Biomass-modified adsorbent for adsorbing coking wastewater, and preparation method and application thereof
A coking wastewater and biomass technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, and other chemical processes, can solve the problems of low adsorption capacity and complicated preparation methods, and achieve simple preparation methods, wide sources, and lighten The effect of dealing with the problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Wash the discarded peanut shells with tap water, dry them at 100 °C, crush them with a plant grinder, pass through a 40-mesh sieve, and take the sieved particles; add 100 mL of phosphoric acid with a mass percentage concentration of 15% to 20 g of the above peanut shell particles The solution was soaked at room temperature for 12 h, filtered out, washed with water until neutral, dried at 105 °C, and calcined at 400 °C for 0.5 h in a muffle furnace to obtain a modified peanut shell adsorbent.
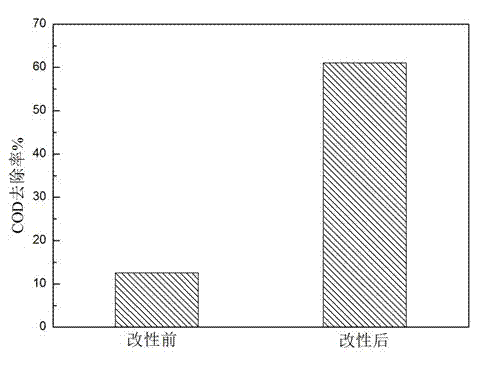
[0027] Weigh 2 g of the peanut shell modified adsorbent obtained above, put it into a conical flask containing 100 mL of coking wastewater raw water, and then place it in a constant temperature shaking box, shake and adsorb at 170 rpm at 25 °C for 8 h, measure The COD removal rate of the water sample after adsorption reached 61%, and compared with the unmodified peanut shell, the removal rate increased by 48%, such as figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Wash the discarded peanut shells with tap water, dry them at 100 °C, crush them with a plant grinder, pass through a 40-mesh sieve, and take the sieved particles; add 100 mL of phosphoric acid with a mass percentage concentration of 10% to 15 g of the above peanut shell particles The solution was soaked at room temperature for 10 h, filtered out, washed with water until neutral, dried at 105 °C, and calcined at 350 °C for 1 h in a muffle furnace to obtain the modified peanut shell adsorbent.
[0030] Weigh 2 g of the peanut shell modified adsorbent obtained above, put it into a conical flask containing 100 mL of coking wastewater raw water, and then place it in a constant temperature shaking box, shake and adsorb at 170 rpm at 25 °C for 8 h, measure The COD removal rate of the water sample after adsorption reached 60%, and compared with the unmodified peanut shell, the removal rate increased by 47%.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Wash the discarded pomelo peels with tap water, dry them at 100 °C, crush them with a plant grinder, pass them through a 40-mesh sieve, and take the particles on the sieve; add 100 mL of phosphoric acid with a mass percentage concentration of 15% to 18 g of the above grapefruit peel particles The solution was soaked at room temperature for 8 h, filtered out, washed with water until neutral, dried at 105 °C, and calcined at 410 °C for 0.5 h in a muffle furnace to obtain the modified adsorbent of pomelo peel.
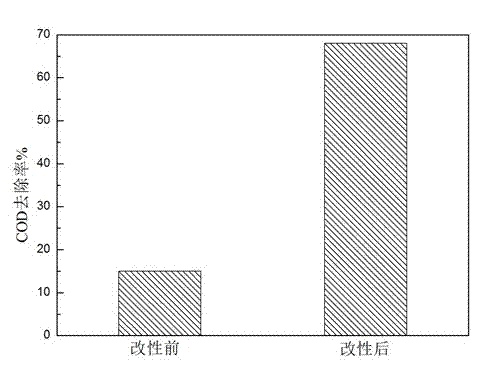
[0033] Weigh 2 g of the grapefruit peel modified adsorbent obtained above, put it into a conical flask containing 100 mL of coking wastewater raw water, and then place it in a constant temperature oscillation box, shake and adsorb at 170 rpm at 25 °C for 8 h, measure The COD removal rate of the water sample after adsorption reached 68%, compared with the unmodified pomelo peel, the removal rate increased by 53%, such as figure 2 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com