Collimator lens, optical scanning device and image forming apparatus using same
A technology of optical scanning device and collimating lens, which is applied in the fields of lens, image communication, electrical recording technology using charge pattern, etc., and can solve the problems of insufficient imaging performance and unavailability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
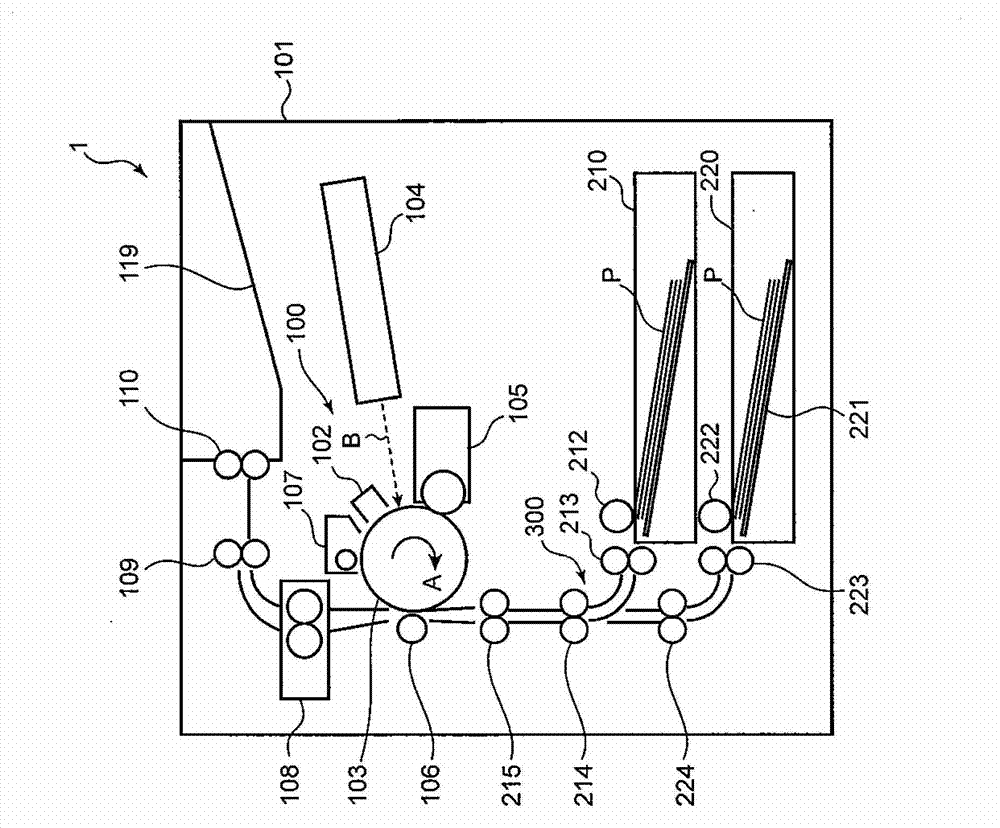
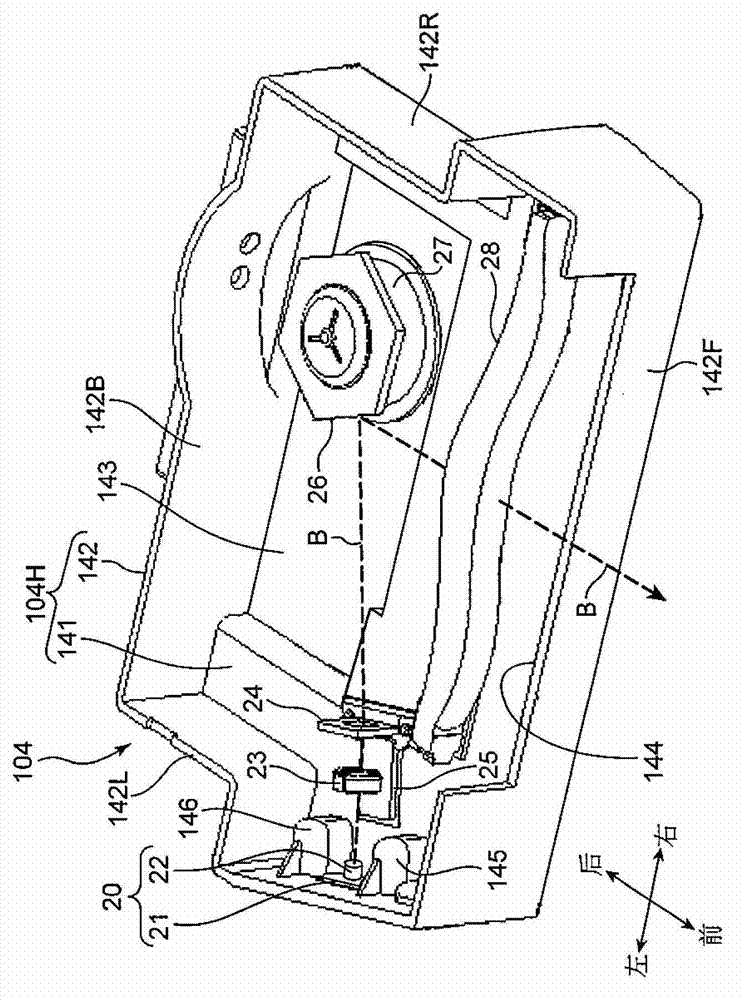
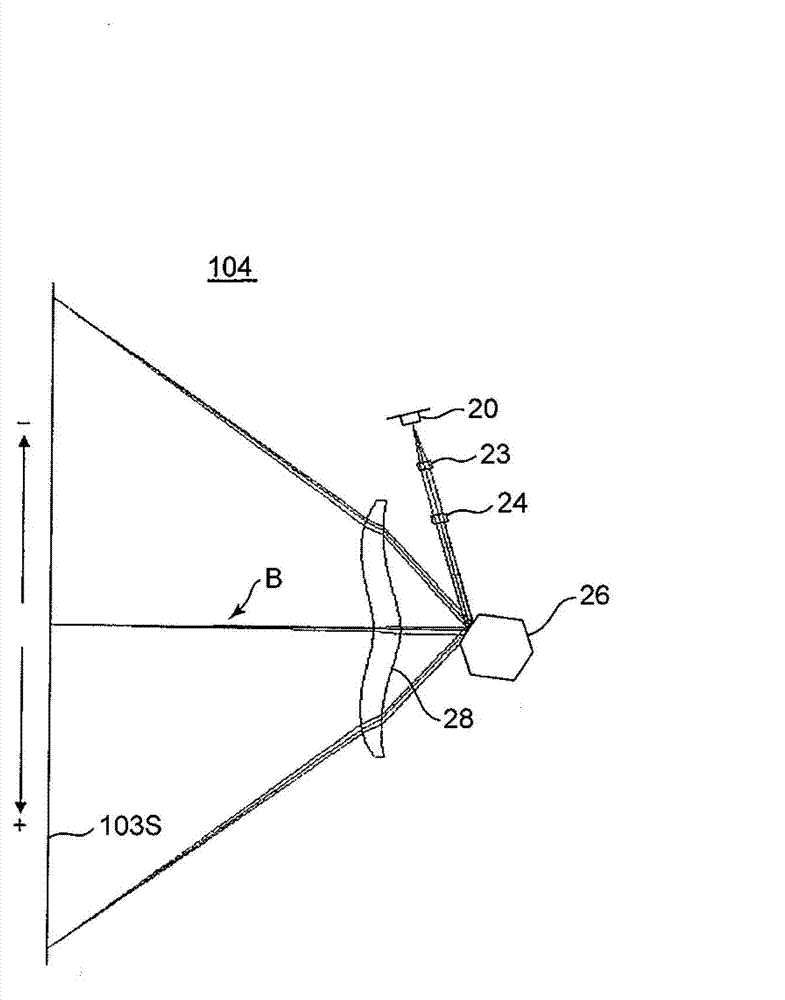
[0040] Next, the detailed structure of the optical scanning device 104 according to the first embodiment will be described. figure 2 Is a perspective view showing the internal structure of the optical scanning device 104, image 3 It is an optical path diagram showing the structure of the main scanning section of the optical scanning device 104. The optical scanning device 104 includes a housing 104H, and a laser unit 20 (light source), a collimator lens 23, a cylindrical lens 24, a polygon mirror 26 (polarizer), and an fθ lens 28 (scanning lens) contained in the housing 104H. figure 2 In the direction indicator shown, the left-right direction is the main scanning direction. The optical scanning device 104 of this embodiment is an optical scanning device in which the scanning lens is composed of only one lens (fθ lens 28).
[0041] The housing 104H includes a bottom plate 141 as a base member on which various members are placed, a side plate 142 erected substantially perpendicul...
no. 1 example
[0071] Next, an example of construction data (construction data) of the collimator lens 23 according to the first embodiment described above is shown in Table 1 as a first example. The collimating lens 23 of the first embodiment has a meniscus shape convex to the side of the polyhedral mirror 26, the first surface 231 and the second surface 232 are both aspherical surfaces, and the second surface 232 is provided with a diffraction structure. In the table, C represents the aspheric coefficient and D represents the diffraction coefficient. The optical system of the first embodiment includes the collimating lens 23 and the cover glass 20G shown in Table 1, as Figure 4 and Figure 5 Optical system as shown.
[0072] [Table 1]
[0073]
[0074] For comparison with the first embodiment, it will be as Image 6 As shown, the configuration data of the collimator lens designed to minimize the wavefront aberration when parallel light is incident from the second surface 232 is shown in Table...
no. 2 approach
[0092] Next, the optical scanning device according to the second embodiment will be described. The internal structure and optical arrangement of the optical scanning device of the second embodiment are the same as those of the optical scanning device 104 described in the first embodiment. In this second embodiment, a description will be given of an embodiment that can prevent the imaging position from shifting even if the arrangement interval between the optical members changes due to the thermal expansion of the housing 104H of the optical scanning device 104.
[0093] When the temperature of the environment in which the light scanning device 104 is installed increases, the refractive indexes of the collimator lens 23, the cylindrical lens 24, and the fθ lens 28 increase, and when the lenses are molded from a resin material, the lens shape changes due to thermal expansion. In addition, the emission wavelength of the semiconductor laser 22 becomes longer. These phenomena act to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com