A controlled release fertilizer, a preparation method thereof and applications thereof
A slow-release fertilizer, fertilizer technology, applied in the direction of application, fertilizer mixture, fertilization device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
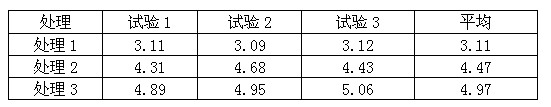
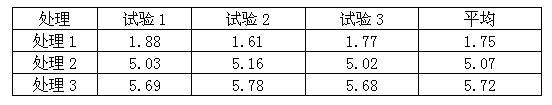
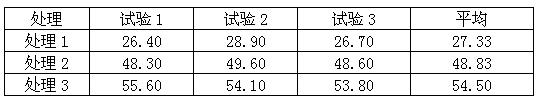
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] The main raw materials include: urea, gelatin, ferrous sulfate, zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate, boric acid, ammonium citrate, formaldehyde, polyvinyl alcohol and water;
[0046] The main special equipment includes: reaction kettle, drum coating machine, dryer.
[0047] The production process consists of three steps:
[0048] The first step, the preparation of the encapsulation material, calculated on the basis of 100 kg per production, 1. Add 15 kg of water, 2 kg of gelatin, and 1.5 kg of polyvinyl alcohol to the reactor A in sequence, stir and heat up to 60-70°C, Then add 10 kg of urea, 0.5 kg of formaldehyde, and continue to stir for 30 minutes; 2. Add 31.5 kg of water, 20 kg of ferrous sulfate, 5 kg of zinc sulfate, 1 kg of manganese sulfate, 1 kg of boric acid, and citric acid in the reactor B. 2.5 kg of ammonium and 10 kg of urea, stirred and heated to 50-60°C; 3. Pour the liquid in the reactor B into the reactor A, and keep stirring for 2 hours to make an encaps...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The main raw materials include: urea, gelatin, ferrous sulfate, zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate, boric acid, ammonium citrate, formaldehyde, polyvinyl alcohol and water;
[0052] The main special equipment includes: reaction kettle, drum coating machine, dryer.
[0053] The production process consists of three steps:
[0054] The first step is the preparation of encapsulation materials, calculated on the basis of 100 kg per production. 1. Add 20 kg of water, 3 kg of gelatin, and 2 kg of polyvinyl alcohol in sequence in reaction kettle A, stir and heat up to 60-70°C, then add 10 kg of urea, 0.5 kg of formaldehyde, and continue stirring for 30 minutes; 2. Add 25 kg of water, 15 kg of ferrous sulfate, 10 kg of zinc sulfate, 1 kg of manganese sulfate, 1 kg of boric acid, 2.5 kg of ammonium citrate, and 10 kg of urea into reaction kettle B, stir and heat to 50-60°C; 3. Pour the liquid in the reactor B into the reactor A and keep stirring for 2 hours to make an encapsulatio...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The main raw materials include: urea, gelatin, ferrous sulfate, zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate, boric acid, ammonium citrate, formaldehyde, polyvinyl alcohol and water;
[0058] The main special equipment includes: reaction kettle, drum coating machine, dryer.
[0059] The production process consists of three steps:
[0060] The first step is the preparation of encapsulation materials, calculated on the basis of 100 kg per production. 1. Add 20 kg of water, 5 kg of gelatin, and 2 kg of polyvinyl alcohol in sequence in reactor A, stir and heat up to 60-70°C, then add 10 kg of urea and 1 kg of formaldehyde, and continue stirring for 30 minutes; 2. Add 21 kg of water, 20 kg of ferrous sulfate, 5 kg of zinc sulfate, 2 kg of manganese sulfate, 1.5 kg of boric acid, 2.5 kg of ammonium citrate, and 10 kg of urea into reaction kettle B, stir and heat to 50-60°C; 3. Pour the liquid in the reactor B into the reactor A and keep stirring for 2 hours to make an encapsulation mate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com