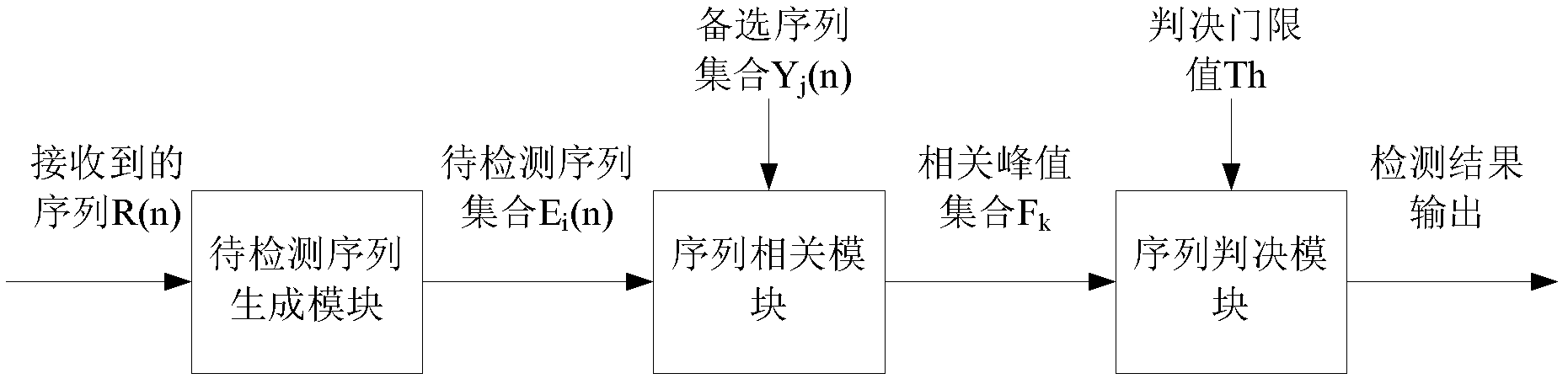
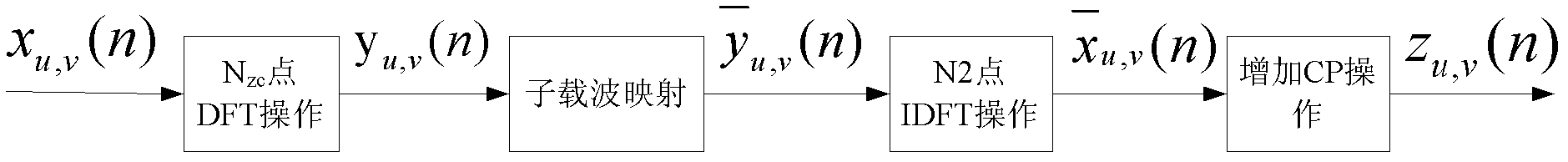Method and device for sending frequency deviation indicating signal and generating random access sequence
A random access sequence and signaling signaling technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of poor detection performance and unsatisfactory actual performance at the receiving end
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example 1
[0116] Random access sequence generation and sending process at the sender:
[0117] (1) In a wireless communication system, the system is configured with a high frequency offset flag (High Frequency Offset Flag, HFOF).
[0118] Wherein, the HFOF is described by N bits, and N is a positive integer;
[0119] Further, the HFOF includes at most 2 N HFOF i , Where 0≤i≤2 N -1;
[0120] Further, the HFOF i Used to indicate the size of the frequency offset;
[0121] Further, the HFOF i The corresponding relationship with the frequency offset is configured by the standard or by the system;
[0122] Further, the HFOF i The corresponding relationship with the frequency offset can be described by the following formula:
[0123] FO=(a*f 1 +b)*HFOF i , Or FO=(a*f 1 +b)*(HFOF i +1),
[0124] Where f 1 Is the frequency offset quantization interval; a and b are preset values.
[0125] Further, the f 1 Can be PRACH channel sub-carrier spacing fPRACH
[0126] Further, a, b, f 1 Configured by the standard or b...
specific example 2
[0183] Random access sequence generation and sending process at the sender:
[0184] In a wireless communication system, the data subcarrier spacing f RE , The subcarrier spacing f of the random access channel PRACH , Random access sequence length N ZC .
[0185] (1) The system is configured with High Frequency Offset Flag (HFOF).
[0186] Wherein, the HFOF is described by 2 bits, including at most 4 HFOF values HFOF i , Where 0≤i≤3;
[0187] In this embodiment, FO=f PRACH *HFOF i , Used to indicate the magnitude of frequency deviation, f PRACH Is the PRACH channel subcarrier spacing;
[0188] In this embodiment, it is assumed that it needs to support 2 times f PRACH The frequency deviation of the size, then HFOF="10"
[0189] (2) The base station sends HFOF="10" to the terminal through the downlink channel;
[0190] (3) After receiving HFOF="10", the terminal knows that the random access sequence used needs to support 2 times f PRACH The size of the frequency offset, and generate...
specific example 3
[0241] Random access sequence generation and sending process at the sender:
[0242] In a wireless communication system, the data subcarrier spacing f RE , The subcarrier spacing f of the random access channel PRACH , Random access sequence length N ZC .
[0243] (1) The system is configured with High Frequency Offset Flag (HFOF).
[0244] Wherein, the HFOF is described by 2 bits, including at most 4 HFOF values HFOF i , Where 0≤i≤3;
[0245] In this embodiment, FO=f PRACH *HFOF i , Used to indicate the magnitude of frequency deviation, f PRACH Is the PRACH channel subcarrier spacing;
[0246] In this embodiment, assuming that there is no need to consider the influence of frequency offset, HFOF="00"
[0247] (2) The base station sends HFOF="00" to the terminal through the downlink channel;
[0248] (3) After receiving HFOF="00", the terminal knows that the random access sequence used does not need to consider the influence of frequency offset, and generates the ZC root sequence x ac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com