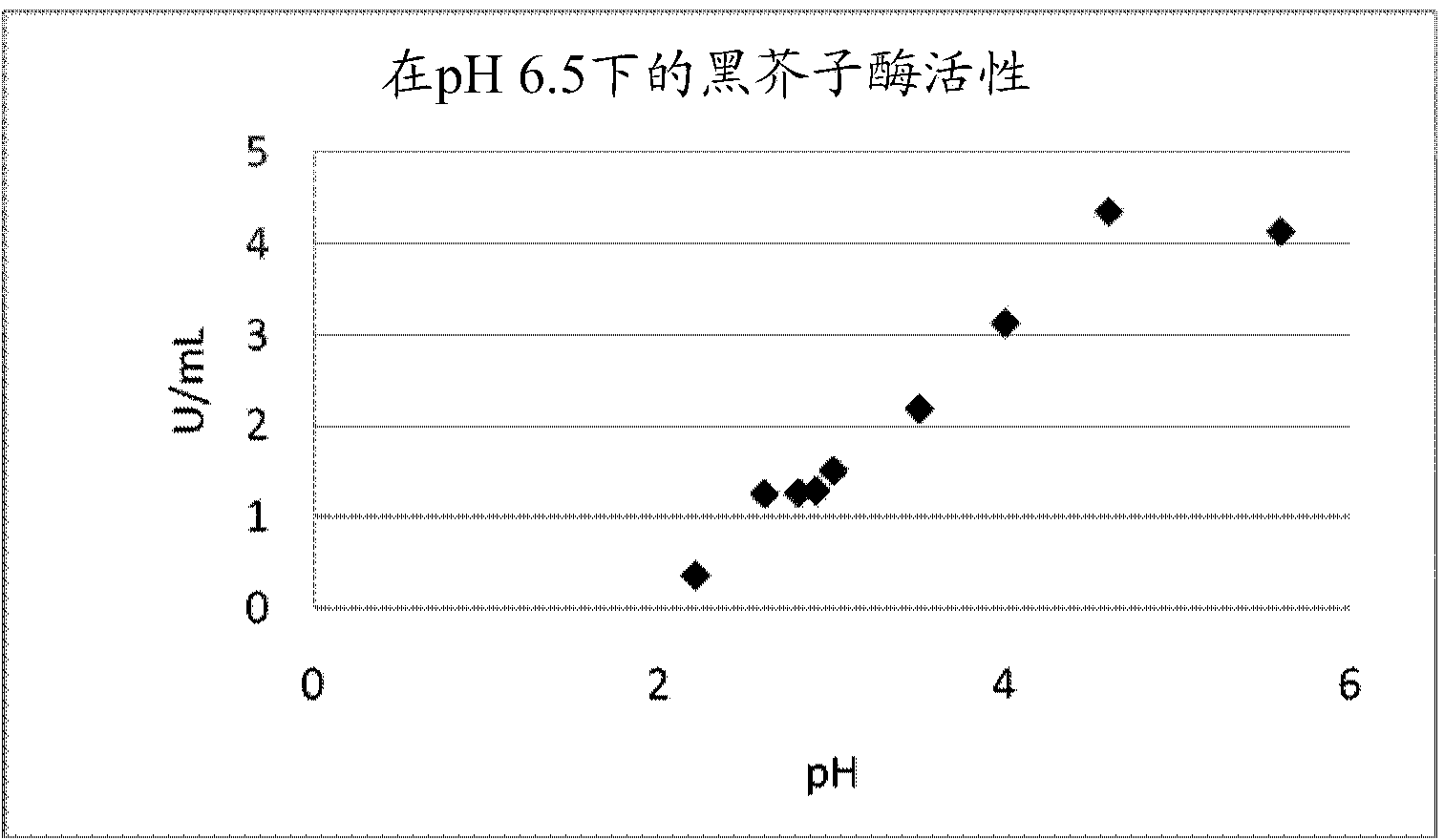
[0093] Example 1 - Recovery of myrosinase activity after low pH treatment
[0094]0.5 grams of Brassica napus (DM8%) full fat seeds were ground in a coffee mill and then mixed with 10.00 mL of citrate buffer varying from 1 to 200 mM. Separately, samples containing 100 mM citrate buffer and 10 mM sulfuric acid or 25 mM citrate buffer and 50 mM sulfuric acid were prepared. Mixing of ground seed material with these different buffers was performed with wet milling using an Ultra Turrax for 2 minutes. The temperature was maintained at 20°C.
[0095] Centrifuge at 4000 x g for 5 minutes to generate a supernatant and a sediment phase. Measure pH in all solutions. Measurements of UV absorbance were also performed at both 280 nm and 325 nm.
[0096] Myrosinase activity after treatment at low pH was measured using spectrophotometry, where myrosinin (1.2 mM, 500 μL) was used as the substrate, ascorbic acid was used as the activator of the reaction (10 mM, 75 μL), and phosphate buffer...
example 2
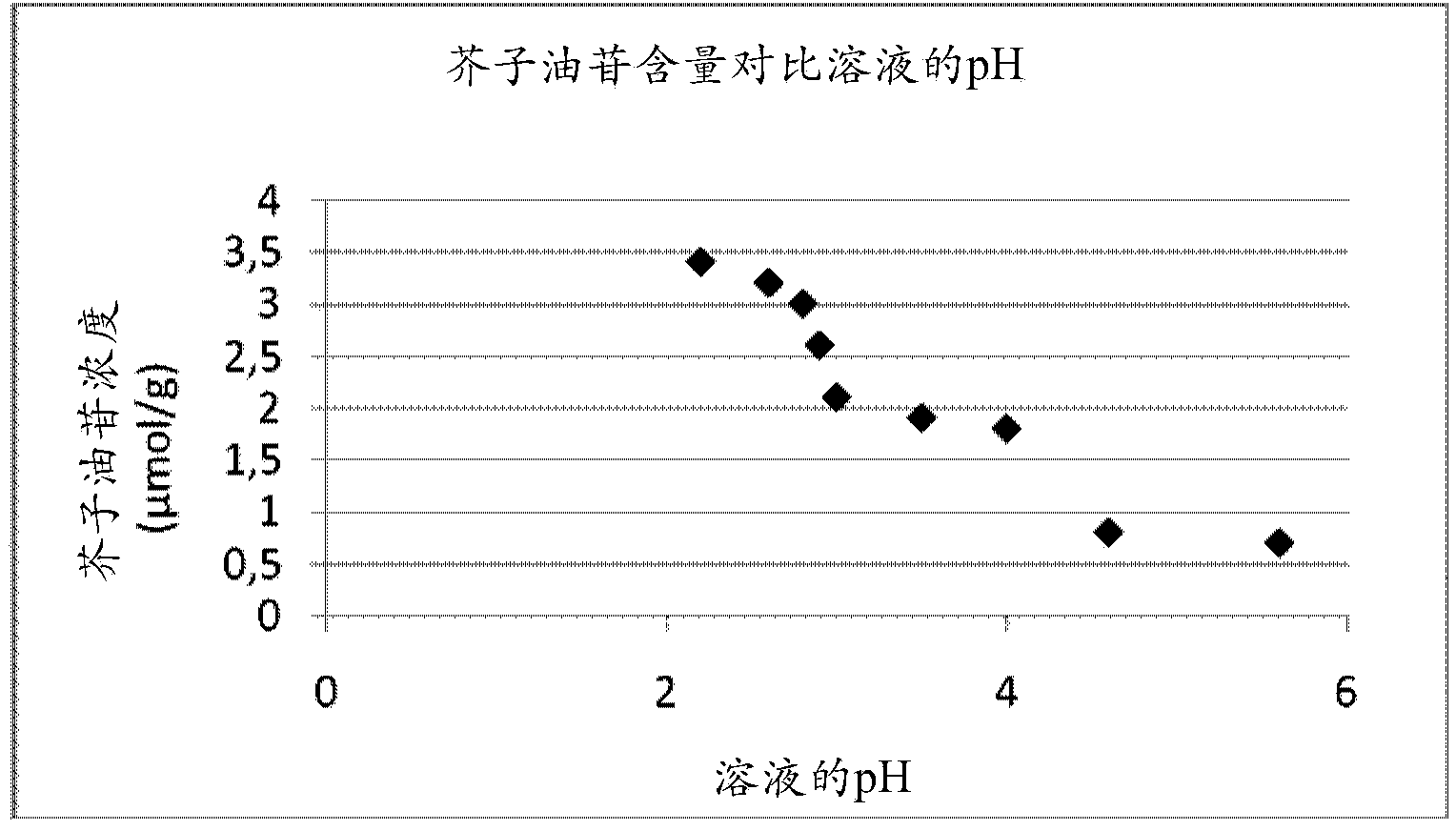
[0099] Example 2 - Glucosinolate levels in solution affected by the pH of the solution
[0100] 0.5 grams of Brassica napus (DM8%) full fat seeds were ground in a coffee mill and then mixed with 10.00 mL of citrate buffer varying from 1 to 200 mM. Separately, samples containing 100 mM citrate buffer and 10 mM sulfuric acid or 25 mM citrate buffer and 50 mM sulfuric acid were prepared. In order to achieve lower pH values, mixtures with increasing concentrations of sulfuric acid were also prepared. The sulfuric acid of these mixtures ranged from 40 mM to 150 mM. Mixing of ground seed material with these different buffers was performed with wet milling using an Ultra Turrax for 2 minutes. The temperature was maintained at 20°C.
[0101] Centrifuge at 4000 x g for 5 minutes to generate a supernatant and a sediment phase. Measure pH in all solutions.
[0102] The supernatant (1 mL) was added to an anion exchange column (1 mL Sephadex DEAE, A-25, GE Healthcare) to adsorb glucos...
example 3
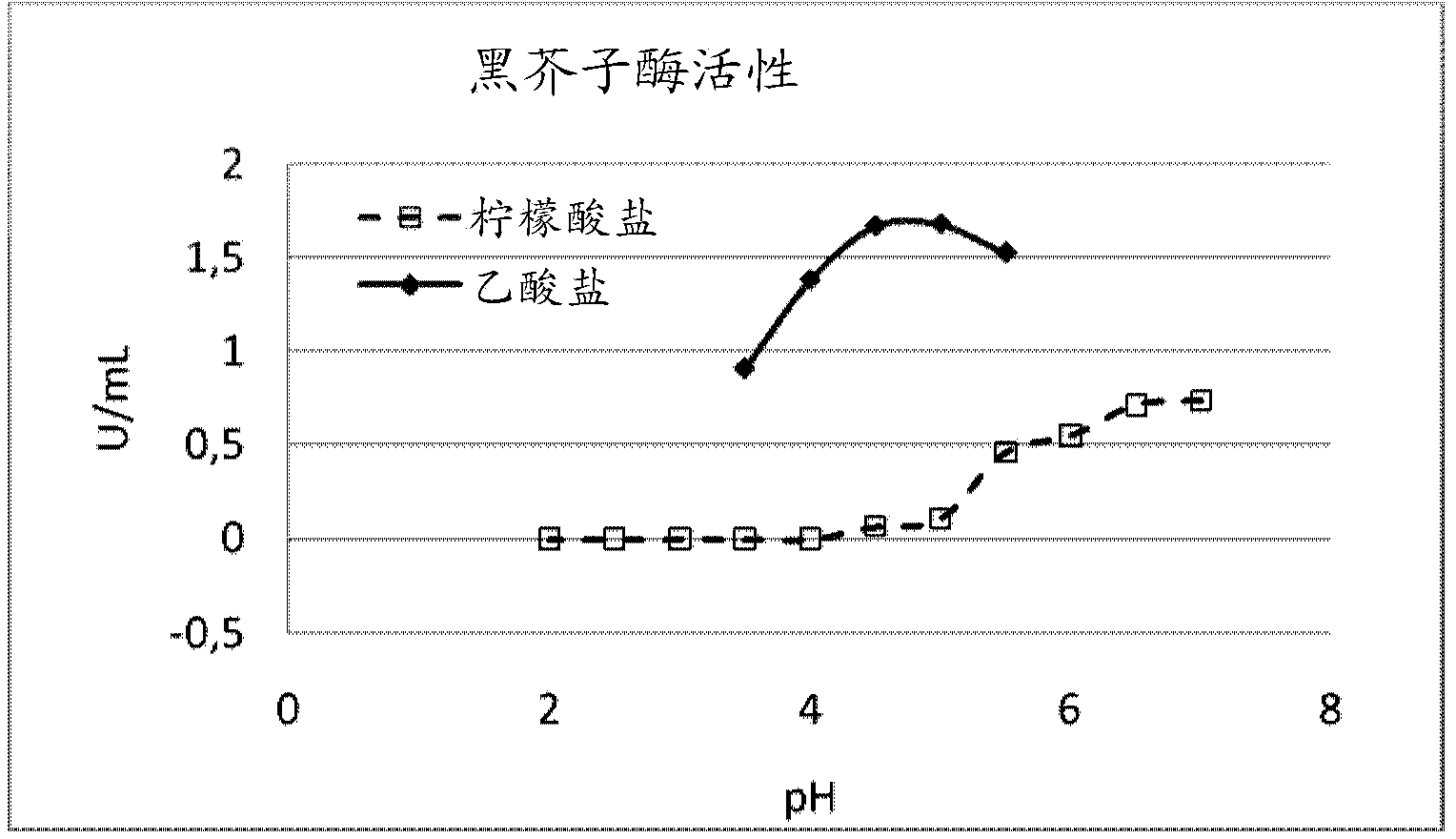
[0105] Example 3 - Myrosinase activity in different pH and different buffer systems
[0106] 0.5 g of full fat seeds of Brassica napus (DM8%) were ground in a coffee mill and then mixed with 10.00 mL of buffer adjusted to range from pH 7 to pH 2 using 50 mM citrate or acetate different pH values. Mixing of ground seed material with these different buffers was performed with wet milling using an Ultra Turrax for 2 min. The temperature was maintained at 20°C.
[0107] Centrifugation was performed at 4000 xg for 5 minutes to generate a supernatant and a sediment phase. Measure pH in all solutions.
[0108] Myrosinase activity was measured using spectrophotometry, in which myrosinin (1.2 mM, 500 μL) was used as the substrate, ascorbic acid was used as the activator of the reaction (10 mM, 75 μL), and buffer (citrate or Acetate) (50 mM, variable volume, variable pH according to sample conditions) was used to keep the pH constant, and the final supernatant (variable volume, typi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com